SGUS033A February 2002 – May 2016 SMJ320C6203
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Description
- 3 Revision History
- 4 Description (continued)
- 5 Characteristics of the C6203 DSP
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.3 Thermal Information
- 7.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.5 Timing Requirements for CLKIN (PLL Used)
- 7.6 Timing Requirements for CLKIN [PLL Bypassed (x1)]
- 7.7 Timing Requirements for XCLKIN
- 7.8 Timing Requirements for Asynchronous Memory Cycles
- 7.9 Timing Requirements for Synchronous-Burst SRAM Cycles
- 7.10 Timing Requirements for Synchronous DRAM Cycles
- 7.11 Timing Requirements for the HOLD/HOLDA Cycles
- 7.12 Timing Requirements for Reset
- 7.13 Timing Requirements for Interrupt Response Cycles
- 7.14 Timing Requirements for Synchronous FIFO Interface
- 7.15 Timing Requirements for Asynchronous Peripheral Cycles
- 7.16 Timing Requirements With External Device as Bus Master
- 7.17 Timing Requirements With C62x as Bus Master
- 7.18 Timing Requirements With External Device as Asynchronous Bus Master
- 7.19 Timing Requirements for Expansion Bus Arbitration (Internal Arbiter Enabled)
- 7.20 Timing Requirements for McBSP
- 7.21 Timing Requirements for FSR when GSYNC = 1
- 7.22 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0
- 7.23 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0
- 7.24 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1
- 7.25 Timing Requirements for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1
- 7.26 Timing Requirements for Timer Inputs
- 7.27 Timing Requirements for JTAG Test Port
- 7.28 Switching Characteristics for CLKOUT2
- 7.29 Switching Characteristics for XFCLK
- 7.30 Asynchronous Memory Timing Switching Characteristics
- 7.31 Switching Characteristics for Synchronous-Burst SRAM Cycles
- 7.32 Switching Characteristics for Synchronous DRAM Cycles
- 7.33 Switching Characteristics for the HOLD/HOLDA Cycles
- 7.34 Switching Characteristics for Reset
- 7.35 Switching Characteristics for Interrupt Response Cycles
- 7.36 Switching Characteristics for Synchronous FIFO Interface
- 7.37 Switching Characteristics for Asynchronous Peripheral Cycles
- 7.38 Switching Characteristics With External Device as Bus Master
- 7.39 Switching Characteristics With C62x as Bus Master
- 7.40 Switching Characteristics With External Device as Asynchronous Bus Master
- 7.41 Switching Characteristics for Expansion Bus Arbitration (Internal Arbiter Enabled)
- 7.42 Switching Characteristics for Expansion Bus Arbitration (Internal Arbiter Disabled)
- 7.43 Switching Characteristics for McBSP
- 7.44 Switching Characteristics for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave
- 7.45 Switching Characteristics for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0
- 7.46 Switching Characteristics for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1
- 7.47 Switching Characteristics for McBSP as SPI Master or Slave: CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1
- 7.48 Switching Characteristics for DMAC Outputs
- 7.49 Switching Characteristics for Timer Outputs
- 7.50 Switching Characteristics for Power-Down Outputs
- 7.51 Switching Characteristics for JTAG Test Port
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
12 Device and Documentation Support
12.1 Device Support
12.1.1 Third-Party Products Disclaimer
TI'S PUBLICATION OF INFORMATION REGARDING THIRD-PARTY PRODUCTS OR SERVICES DOES NOT CONSTITUTE AN ENDORSEMENT REGARDING THE SUITABILITY OF SUCH PRODUCTS OR SERVICES OR A WARRANTY, REPRESENTATION OR ENDORSEMENT OF SUCH PRODUCTS OR SERVICES, EITHER ALONE OR IN COMBINATION WITH ANY TI PRODUCT OR SERVICE.
12.1.2 Development Support
TI offers an extensive line of development tools for the TMS320C6000 DSP platform, including tools to evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software and hardware modules.
The following products support development of C6000 DSP-based applications:
12.1.2.1 Software Development Tools
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE) including Editor C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools Scalable, Real-Time Foundation Software (DSP/BIOS™), which provides the basic run-time target software needed to support any DSP application.
12.1.2.2 Hardware Development Tools
Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator (supports C6000 DSP multiprocessor system debug) EVM (Evaluation Module)
The TMS320 DSP Development Support Reference Guide (SPRU011) contains information about development-support products for all TMS320 DSP family member devices, including documentation. See this document for further information on TMS320 DSP documentation or any TMS320 DSP support products from Texas Instruments. An additional document, the TMS320 Third-Party Support Reference Guide (SPRU052), contains information about TMS320 DSP-related products from other companies in the industry. To receive TMS320 DSP literature, contact the Literature Response Center at 800/477-8924.
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the TMS320C6000 DSP platform, visit the Texas Instruments web site at www.ti.com and select “Find Development Tools”. For device-specific tools, under “Semiconductor Products” select “Digital Signal Processors”, choose a product family, and select the particular DSP device. For information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
12.1.3 Device and Development-Support Tool Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all SMJ320 DSP devices and support tools. Each SMJ320 DSP commercial family member has one of three prefixes: SMX, SM, or SMJ. Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (SMX/TMDX) through fully qualified production devices/tools (SMJ/TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
-
SMX Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device’s electrical specifications
-
SM Final silicon die that conforms to the device’s electrical specifications but has not completed quality and reliability verification
-
SMJ Fully qualified production device processed to MIL-PRF-38535
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
-
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing.
-
TMDS Fully qualified development-support product
SMX and TMP devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
“Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes.”
SMJ devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI’s standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (SMX or SM) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, GLP), the temperature range, and the device speed range in megahertz (for example, 20 is 200 MHz).
Figure 56 provides a legend for reading the complete device name. For the C6203 device orderable part numbers (P/Ns), see the Texas Instruments web site at www.ti.com, or contact the nearest TI field sales office, or authorized distributor.
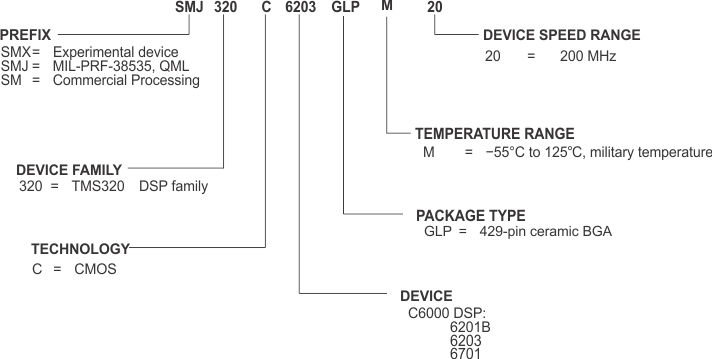 Figure 56. SMJ320C6000 DSP Platform Device Nomenclature
Figure 56. SMJ320C6000 DSP Platform Device Nomenclature
12.2 Documentation Support
12.2.1 Related Documentation
Extensive documentation supports all SMJ320 DSP family devices from product announcement through applications development. The types of documentation available include: data sheets, such as this document, with design specifications; complete user’s reference guides for all devices and tools; technical briefs; development-support tools; on-line help; and hardware and software applications. The following is a brief, descriptive list of support documentation specific to the C6000 DSP devices:
The TMS320C6000 CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (SPRU189) describes the C6000 CPU (DSP core) architecture, instruction set, pipeline, and associated interrupts.
The TMS320C6000 Peripherals Reference Guide (SPRU190) describes the functionality of the peripherals available on the C6000 DSP platform of devices, such as the 64-/32-/16-bit external memory interfaces (EMIFs), 32-/16-bit host-port interfaces (HPIs), multichannel buffered serial ports (McBSPs), direct memory access (DMA), enhanced direct-memory-access (EDMA) controller, expansion bus, peripheral component interconnect (PCI), clocking and phase-locked loop (PLL); and power-down modes. This guide also includes information on internal data and program memories.
The TMS320C6000 Technical Brief (SPRU197) gives an introduction to the TMS320C62x/TMS320C67x devices, associated development tools, and third-party support.
The tools support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ IDE. For a complete listing of the latest C6000 DSP documentation, visit the Texas Instruments website at www.ti.com.
12.3 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
Design Support TI's Design Support Quickly find helpful E2E forums along with design support tools and contact information for technical support.
12.4 Trademarks
C6000, Code Composer Studio, DSP/BIOS, XDS, E2E are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Motorola is a registered trademark of Motorola Trademark Holdings, LLC.
SMJ320C62x, VelociTI, C62x are trademarks of TI.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
12.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

These devices have limited built-in ESD protection. The leads should be shorted together or the device placed in conductive foam during storage or handling to prevent electrostatic damage to the MOS gates.
12.6 Glossary
SLYZ022 — TI Glossary.
This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.