ZHCSB64C June 2013 – March 2021 SN6501-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
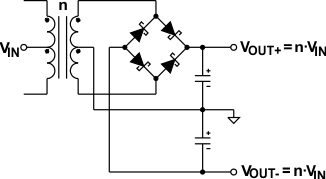
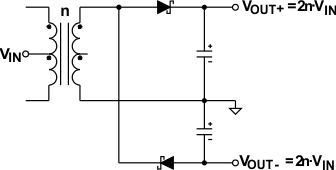
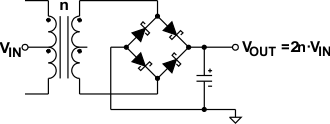
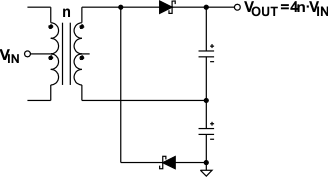
9.2.4 Higher Output Voltage Designs
The SN6501 can drive push-pull converters that provide high output voltages of up to 30 V, or bipolar outputs of up to ±15 V. Using commercially available center-tapped transformers, with their rather low turns ratios of 0.8 to 5, requires different rectifier topologies to achieve high output voltages. #SLLSEA04407 to #SLLSEA0920 show some of these topologies together with their respective open-circuit output voltages.