ZHCSFS1A December 2016 – June 2018 SN65DSI84-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Control and Status Registers Overview
- 8.6.1.1 CSR Bit Field Definitions – ID Registers
- 8.6.1.2 CSR Bit Field Definitions – Reset and Clock Registers
- 8.6.1.3 CSR Bit Field Definitions – DSI Registers
- 8.6.1.4 CSR Bit Field Definitions – LVDS Registers
- 8.6.1.5
CSR Bit Field Definitions – Video Registers
- 8.6.1.5.1 Register 0x20
- 8.6.1.5.2 Register 0x21
- 8.6.1.5.3 Register 0x24
- 8.6.1.5.4 Register 0x25
- 8.6.1.5.5 Register 0x28
- 8.6.1.5.6 Register 0x29
- 8.6.1.5.7 Register 0x2C
- 8.6.1.5.8 Register 0x2D
- 8.6.1.5.9 Register 0x30
- 8.6.1.5.10 Register 0x31
- 8.6.1.5.11 Register 0x34
- 8.6.1.5.12 Register 0x36
- 8.6.1.5.13 Register 0x38
- 8.6.1.5.14 Register 0x3A
- 8.6.1.5.15 Register 0x3C
- 8.6.1.6 CSR Bit Field Definitions – IRQ Registers
- 8.6.1
Control and Status Registers Overview
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.4.3 LVDS Output Formats
The SN65DSI84-Q1 processes DSI packets and produces video data driven to the LVDS interface in an industry standard format. Single-Link LVDS and Dual-Link LVDS are supported by the SN65DSI84-Q1; when the LVDS output is implemented in a Dual-Link configuration, channel A carries the odd pixel data, and channel B carries the even pixel data. During conditions such as the default condition, and some video synchronization periods, where no video stream data is passing from the DSI input to the LVDS output, the SN65DSI84-Q1 transmits zero value pixel data on the LVDS outputs while maintaining transmission of the vertical sync and horizontal sync status.
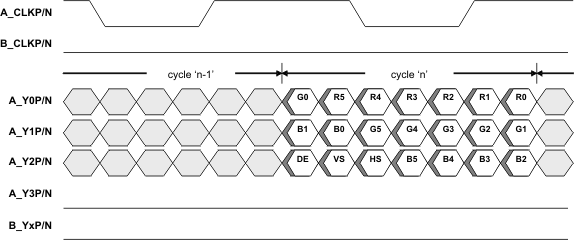
Figure 8 illustrates a Single-Link LVDS 18bpp application.
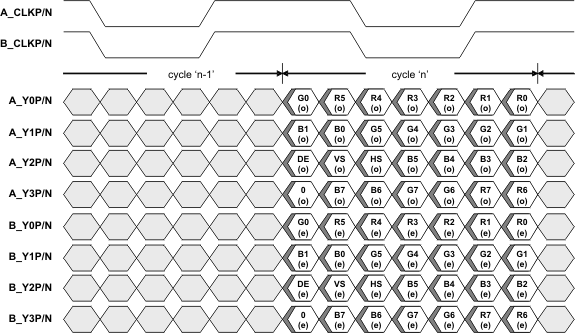
Figure 9 illustrates a Dual-Link 24 bpp application using Format 2, controlled by CHA_24BPP_FORMAT1 (CSR 0x18.1) and CHB_24BPP_FORMAT1 (CSR 0x18.0). In data Format 2, the two MSB per color are transferred on the Y3P/N LVDS lane.
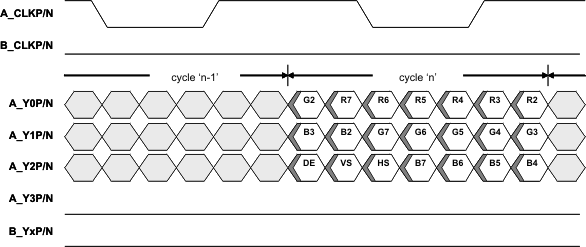
Figure 10 illustrates a 24 bpp Single-Link application using Format 1. In data Format 1, the two LSB per color are transferred on the Y3P/N LVDS lane.
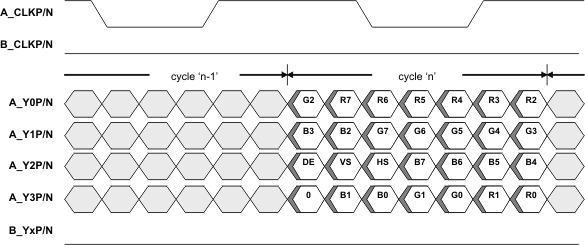
Figure 11 illustrates a Single-Link LVDS application where 24 bpp data is received from DSI and converted to 18 bpp data for transmission to an 18 bpp panel. This application is configured by setting CHA_24BPP_FORMAT1 (CSR 0x18.1) to ‘1’ and CHA_24BPP_MODE (CSR 0x18.3) to ‘0’. In this configuration, the SN65DSI84-Q1 will not transmit the 2 LSB per color because the Y3P/N LVDS lane is disabled.
NOTE
Note: Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, and Figure 11 only illustrate a few example applications for the SN65DSI84-Q1. Other applications are also supported.