ZHCSBN6A September 2013 – November 2015 SN65HVD265 , SN65HVD266 , SN65HVD267
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 (说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted).(1)(2)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| VRXD | RXD Output supply voltage | SN65HVD266 | –0.3 | 6 and VRXD ≤ VCC + 0.3 | V |
| VBUS | CAN Bus I/O voltage (CANH, CANL) | –27 | 40 | V | |
| V(Logic_Input) | Logic input terminal voltage (TXD, S) | –0.3 | 6 | V | |
| V(Logic_Output) | Logic output terminal voltage (RXD) | SN65HVD265, SN65HVD267 | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| SN65HVD266 | –0.3 | 6 and VI ≤ VRXD + 0.3 | V | ||
| IO(RXD) | RXD (Receiver) output current | 12 | mA | ||
| IO(FAULT) | FAULT output current | SN65HVD267 | 20 | mA | |
| TJ | Operating virtual junction temperature (see Thermal Information) | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| TA | Ambient temperature (see Thermal Information) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values, except differential I/O bus voltages, are with respect to ground terminal.
7.2 ESD Ratings: AEC
| VALUE | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | All pins | ±2500 | V | |
| CAN bus pins (CANH, CANL)(3) | ±12000 | |||||
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±750 | |||||
| Machine Model | ±250 | |||||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(3) Test method based upon JEDEC Standard 22 Test Method A114, CAN bus stressed with respect to GND.
7.3 ESD Ratings: IEC
| VALUE | UNIT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | IEC 61400-4-2 according to GIFT-ICT CAN EMC test spec(1) | ±8000 | V | ||
(1) IEC 61400-4-2 is a system level ESD test. Results given here are specific to the GIFT-ICT CAN EMC Test specification conditions. Different system level configurations may lead to different results.
7.4 Transient Protection
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO7637 Transients according to GIFT - ICT CAN EMC test spec(1) | CAN bus pins (CANH, CANL) |
Pulse 1 | –100 | V |
| Pulse 2 | +75 | V | ||
| Pulse 3a | –150 | V | ||
| Pulse 3b | +100 | V | ||
(1) ISO7637 is a system level transient test. Results given here are specific to the GIFT-ICT CAN EMC Test specification conditions. Different system level configurations may lead to different results.
7.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 4.5 | 5.5 | V | |
| VRXD | RXD supply (SN65HVD266 only) | 2.8 | 5.5 | V | |
| VI or VIC | CAN bus terminal voltage (separately or common mode) | –2 | 7 | V | |
| VID | CAN bus differential voltage | -6 | 6 | V | |
| VIH | Logic HIGH level input (TXD, S) | 2 | 5.5 | V | |
| VIL | Logic LOW level input (TXD, S) | 0 | 0.8 | V | |
| IOH(DRVR) | CAN BUS Driver High level output current | –70 | mA | ||
| IOL(DRVR) | CAN BUS Driver Low level output current | 70 | mA | ||
| IOH(RXD) | RXD terminal HIGH level output current | –2 | mA | ||
| IOL(RXD) | RXD terminal LOW level output current | 2 | mA | ||
| IO(FAULT) | FAULT terminal LOW level output current | SN65HVD267 | 2 | mA | |
| TA | Operational free-air temperature (see Thermal Information) | –40 | 125 | °C | |
7.6 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | SN65HVD265, SN65HVD266, SN65HVD267 |
UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (SOIC) | ||||
| 8 PINS | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-air thermal resistance, High-K thermal resistance | 107.5 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 48.9 | °C/W | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 56.7 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 12.1 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 48.2 | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.7 Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted): TA = –40°C to 125°C, SN65HVD266 device VRXD = VCC.| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| ICC | 5-V Supply current | Normal Mode (Driving Dominant) | See Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, RL = 50 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0V | 60 | 85 | mA | |
| Normal Mode (Driving Dominant – bus fault) | See Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, S = 0V, CANH = -12V, RL = open, CL = open, RCM = open | 130 | 180 | ||||
| Normal Mode (Driving Dominant) | See Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, RL = open (no load), CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0V |
10 | 20 | ||||
| Normal Mode (Recessive) | See Figure 4, TXD = VCC, RL = 50 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open, S = 0V |
10 | 20 | ||||
| Silent Mode | See Figure 4, TXD = VCC, RL = 50 Ω,CL = open, RCM = open, S = VCC |
2.5 | 5 | ||||
| I(RXD) | RXD Supply current (SN65HVD266 only) | All modes | RXD Floating, TXD = 0V | 500 | µA | ||
| UVVCC | Undervoltage detection on VCC for protected mode | 3.5 | 4.45 | V | |||
| VHYS(UVVCC) | Hysteresis voltage on UVVCC | 200 | mV | ||||
| SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED) | |||||||
| UV(RXD) | Undervoltage detection on VRXD for protected mode (SN65HVD266 only) | 1.3 | 2.75 | V | |||
| VHYS(UVRXD) | Hysteresis voltage on UVRXD (SN65HVD266 only) | 80 | mV | ||||
| S TERMINAL (MODE SELECT INPUT) | |||||||
| VIH | HIGH-level input voltage | 2 | V | ||||
| VIL | LOW-level input voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| IIH | HIGH-level input leakage current | S = VCC = 5.5 V | 7 | 100 | µA | ||
| IIL | Low-level input leakage current | S = 0 V, VCC = 5.5 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| Ilkg(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | S = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, V(RXD) = 0 V | 7 | 35 | 100 | µA | |
| TXD TERMINAL (CAN TRANSMIT DATA INPUT) | |||||||
| VIH | HIGH level input voltage | 2 | V | ||||
| VIL | LOW level input voltage | 0.8 | V | ||||
| IIH | HIGH level input leakage current | TXD = VCC = 5.5 V | –2.5 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| IIL | Low level input leakage current | TXD = 0 V, VCC = 5.5 V | –100 | -25 | –7 | µA | |
| Ilkg(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | TXD = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, V(RXD) = 0 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| CI | Input Capacitance | 3.5 | pF | ||||
| RXD TERMINAL (CAN RECEIVE DATA OUTPUT) | |||||||
| VOH | HIGH level output voltage | See Figure 5, IO = –2 mA. For devices with V(RXD) supply VOH = 0.8 × V(RXD) | 0.8×VCC | V | |||
| VOL | LOW level output voltage | See Figure 5, IO = 2 mA | 0.4 | V | |||
| Ilkg(OFF) | Unpowered leakage current | RXD = 5.5 V, VCC = 0 V, V(RXD) = 0 V | –1 | 0 | 1 | µA | |
| DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VO(D) | Bus output voltage (dominant | CANH | See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open | 2.75 | 4.5 | V | |
| CANL | 0.5 | 2.25 | |||||
| VO(R) | Bus output voltage (recessive) | See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = VCC, V(RXD) = VCC, S = VCC or 0 V (3), RL = open (no load), RCM = open | 2 | 0.5×VCC | 3 | V | |
| VOD(D) | Differential output voltage (dominant) | See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, 45 Ω ≤ RL ≤ 65 Ω, CL = open, RCM = 330 Ω, –2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 7 V, 4.75 V≤ VCC ≤ 5.25 V | 1.5 | 3 | V | ||
| See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = 0 V, S = 0 V, 45 Ω ≤ RL ≤ 65 Ω, CL = open, RCM = 330 Ω, –2 V ≤ VCM ≤ 7 V, 4.5V ≤ VCC ≤ 5.5 V | 1.25 | 3.2 | |||||
| VOD(R) | Differential output voltage (recessive) | See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = VCC, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open | –0.12 | 0.012 | V | ||
| See Figure 14 and Figure 4, TXD = VCC, S = 0 V, RL = open (no load), CL = open, RCM = open, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C | –0.100 | 0.050 | |||||
| VSYM | Output symmetry (dominant or recessive) (VCC – VO(CANH) – VO(CANL)) |
See Figure 14 and Figure 4, S at 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open, RCM = open | –0.4 | 0.4 | V | ||
| DRIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED) | |||||||
| IOS(SS_DOM) | Short circuit steady-state output current, Dominant | See Figure 14 and Figure 10, VCANH = 0 V, CANL = open, TXD = 0 V | –160 | mA | |||
| See Figure 14 and Figure 10, VCANL = 32 V, CANH = open, TXD = 0 V | 160 | ||||||
| IOS(SS_REC) | Short circuit steady-state output current, Recessive | See Figure 14 and Figure 10, –20 V ≤ VBUS ≤ 32 V, Where VBUS = CANH = CANL, TXD = VCC, Normal and Silent Modes | –8 | 8 | mA | ||
| RECEIVER ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VIT+ | Positive-going input threshold voltage, normal mode | See Figure 5, Table 6 and Table 1 | 900 | mV | |||
| VIT– | Negative-going input threshold voltage, normal mode | 500 | mV | ||||
| VHYS | Hysteresis voltage (VIT+ - VIT–) | 125 | mV | ||||
| Ilkg(IOFF) | Power-off (unpowered) bus input leakage current | CANH = CANL = 5 V, VCC = 0 V, V(RXD) = 0 V | 5.5 | µA | |||
| CI | Input capacitance to ground (CANH or CANL) | TXD = VCC, V(RXD) = VCC, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6 π t) + 2.5 V | 25 | pF | |||
| CID | Differential input capacitance | TXD = VCC, V(RXD) = VCC, VI = 0.4 sin (4E6 π t) | 10 | pF | |||
| RID | Differential input resistance | TXD = VCC = V(RXD) = 5 V, S = 0 V | 30 | 80 | kΩ | ||
| RIN | Input resistance (CANH or CANL) | 15 | 40 | kΩ | |||
| RIN(M) | Input resistance matching: [1 – RIN(CANH) / RIN(CANL)] × 100% |
V(CANH) = V(CANL), –40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C | –3% | 3% | |||
| FAULT terminal (Fault Output), SN65HVD267 only | |||||||
| ICH | Output current high level | FAULT = VCC, See Figure 3 | –10 | 10 | µA | ||
| ICL | Output current low level | FAULT = 0.4 V, See Figure 3 | 5 | 12 | mA | ||
| POWER DISSIPATION | |||||||
| PD | Average power dissipation | VCC = 5 V, VRXD = 5 V, TJ = 27°C, RL = 60 Ω, S at 0 V, Input to TXD at 250 kHz, 25% duty cycle square wave, CL_RXD = 15 pF. Typical CAN operating conditions at 500kbps with 25% transmission (dominant) rate. | 115 | mW | |||
| VCC = 5.5 V, VRXD = 5.5 V, TJ = 150°C, RL = 50 Ω, S at 0 V, Input to TXD at 500 kHz, 50% duty cycle square wave, CL_RXD = 15 pF. Typical high load CAN operating conditions at 1mbps with 50% transmission (dominant) rate and loaded network. | 268 | ||||||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | |||||||
| Thermal shutdown temperature | 170 | °C | |||||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | 5 | °C | |||||
(1) All typical values are at 25°C and supply voltages of VCC = 5 V and V(RXD) = 5 V, RL = 60 Ω.
(2) Loop delay symmetry for CAN with flexible data rate or "improved CAN" for data rates in excess of 1Mbps. Specified in accordance with working draft 2Mbps specification from physical layer task force within CAN in Automation.
(3) For the bus output voltage (recessive) will be the same if the device is in normal mode with S terminal LOW or if the device is in silent mode with the S terminal is HIGH.
(4) The TXD dominant timeout (t(TXD_DTO)) disables the driver of the transceiver once the TXD has been dominant longer than t(TXD_DTO), which releases the bus lines to recessive, preventing a local failure from locking the bus dominant. The driver may only transmit dominant again after TXD has been returned HIGH (recessive). While this protects the bus from local faults, locking the bus dominant, it limits the minimum data rate possible. The CAN protocol allows a maximum of eleven successive dominant bits (on TXD) for the worst case, where five successive dominant bits are followed immediately by an error frame. This, along with the t(TXD_DTO) minimum, limits the minimum bit rate. The minimum bit rate may be calculated by: Minimum Bit Rate = 11 / t(TXD_DTO) = 11 bits / 1175 µs = 9.4 kbps.
(5) The RXD timeout (t(RXD_DTO)) disables the driver of the transceiver once the RXD has been dominant longer than t(RXD_DTO), which releases the bus lines to recessive, preventing a local failure from locking the bus dominant. The driver may only transmit dominant again after RXD has been returned HIGH (recessive). While this protects the bus from local faults, locking the bus dominant, it limits the minimum data rate possible. The CAN protocol allows a maximum of eleven successive dominant bits (on RXD) for the worst case, where five successive dominant bits are followed immediately by an error frame. This, along with the t(RXD_DTO) minimum, limits the minimum bit rate. The minimum bit rate may be calculated by: Minimum Bit Rate = 11 / t(RXD_DTO) = 11 bits / 1380 µs = 8 kbps.
7.8 Switching Characteristics
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted).| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEVICE SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| tPROP(LOOP1) | Total loop delay, driver input (TXD) to receiver output (RXD), recessive to dominant | See Figure 7, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = 100 pF, CL(RXD) = 15 pF |
150 | ns | |||
| tPROP(LOOP2) | Total loop delay, driver input (TXD) to receiver output (RXD), dominant to recessive | 150 | |||||
| tREC(2Mbps) | Loop Delay Symmetry for 2Mbps CAN with Flexible Data Rate.(2) | See Figure 8 , S = 0 V, RL = 60Ω, CL = 100pF, CL(RXD) = 15pF, tBIT = 500ns | 400 | 550 | |||
| IMODE | Mode change time, from Normal to Silent or from Silent to Normal | See Figure 6 | 20 | µS | |||
| DRIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| tpHR | Propagation delay time, HIGH TXD to Driver Recessive | See Figure 4, S = 0 V, RL = 60 Ω, CL = 100 pF, RCM = open |
50 | 70 | ns | ||
| tpLD | Propagation delay time, LOW TXD to Driver Dominant | 40 | 70 | ||||
| tsk(p) | Pulse skew (|tpHR - tpLD|) | 10 | |||||
| tR | Differential output signal rise time | 10 | 30 | ||||
| tF | Differential output signal fall time | 17 | 30 | ||||
| tR(10k) | Differential output signal rise time, RL = 10 kΩ |
See Figure 4, S = 0 V, RL = 10 kΩ, CL = 10 pF, RCM = open | 35 | ns | |||
| tF(10k) | Differential output signal fall time, RL = 10 kΩ |
100 | |||||
| tTXD_DTO | Dominant timeout(4) | See Figure 9, RL = 60 Ω, CL = open | 1175 | 3700 | µs | ||
| RECEIVER SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| tpRH | Propagation delay time, recessive input to high output | See Figure 5, CL(RXD) = 15 pF | 70 | 90 | ns | ||
| tpDL | Propagation delay time, dominant input to low output | 70 | 90 | ns | |||
| tR | Output signal rise time | 4 | 20 | ns | |||
| tF | Output signal fall time | 4 | 20 | ns | |||
| t(RXD_DTO) (5) | Receiver dominant time out (SN65HVD267 only) See Figure 2, CL(RXD) = 15 pF | 1380 | 4200 | µs | |||
7.9 Typical Characteristics
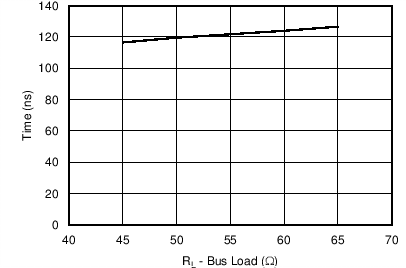 Figure 1. Typical Loop Delay With Respect To Bus Load
Figure 1. Typical Loop Delay With Respect To Bus Load