ZHCSKM5 December 2019 TAS2110
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 PurePath™ Console 3 Software
- 8.3.2 Device Mode and Address Selection
- 8.3.3 General I2C Operation
- 8.3.4 Single-Byte and Multiple-Byte Transfers
- 8.3.5 Single-Byte Write
- 8.3.6 Multiple-Byte Write and Incremental Multiple-Byte Write
- 8.3.7 Single-Byte Read
- 8.3.8 Multiple-Byte Read
- 8.3.9 Register Organization
- 8.3.10 Operational Modes
- 8.3.11 Faults and Status
- 8.3.12 Power Sequencing Requirements
- 8.3.13 Digital Input Pull Downs
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 TDM Port
- 8.4.2 Playback Signal Path
- 8.4.3 SAR ADC
- 8.4.4 Boost
- 8.4.5 Clocks and PLL
- 8.4.6 Thermal Foldback
- 8.4.7 Internal Tone Generator
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 Register Summary Table Page=0x00
- 8.5.2 Register Summary Table Page=0x01
- 8.5.3 Register Summary Table Page=0x02
- 8.5.4 Register Summary Table Page=0x04
- 8.5.5 PAGE0 (page=0x00 address=0x00) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.6 SW_RESET (page=0x00 address=0x01) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.7 PWR_CTL (page=0x00 address=0x02) [reset=Eh]
- 8.5.8 PB_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x03) [reset=20h]
- 8.5.9 MISC_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x04) [reset=C6h]
- 8.5.10 MISC_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x05) [reset=22h]
- 8.5.11 TDM_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x06) [reset=9h]
- 8.5.12 TDM_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x07) [reset=2h]
- 8.5.13 TDM_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x08) [reset=Ah]
- 8.5.14 TDM_CFG3 (page=0x00 address=0x09) [reset=10h]
- 8.5.15 TDM_CFG4 (page=0x00 address=0x0A) [reset=13h]
- 8.5.16 TDM_CFG7 (page=0x00 address=0x0D) [reset=4h]
- 8.5.17 TDM_CFG8 (page=0x00 address=0x0E) [reset=5h]
- 8.5.18 TDM_CFG9 (page=0x00 address=0x0F) [reset=6h]
- 8.5.19 TDM_CFG10 (page=0x00 address=0x10) [reset=7h]
- 8.5.20 TDM_DET (page=0x00 address=0x11) [reset=7Fh]
- 8.5.21 LIM_CFG_0 (page=0x00 address=0x12) [reset=12h]
- 8.5.22 LIM_CFG_1 (page=0x00 address=0x13) [reset=76h]
- 8.5.23 BOP_CFG_0 (page=0x00 address=0x14) [reset=1h]
- 8.5.24 BOP_CFG_1 (page=0x00 address=0x15) [reset=2Eh]
- 8.5.25 ICLA_CFG (page=0x00 address=0x16) [reset=60h]
- 8.5.26 GAIN_ICLA_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x18) [reset=Ch]
- 8.5.27 ICLA_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x19) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.28 INT_MASK0 (page=0x00 address=0x1A) [reset=FCh]
- 8.5.29 INT_MASK1 (page=0x00 address=0x1B) [reset=A6h]
- 8.5.30 INT_LIVE0 (page=0x00 address=0x1F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.31 INT_LIVE1 (page=0x00 address=0x20) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.32 INT_LTCH0 (page=0x00 address=0x24) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.33 INT_LTCH1 (page=0x00 address=0x25) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.34 VBAT_MSB (page=0x00 address=0x2A) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.35 VBAT_LSB (page=0x00 address=0x2B) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.36 TEMP (page=0x00 address=0x2C) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.37 INT_CLK (page=0x00 address=0x30) [reset=19h]
- 8.5.38 DIN_PD (page=0x00 address=0x31) [reset=40h]
- 8.5.39 MISC_CFG3 (page=0x00 address=0x32) [reset=80h]
- 8.5.40 BOOST_CFG1 (page=0x00 address=0x33) [reset=34h]
- 8.5.41 BOOST_CFG2 (page=0x00 address=0x34) [reset=4Bh]
- 8.5.42 BOOST_CFG3 (page=0x00 address=0x35) [reset=74h]
- 8.5.43 MISC_CFG4 (page=0x00 address=0x3D) [reset=8h]
- 8.5.44 TG_CFG0 (page=0x00 address=0x3F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.45 BOOST_CFG4 (page=0x00 address=0x40) [reset=36h]
- 8.5.46 REV_ID (page=0x00 address=0x7D) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.47 I2C_CKSUM (page=0x00 address=0x7E) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.48 BOOK (page=0x00 address=0x7F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.49 PAGE1 (page=0x01 address=0x00) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.50 TF_CFG21 (page=0x01 address=0x08) [reset=40h]
- 8.5.51 PAGE2 (page=0x02 address=0x00) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.52 DVC_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x0C) [reset=40h]
- 8.5.53 DVC_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x0D) [reset=40h]
- 8.5.54 DVC_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x0E) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.55 DVC_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x0F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.56 DVC_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x10) [reset=3h]
- 8.5.57 DVC_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x11) [reset=4Ah]
- 8.5.58 DVC_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x12) [reset=51h]
- 8.5.59 DVC_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x13) [reset=6Ch]
- 8.5.60 LIM_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x14) [reset=2Dh]
- 8.5.61 LIM_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x15) [reset=6Ah]
- 8.5.62 LIM_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x16) [reset=86h]
- 8.5.63 LIM_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x17) [reset=6Fh]
- 8.5.64 LIM_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x18) [reset=47h]
- 8.5.65 LIM_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x19) [reset=5Ch]
- 8.5.66 LIM_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x1A) [reset=28h]
- 8.5.67 LIM_CFG8 (page=0x02 address=0x1B) [reset=F6h]
- 8.5.68 LIM_CFG9 (page=0x02 address=0x1C) [reset=16h]
- 8.5.69 LIM_CFG10 (page=0x02 address=0x1D) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.70 LIM_CFG11 (page=0x02 address=0x1E) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.71 LIM_CFG12 (page=0x02 address=0x1F) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.72 LIM_CFG13 (page=0x02 address=0x20) [reset=34h]
- 8.5.73 LIM_CFG14 (page=0x02 address=0x21) [reset=CCh]
- 8.5.74 LIM_CFG15 (page=0x02 address=0x22) [reset=CCh]
- 8.5.75 LIM_CFG16 (page=0x02 address=0x23) [reset=CDh]
- 8.5.76 LIM_CFG17 (page=0x02 address=0x24) [reset=10h]
- 8.5.77 LIM_CFG18 (page=0x02 address=0x25) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.78 LIM_CFG19 (page=0x02 address=0x26) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.79 LIM_CFG20 (page=0x02 address=0x27) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.80 BOP_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x28) [reset=2Eh]
- 8.5.81 BOP_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x29) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.82 BOP_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x2A) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.83 BOP_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x2B) [reset=66h]
- 8.5.84 BOP_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x2C) [reset=2Bh]
- 8.5.85 BOP_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x2D) [reset=33h]
- 8.5.86 BOP_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x2E) [reset=33h]
- 8.5.87 BOP_CFG8 (page=0x02 address=0x2F) [reset=33h]
- 8.5.88 HPFC_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x30) [reset=7Fh]
- 8.5.89 HPFC_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x31) [reset=FBh]
- 8.5.90 HPFC_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x32) [reset=B6h]
- 8.5.91 HPFC_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x33) [reset=14h]
- 8.5.92 HPFC_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x34) [reset=80h]
- 8.5.93 HPFC_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x35) [reset=4h]
- 8.5.94 HPFC_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x36) [reset=49h]
- 8.5.95 HPFC_CFG8 (page=0x02 address=0x37) [reset=ECh]
- 8.5.96 HPFC_CFG9 (page=0x02 address=0x38) [reset=7Fh]
- 8.5.97 HPFC_CFG10 (page=0x02 address=0x39) [reset=7Fh]
- 8.5.98 HPFC_CFG11 (page=0x02 address=0x3A) [reset=6Ch]
- 8.5.99 HPFC_CFG12 (page=0x02 address=0x3B) [reset=28h]
- 8.5.100 TG_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x3C) [reset=3Fh]
- 8.5.101 TG_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x3D) [reset=FFh]
- 8.5.102 TG_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x3E) [reset=7Ah]
- 8.5.103 TG_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x3F) [reset=E3h]
- 8.5.104 TG_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x40) [reset=1h]
- 8.5.105 TG_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x41) [reset=1h]
- 8.5.106 TG_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x42) [reset=5Bh]
- 8.5.107 TG_CFG8 (page=0x02 address=0x43) [reset=4Ch]
- 8.5.108 TG_CFG9 (page=0x02 address=0x44) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.109 TG_CFG10 (page=0x02 address=0x45) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.110 TG_CFG11 (page=0x02 address=0x46) [reset=3h]
- 8.5.111 TG_CFG12 (page=0x02 address=0x47) [reset=1Fh]
- 8.5.112 TG_CFG13 (page=0x02 address=0x48) [reset=2h]
- 8.5.113 TG_CFG14 (page=0x02 address=0x49) [reset=46h]
- 8.5.114 TG_CFG15 (page=0x02 address=0x4A) [reset=B4h]
- 8.5.115 TG_CFG16 (page=0x02 address=0x4B) [reset=E4h]
- 8.5.116 TG_CFG17 (page=0x02 address=0x4C) [reset=E0h]
- 8.5.117 TG_CFG18 (page=0x02 address=0x4D) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.118 TG_CFG19 (page=0x02 address=0x4E) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.119 TG_CFG20 (page=0x02 address=0x4F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.120 TG_CFG21 (page=0x02 address=0x50) [reset=6Eh]
- 8.5.121 TG_CFG22 (page=0x02 address=0x51) [reset=D9h]
- 8.5.122 TG_CFG23 (page=0x02 address=0x52) [reset=EBh]
- 8.5.123 TG_CFG24 (page=0x02 address=0x53) [reset=A1h]
- 8.5.124 TG_CFG25 (page=0x02 address=0x54) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.125 TG_CFG26 (page=0x02 address=0x55) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.126 TG_CFG27 (page=0x02 address=0x56) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.127 TG_CFG28 (page=0x02 address=0x57) [reset=2Ch]
- 8.5.128 TG_CFG29 (page=0x02 address=0x58) [reset=8h]
- 8.5.129 TG_CFG30 (page=0x02 address=0x59) [reset=9h]
- 8.5.130 TG_CFG31 (page=0x02 address=0x5A) [reset=BCh]
- 8.5.131 TG_CFG32 (page=0x02 address=0x5B) [reset=C4h]
- 8.5.132 LD_CFG0 (page=0x02 address=0x5C) [reset=64h]
- 8.5.133 LD_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x5D) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.134 LD_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x5E) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.135 LD_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x5F) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.136 LD_CFG4 (page=0x02 address=0x60) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.137 LD_CFG5 (page=0x02 address=0x61) [reset=80h]
- 8.5.138 LD_CFG6 (page=0x02 address=0x62) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.139 LD_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x63) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.140 IDC_CFG0 (page=0x02 address=0x64) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.141 IDC_CFG1 (page=0x02 address=0x65) [reset=20h]
- 8.5.142 IDC_CFG2 (page=0x02 address=0x66) [reset=C4h]
- 8.5.143 IDC_CFG3 (page=0x02 address=0x67) [reset=9Ch]
- 8.5.144 IDC_CFG7 (page=0x02 address=0x6C) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.145 IDC_CFG8 (page=0x02 address=0x6D) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.146 IDC_CFG9 (page=0x02 address=0x6E) [reset=12h]
- 8.5.147 IDC_CFG10 (page=0x02 address=0x6F) [reset=C0h]
- 8.5.148 TF_CFG_1 (page=0x02 address=0x7C) [reset=72h]
- 8.5.149 TF_CFG_2 (page=0x02 address=0x7D) [reset=14h]
- 8.5.150 TF_CFG_3 (page=0x02 address=0x7E) [reset=82h]
- 8.5.151 TF_CFG_4 (page=0x02 address=0x7F) [reset=C0h]
- 8.5.152 PAGE4 (page=0x04 address=0x00) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.153 LD_CFG8 (page=0x04 address=0x18) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.154 LD_CFG9 (page=0x04 address=0x19) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.155 LD_CFG10 (page=0x04 address=0x1A) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.156 LD_CFG11 (page=0x04 address=0x1B) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.157 TF_CFG4 (page=0x04 address=0x58) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.158 TF_CFG5 (page=0x04 address=0x59) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.159 TF_CFG6 (page=0x04 address=0x5A) [reset=0h]
- 8.5.160 TF_CFG7 (page=0x04 address=0x5B) [reset=64h]
- 8.5.161 TF_CFG8 (page=0x04 address=0x5C) [reset=40h]
- 8.5.162 TF_CFG9 (page=0x04 address=0x5D) [reset=BDh]
- 8.5.163 TF_CFG10 (page=0x04 address=0x5E) [reset=B7h]
- 8.5.164 TF_CFG11 (page=0x04 address=0x5F) [reset=B0h]
- 8.5.165 TF_CFG12 (page=0x04 address=0x60) [reset=39h]
- 8.5.166 TF_CFG13 (page=0x04 address=0x61) [reset=82h]
- 8.5.167 TF_CFG14 (page=0x04 address=0x62) [reset=60h]
- 8.5.168 TF_CFG16 (page=0x04 address=0x63) [reset=7Fh]
- 8.5.169 TF_CFG17 (page=0x04 address=0x64) [reset=2Dh]
- 8.5.170 TF_CFG18 (page=0x04 address=0x65) [reset=6Ah]
- 8.5.171 TF_CFG19 (page=0x04 address=0x66) [reset=86h]
- 8.5.172 TF_CFG20 (page=0x04 address=0x67) [reset=6Fh]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.4.1 TDM Port
The TAS2110 provides a flexible TDM serial audio port. The port can be configured to support a variety of formats including stereo I2S, Left Justified and TDM. Mono audio playback is available via the SDIN pin. The SDOUT pin is used to transmit sample streams including VBAT voltage, die temperature and channel gain.
The TDM serial audio port supports up to 16 32-bit time slots at 44.1/48 kHz, 8 32-bit time slots at a 88.2/96 kHz sample rate and 4 32-bit time slots at a 176.4/192 kHz sample rate. The device supports 2 time slots at 32 bits in width and 4 or 8 time slots at 16, 24 or 32 bits in width. Valid SBCLK to FSYNC ratios are 64, 96, 128, 192, 256, 384 and 512. The device will automatically detect the number of time slots and this does not need to be programmed.
By default, the TAS2110 will automatically detect the PCM playback sample rate. This can be disabled by setting the AUTO_RATE register bit high and manually configuring the device.
The SAMP_RATE register bits set the PCM audio sample rate when AUTO_RATE is enabled. The TAS2110 employs a robust clock fault detection engine that will automatically volume ramp down the playback path if FSYNC does not match the configured sample rate (AUTO_RATE enabled) or the ratio of SBCLK to FSYNC is not supported (minimizing any audible artifacts). Once the clocks are detected to be valid in both frequency and ratio, the device will automatically volume ramp the playback path back to the configured volume and resume playback.
When using the auto rate detection the sampling rate and SBCLK to FSYNC ration detected on the TDM bus is reported back on the read-only register FS_RATE and FS_RATIO respectively.
While the sampling rate of 192 kHz is supported, it is internally down-sampled to 96 kHz. Therefore audio content greater than 40 kHz should not be applied to prevent aliasing. This additionally effects all processing blocks like BOP and limiter which should use 96 kHz fs when accepting 192 kHz audio. It is recommend to use PurePath™ Console 3 Software to configure the device.
Table 16. PCM Auto Sample Rate Detection
| AUTO_RATE | SETTING |
|---|---|
0
|
Enabled (default) |
1
|
Disabled |
Table 17. PCM Audio Sample Rates
| SAMP_RATE[2:0] | FS_RATE(read only) | SAMPLE RATE |
|---|---|---|
000
|
000
|
7.35kHz / 8 kHz |
001
|
001
|
14.7kHz / 16kHz |
010
|
010
|
22.05 kHz / 24 kHz |
011
|
011
|
29.4 kHz / 32 kHz |
100
|
100
|
44.1 kHz / 48 kHz (default) |
101
|
101
|
88.2 kHz / 96 kHz |
110
|
110
|
176.4 kHz / 192 kHz |
111
|
111
|
Reserved |
Table 18. PCM SBCLK to FSYNC Ratio Rates
| FS_RATIO[3:0] | SAMPLE RATE |
|---|---|
0x0-0x3
|
Reserved |
0x4
|
64 |
0x5
|
96 |
0x6
|
128 |
0x7
|
192 |
0x8
|
256 |
0x9
|
384 |
0xA
|
512 |
0xB-0xE
|
Reserved |
0xF
|
Error Condition |
Figure 39 and Figure 40 below illustrates the receiver frame parameters required to configure the port for playback. A frame begins with the transition of FSYNC from either high to low or low to high (set by the FRAME_START register bit). FSYNC and SDIN are sampled by SBCLK using either the rising or falling edge (set by the RX_EDGE register bit). The RX_OFFSET register bits define the number of SBCLK cycles from the transition of FSYNC until the beginning of time slot 0. This is typically set to a value of 0 for Left Justified format and 1 for an I2S format.
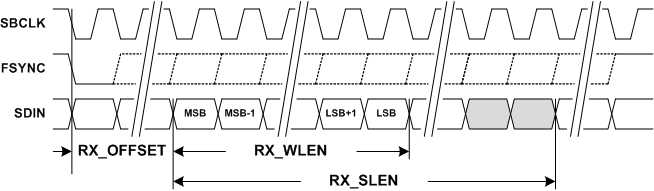 Figure 39. TDM RX Time Slot with Left Justification
Figure 39. TDM RX Time Slot with Left Justification 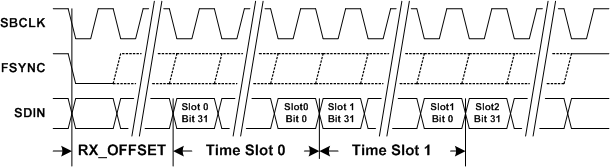 Figure 40. TDM RX Time Slots
Figure 40. TDM RX Time Slots Table 19. TDM Start of Frame Polarity
| FRAME_START | POLARITY |
|---|---|
0
|
Low to High on FSYNC(1) |
1
|
High to Low on FSYNC (default)(2) |
Table 20. TDM RX Capture Polarity
| RX_EDGE | FSYNC AND SDIN CAPTURE EDGE |
|---|---|
0
|
Rising edge of SBCLK (default) |
1
|
Falling edge of SBCLK |
Table 21. TDM RX Start of Frame to Time Slot 0 Offset
| RX_OFFSET[4:0] | SBCLK CYCLES |
|---|---|
0x00
|
0 |
0x01
|
1 (default) |
0x02
|
2 |
...
|
... |
0x1E
|
30 |
0x1F
|
31 |
The RX_SLEN[1:0] register bits set the length of the RX time slot. The length of the audio sample word within the time slot is configured by the RX_WLEN[1:0] register bits. The RX port will left justify the audio sample within the time slot by default, but this can be changed to right justification via the RX_JUSTIFY register bit. The TAS2110 supports mono and stereo down mix playback ([L+R]/2) via the left time slot, right time slot and time slot configuration register bits (RX_SLOT_L[3:0], RX_SLOT_R[3:0] and RX_SCFG[1:0] respectively). By default the device will playback mono from the time slot equal to the I2C base address offset for playback. The RX_SCFG[1:0] register bits can be used to override the playback source to the left time slot, right time slot or stereo down mix set by the RX_SLOT_L[3:0] and RX_SLOT_R[3:0] register bits.
If time slot selections places reception either partially or fully beyond the frame boundary, the receiver will return a null sample equivalent to a digitally muted sample.
Table 22. TDM RX Time Slot Length
| RX_SLEN[1:0] | TIME SLOT LENGTH |
|---|---|
00
|
16-bits |
01
|
24-bits |
10
|
32-bits (default) |
11
|
reserved |
Table 23. TDM RX Sample Word Length
| RX_WLEN[1:0] | LENGTH |
|---|---|
00
|
16-bits |
01
|
20-bits |
10
|
24-bits (default) |
11
|
32-bits |
Table 24. TDM RX Sample Justification
| RX_JUSTIFY | JUSTIFICATION |
|---|---|
0
|
Left (default) |
1
|
Right |
Table 25. TDM RX Time Slot Select Configuration
| RX_SCFG[1:0] | CONFIG ORIGIN |
|---|---|
00
|
Mono with Time Slot equal to I2C Address Offset (default) |
01
|
Mono Left Channel |
10
|
Mono Right Channel |
10
|
Stereo Down Mix [L+R]/2 |
Table 26. TDM RX Left Channel Time Slot
| RX_SLOT_L[3:0] | TIME SLOT |
|---|---|
0x0
|
0 (default) |
0x1
|
1 |
...
|
... |
0xE
|
14 |
0xF
|
15 |
Table 27. TDM RX Right Channel Time Slot
| RX_SLOT_R[3:0] | TIME SLOT |
|---|---|
0x0
|
0 |
0x1
|
1 (default) |
...
|
... |
0xE
|
14 |
0xF
|
15 |
The TDM port can transmit a number sample streams on the SDOUT pin including, VBAT voltage, die temperature and channel gain. below illustrates the alignment of time slots to the beginning of a frame and how a given sample stream is mapped to time slots. Either the rising or falling edge of SBCLK can be used to transmit data on the SDOUT pin, which can be configured by setting the TX_EDGE register bit. The TX_OFFSET register defines the number SBCLK cycles between the start of a frame and the beginning of time slot 0. This would typically be programmed to 0 for Left Justified format and 1 for I2S format. The TDM TX can either transmit logic 0 or Hi-Z depending on the setting of the TX_FILL register bit setting. An optional bus keeper will weakly hold the state of SDOUT when all devices driving are Hi-Z. Since only one bus keeper is required on SDOUT, this feature can be disabled via the TX_KEEPEN register bit. The bus-keeper can additionally be configured to be enabled for only 1LSB cycle or always using TX_KEEPLN and to drive the full or half cycle of the LSB using TX_KEEPCY.
Each sample stream is composed of either one or two 8-bit time slots.. The VBAT voltage stream is 10-bit precision, and can either be transmitted left justified in a 16-bit word (using two time slots) or can be truncated to 8-bits (the top 8 MSBs) and be transmitted in a single time slot. This is configured by setting VBAT_SLEN register bit. The Die temperature and gain are both 8-bit precision and are transmitted in a single time slot.
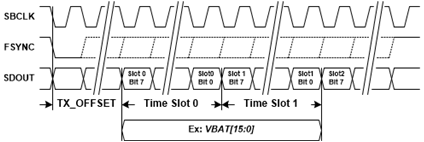 Figure 41. TDM Port TX Diagram
Figure 41. TDM Port TX Diagram Table 28. TDM TX Transmit Polarity
| TX_EDGE | SDOUT TRANSMIT EDGE |
|---|---|
0
|
Rising edge of SBCLK |
1
|
Falling edge of SBCLK (default) |
Table 29. TDM TX Start of Frame to Time Slot 0 Offset
| TX_OFFSET[2:0] | SBCLK CYCLES |
|---|---|
0x0
|
0 |
0x1
|
1 (default) |
0x2
|
2 |
...
|
... |
0x6
|
6 |
0x7
|
7 |
Table 30. TDM TX Unused Bit Field Fill
| TX_FILL | SDOUT UNUSED BIT FIELDS |
|---|---|
0
|
Transmit 0 |
1
|
Transmit Hi-Z (default) |
Table 31. TDM TX SDOUT Bus Keeper Enable
| TX_KEEPEN | SDOUT BUS KEEPER |
|---|---|
0
|
Disable bus keeper |
1
|
Enable bus keeper (default) |
Table 32. TDM TX SDOUT Bus Keeper Length
| TX_KEEPLN | SDOUT BUS KEEPER ENABLED FOR |
|---|---|
0
|
1 LSB cycle (default) |
1
|
Always |
Table 33. TDM TX SDOUT Bus Keeper LSB Cycle
| TX_KEEPCY | SDOUT BUS KEEPER DRIVEN |
|---|---|
0
|
full-cycle (default) |
1
|
half-cycle |
The time slot register for each sample stream defines where the MSB transmission begins. Each sample stream can be individually enabled or disabled. This is useful to manage limited TDM bandwidth since it may not be necessary to transmit all streams for all devices on the bus.
It is important to ensure that time slot assignments for actively transmitted sample streams do not conflict. This will produce unpredictable transmission results in the conflicting bit slots
If time slot selections place transmission beyond the frame boundary, the transmitter will truncate transmission at the frame boundary.
It is recommended to keep the following slot ordering:
VBAT_SLOT<TEMP_SLOT<GAIN_SLOT.
Table 34. TDM VBAT Time Slot
| VBAT_SLOT[5:0] | SLOT |
|---|---|
0x00
|
0 |
0x01
|
1 |
...
|
... |
0x04
|
4 (default) |
...
|
... |
0x3E
|
62 |
0x3F
|
63 |
Table 35. TDM VBAT Time Slot Length
| VBAT_SLEN | SLOT LENGTH |
|---|---|
0
|
Truncate to 8-bits (default) |
1
|
Left justify to 16-bits |
Table 36. TDM VBAT Transmit Enable
| VBAT_TX | STATE |
|---|---|
0
|
Disabled (default) |
1
|
Enabled |
Table 37. TDM Temp Sensor Time Slot
| TEMP_SLOT[5:0] | SLOT |
|---|---|
0x00
|
0 |
0x01
|
1 |
...
|
... |
0x05
|
5 (default) |
...
|
... |
0x3E
|
62 |
0x3F
|
63 |
Table 38. TDM Temp Sensor Transmit Enable
| TEMP_TX | STATE |
|---|---|
0
|
Disabled (default) |
1
|
Enabled |
The following sample streams are part of the Inter Chip Limiter Alignment system. These data streams can be routed over the audio TDM bus.
Table 39. TDM Limiter Gain Reduction Time Slot
| GAIN_SLOT[5:0] | SLOT |
|---|---|
0x00
|
0 |
0x01
|
1 |
...
|
... |
0x06
|
6 (default) |
...
|
... |
0x3E
|
62 |
0x3F
|
63 |
Table 40. TDM Limiter Gain Reduction Transmit Enable
| GAIN_TX | STATE |
|---|---|
0
|
Disabled (default) |
1
|
Enabled |
Table 41. TDM Boost Sync Time Slot
| BST_SLOT[5:0] | SLOT |
|---|---|
0x00
|
0 |
0x01
|
1 |
...
|
... |
0x07
|
7 (default) |
...
|
... |
0x3E
|
62 |
0x3F
|
63 |
Table 42. TDM Boost Sync Enable
| BST_TX | STATE |
|---|---|
0
|
Disabled (default) |
1
|
Enabled |