ZHCSH30C August 2017 – April 2018 TAS5755M
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 PWM Operation at Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.6 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 AC Electrical Characteristics (BTL, PBTL)
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics - PLL External Filter Components
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristic - I2C Serial Control Port Operation
- 7.10 Timing Requirements - PLL Input Parameters
- 7.11 Timing Requirements - Serial Audio Ports Slave Mode
- 7.12 Timing Requirements - I2C Serial Control Port Operation
- 7.13 Timing Requirements - Reset (RESET)
- 7.14 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power Supply
- 9.3.2 I2C Address Selection and Fault Output
- 9.3.3 Single-Filter PBTL Mode
- 9.3.4 Device Protection System
- 9.3.5 SSTIMER Functionality
- 9.3.6 Clock, Autodetection, and PLL
- 9.3.7 PWM Section
- 9.3.8 2.1-Mode Support
- 9.3.9 I2C Compatible Serial Control Interface
- 9.3.10 Audio Serial Interface
- 9.3.11 Dynamic Range Control (DRC)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1 Register Map Summary
- 9.6.2
Register Maps
- 9.6.2.1 Clock Control Register (0x00)
- 9.6.2.2 Device ID Register (0x01)
- 9.6.2.3 Error Status Register (0x02)
- 9.6.2.4 System Control Register 1 (0x03)
- 9.6.2.5 Serial Data Interface Register (0x04)
- 9.6.2.6 System Control Register 2 (0x05)
- 9.6.2.7 Soft Mute Register (0x06)
- 9.6.2.8 Volume Registers (0x07, 0x08, 0x09, 0x0A)
- 9.6.2.9 Volume Configuration Register (0x0E)
- 9.6.2.10 Modulation Limit Register (0x10)
- 9.6.2.11 Interchannel Delay Registers (0x11, 0x12, 0x13, and 0x14)
- 9.6.2.12 PWM Shutdown Group Register (0x19)
- 9.6.2.13 Start/Stop Period Register (0x1A)
- 9.6.2.14 Oscillator Trim Register (0x1B)
- 9.6.2.15 BKND_ERR Register (0x1C)
- 9.6.2.16 Input Multiplexer Register (0x20)
- 9.6.2.17 Channel 4 Source Select Register (0x21)
- 9.6.2.18 PWM Output Mux Register (0x25)
- 9.6.2.19 DRC Control Register (0x46)
- 9.6.2.20 Bank Switch and EQ Control Register (0x50)
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Stereo Bridge Tied Load Application
- 10.2.2 Mono Parallel Bridge Tied Load Application
- 10.2.3 2.1 Application
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
9.5.1.5 Single-Byte Read
As shown in Figure 63, a single-byte data-read transfer begins with the master device transmitting a start condition, followed by the I2C device address and the read/write bit. For the data read transfer, both a write followed by a read are actually done. Initially, a write is done to transfer the address byte or bytes of the internal memory address to be read. As a result, the read/write bit becomes a 0. After receiving the TAS5755M address and the read/write bit, TAS5755M responds with an acknowledge bit. In addition, after sending the internal memory address byte or bytes, the master device transmits another start condition followed by the TAS5755M address and the read/write bit again. This time, the read/write bit becomes a 1, indicating a read transfer. After receiving the address and the read/write bit, the TAS5755M again responds with an acknowledge bit. Next, the TAS5755M transmits the data byte from the memory address being read. After receiving the data byte, the master device transmits a not-acknowledge followed by a stop condition to complete the single-byte data-read transfer.
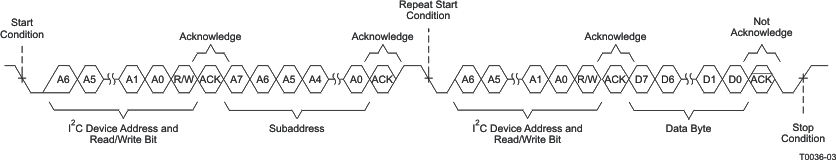 Figure 63. Single-Byte Read Transfer
Figure 63. Single-Byte Read Transfer