ZHCSGH3A March 2016 – July 2017 TAS5782M
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Power Dissipation Characteristics
- 7.7 MCLK Timing
- 7.8 Serial Audio Port Timing – Slave Mode
- 7.9 Serial Audio Port Timing – Master Mode
- 7.10 I2C Bus Timing – Standard
- 7.11 I2C Bus Timing – Fast
- 7.12 SPK_MUTE Timing
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parametric Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Power-on-Reset (POR) Function
- 9.3.2 Device Clocking
- 9.3.3
Serial Audio Port
- 9.3.3.1 Clock Master Mode from Audio Rate Master Clock
- 9.3.3.2 Clock Master from a Non-Audio Rate Master Clock
- 9.3.3.3 Clock Slave Mode with 4-Wire Operation (SCLK, MCLK, LRCK/FS, SDIN)
- 9.3.3.4 Clock Slave Mode with SCLK PLL to Generate Internal Clocks (3-Wire PCM)
- 9.3.3.5 Serial Audio Port – Data Formats and Bit Depths
- 9.3.3.6 Input Signal Sensing (Power-Save Mode)
- 9.3.4 Enable Device
- 9.3.5 Volume Control
- 9.3.6 Adjustable Amplifier Gain and Switching Frequency Selection
- 9.3.7
Error Handling and Protection Suite
- 9.3.7.1 Device Overtemperature Protection
- 9.3.7.2 SPK_OUTxx Overcurrent Protection
- 9.3.7.3 DC Offset Protection
- 9.3.7.4 Internal VAVDD Undervoltage-Error Protection
- 9.3.7.5 Internal VPVDD Undervoltage-Error Protection
- 9.3.7.6 Internal VPVDD Overvoltage-Error Protection
- 9.3.7.7 External Undervoltage-Error Protection
- 9.3.7.8 Internal Clock Error Notification (CLKE)
- 9.3.8 GPIO Port and Hardware Control Pins
- 9.3.9 I2C Communication Port
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
-
13Register Maps
- 13.1
Registers - Page 0
- 13.1.1 Register 1 (0x01)
- 13.1.2 Register 6 (0x06)
- 13.1.3 Register 7 (0x07)
- 13.1.4 Register 8 (0x08)
- 13.1.5 Register 9 (0x09)
- 13.1.6 Register 12 (0x0C)
- 13.1.7 Register 13 (0x0D)
- 13.1.8 Register 14 (0x0E)
- 13.1.9 Register 15 (0x0F)
- 13.1.10 Register 16 (0x10)
- 13.1.11 Register 17 (0x11)
- 13.1.12 Register 18 (0x12)
- 13.1.13 Register 20 (0x14)
- 13.1.14 Register 21 (0x15)
- 13.1.15 Register 22 (0x16)
- 13.1.16 Register 23 (0x17)
- 13.1.17 Register 24 (0x18)
- 13.1.18 Register 27 (0x1B)
- 13.1.19 Register 28 (0x1C)
- 13.1.20 Register 29 (0x1D)
- 13.1.21 Register 30 (0x1E)
- 13.1.22 Register 32 (0x20)
- 13.1.23 Register 33 (0x21)
- 13.1.24 Register 34 (0x22)
- 13.1.25 Register 37 (0x25)
- 13.1.26 Register 40 (0x28)
- 13.1.27 Register 41 (0x29)
- 13.1.28 Register 42 (0x2A)
- 13.1.29 Register 43 (0x2B)
- 13.1.30 Register 44 (0x2C)
- 13.1.31 Register 59 (0x3B)
- 13.1.32 Register 60 (0x3C)
- 13.1.33 Register 61 (0x3D)
- 13.1.34 Register 62 (0x3E)
- 13.1.35 Register 63 (0x3F)
- 13.1.36 Register 64 (0x40)
- 13.1.37 Register 65 (0x41)
- 13.1.38 Register 67 (0x43)
- 13.1.39 Register 68 (0x44)
- 13.1.40 Register 69 (0x45)
- 13.1.41 Register 70 (0x46)
- 13.1.42 Register 71 (0x47)
- 13.1.43 Register 72 (0x48)
- 13.1.44 Register 73 (0x49)
- 13.1.45 Register 74 (0x4A)
- 13.1.46 Register 75 (0x4B)
- 13.1.47 Register 76 (0x4C)
- 13.1.48 Register 78 (0x4E)
- 13.1.49 Register 79 (0x4F)
- 13.1.50 Register 83 (0x53)
- 13.1.51 Register 85 (0x55)
- 13.1.52 Register 86 (0x56)
- 13.1.53 Register 87 (0x57)
- 13.1.54 Register 88 (0x58)
- 13.1.55 Register 91 (0x5B)
- 13.1.56 Register 92 (0x5C)
- 13.1.57 Register 93 (0x5D)
- 13.1.58 Register 94 (0x5E)
- 13.1.59 Register 95 (0x5F)
- 13.1.60 Register 108 (0x6C)
- 13.1.61 Register 119 (0x77)
- 13.1.62 Register 120 (0x78)
- 13.2 Registers - Page 1
- 13.1
Registers - Page 0
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
10.2.2 Mono (PBTL) Systems
For the mono (PBTL) PCB layout, see Figure 87.
A mono system refers to a system in which the amplifier is used to drive a single loudspeaker. Parallel Bridge Tied Load (PBTL) indicates that the two full-bridge channels of the device are placed in parallel and drive the loudspeaker simultaneously using an identical audio signal. The primary benefit of operating the TAS5782M device in PBTL operation is to reduce the power dissipation and increase the current sourcing capabilities of the amplifier output. In this mode of operation, the current limit of the audio amplifier is approximately doubled while the on-resistance is approximately halved.
The loudspeaker can be a full-range transducer or one that only reproduces the low-frequency content of an audio signal, as in the case of a powered subwoofer. Often in this use case, two stereo signals are mixed together and sent through a low-pass filter to create a single audio signal which contains the low frequency information of the two channels. Conversely, advanced digital signal processing can create a low-frequency signal for a multichannel system, with audio processing which is specifically targeted on low-frequency effects.
Because low-frequency signals are not perceived as having a direction (at least to the extent of high-frequency signals) it is common to reproduce the low-frequency content of a stereo signal that is sent to two separate channels. This configuration pairs one device in Mono PBTL configuration and another device in Stereo BTL configuration in a single system called a 2.1 system. The Mono PBTL configuration is detailed in the 2.1 (Stereo BTL + External Mono Amplifier) Systems section. shows the Mono (PBTL) system application
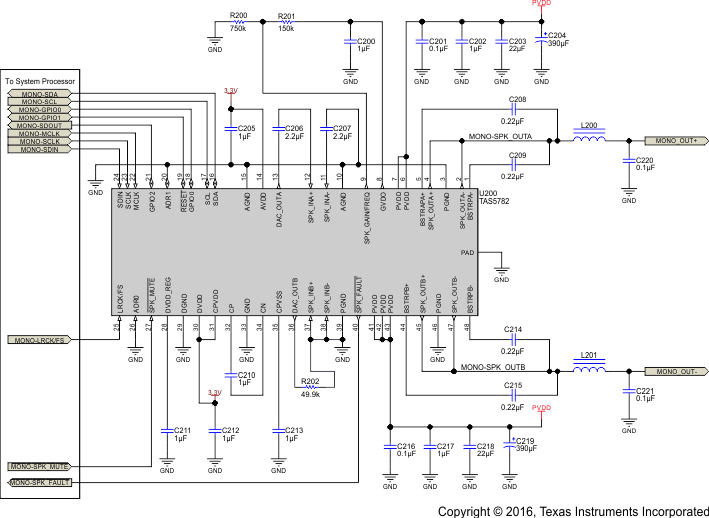 Figure 81. Mono (PBTL) System Application Schematic
Figure 81. Mono (PBTL) System Application Schematic