ZHCSCR9C September 2014 – February 2017 TCA9534A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DW|16
订购信息
8.5.1 I2C Interface
The TCA9534A has a standard bidirectional I2C interface that is controlled by a master device in order to be configured or read the status of this device. Each slave on the I2C bus has a specific device address to differentiate between other slave devices that are on the same I2C bus. Many slave devices require configuration upon startup to set the behavior of the device. This is typically done when the master accesses internal register maps of the slave, which have unique register addresses. A device can have one or multiple registers where data is stored, written, or read. For more information see the Understanding the I2C Bus application report.
The physical I2C interface consists of the serial clock (SCL) and serial data (SDA) lines. Both SDA and SCL lines must be connected to VCC through a pull-up resistor. The size of the pull-up resistor is determined by the amount of capacitance on the I2C lines. For further details, see the I2C Pull-up Resistor Calculation application report. Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is idle. A bus is considered idle if both SDA and SCL lines are high after a STOP condition.
Figure 24 and Figure 25 show the general procedure for a master to access a slave device:
- If a master wants to send data to a slave:
- Master-transmitter sends a START condition and addresses the slave-receiver.
- Master-transmitter sends data to slave-receiver.
- Master-transmitter terminates the transfer with a STOP condition.
- If a master wants to receive or read data from a slave:
- Master-receiver sends a START condition and addresses the slave-transmitter.
- Master-receiver sends the requested register to read to slave-transmitter.
- Master-receiver receives data from the slave-transmitter.
- Master-receiver terminates the transfer with a STOP condition.
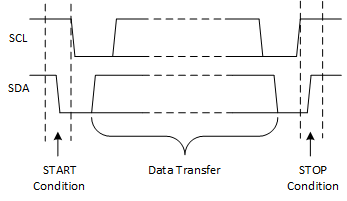 Figure 24. Definition of Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 24. Definition of Start and Stop Conditions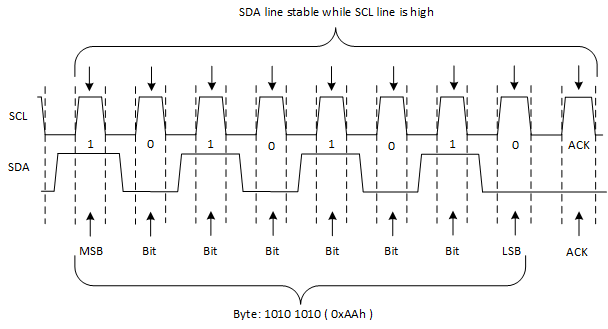 Figure 25. Bit Transfer
Figure 25. Bit TransferTable 1 shows the TCA9534A interface definition.