SLIS142D December 2012 – September 2016 TLC6C598-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TLC6C598-Q1 device is a monolithic, medium-voltage, low-current 8-bit shift register designed to drive relatively moderate load power such LEDs. The device contains an 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register that feeds an 8-bit D-type storage register. Thermal shutdown protection is also built-into the device.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
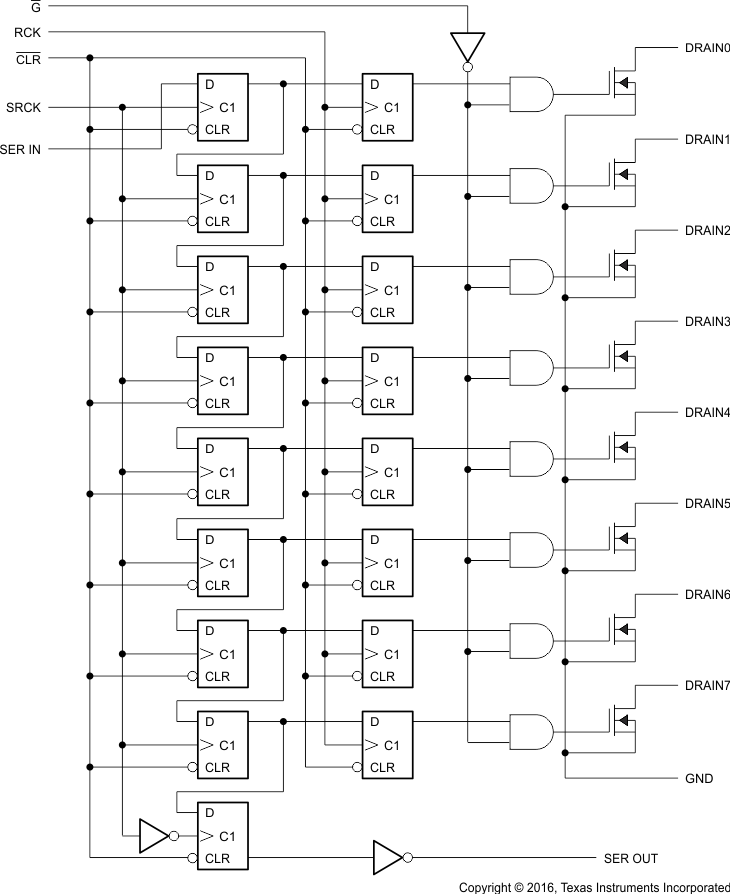 Figure 13. Logic Diagram (Positive) of TLC6C598-Q1
Figure 13. Logic Diagram (Positive) of TLC6C598-Q1
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Thermal Shutdown
The device implements an internal thermal shutdown to protect itself if the junction temperature exceeds 175°C (typical). The thermal shutdown forces the device to have an open state when the junction temperature exceeds the thermal trip threshold. Once the junction temperature decreases below 160°C (typical), the device begins to operate again.
8.3.2 Serial-In Interface
The TLC6C598-Q1 device contains an 8-bit serial-in, parallel-out shift register that feeds an 8-bit D-type storage register. Data transfer through the shift and storage registers is on the rising edge of the shift register clock (SRCK) and the register clock (RCK), respectively. The storage register transfers data to the output buffer when shift register clear (CLR) is high.
8.3.3 Clear Registers
A logic low the CLR pin clears all registers in the device. TI suggests clearing the device during power up or initialization.
8.3.4 Output Channels
DRAIN0–DRAIN7. These pins can survive up to 40-V LED supply voltage. This is quite helpful during automotive load-dump conditions.
8.3.5 Register Clock
RCK is the storage-register clock. Data in the storage register appears at the output whenever the output enable (G) input signal is high.
8.3.6 Cascade Through SER OUT
By connecting the SER OUT pin to the SER IN input of the next device on the serial bus to cascade, the data transfers to the next device on the falling edge of SRCK. This can improve the cascade application reliability, as it can avoid the issue that the second device receives SRCK and data input at the same rising edge of SRCK.
8.3.7 Output Control
Holding the output enable (pin G) high holds all data in the output buffers low, and all drain outputs are off. Holding G low makes data from the storage register transparent to the output buffers. When data in the output buffers is low, the DMOS transistor outputs are off. When data is high, the DMOS transistor outputs are capable of sinking current. This pin also can be used for global PWM dimming.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Operation With VCC < 3 V
This device works normally within the range 3 V ≤ VCC ≤ 5.5 V. When the operating voltage is lower than 3 V, correct behavior of the device, including communication interface and current capability, is not assured.
8.4.2 Operation With 5.5 V ≤ VCC ≤ 8 V
The device works normally in this voltage range, but reliability issues may occur if the device works for a long time in this voltage range.