ZHCSLZ2B October 2022 – September 2023 TLV1811-Q1 , TLV1812-Q1 , TLV1814-Q1 , TLV1821-Q1 , TLV1822-Q1 , TLV1824-Q1
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.1.2.1 Inverting Comparator With Hysteresis
The inverting comparator with hysteresis requires a three-resistor network that is referenced to the comparator supply voltage (VCC), as shown in Figure 9-3.
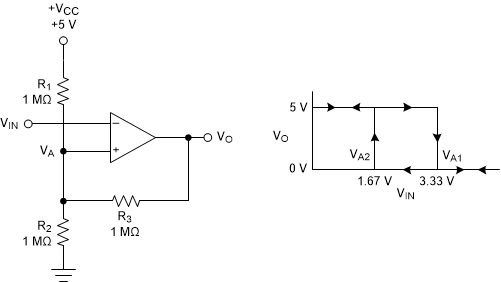 Figure 9-3 TLV181x-Q1in an Inverting Configuration With Hysteresis
Figure 9-3 TLV181x-Q1in an Inverting Configuration With HysteresisThe equivalent resistor networks when the output is high and low are shown in Figure 9-3.
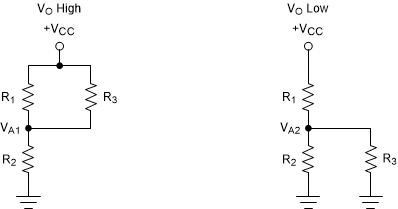 Figure 9-4 Inverting Configuration Resistor Equivalent Networks
Figure 9-4 Inverting Configuration Resistor Equivalent NetworksWhen VIN is less than VA, the output voltage is high (for simplicity, assume VO switches as high as VCC). The three network resistors can be represented as R1 || R3 in series with R2, as shown in Figure 9-4.
Equation 1 below defines the high-to-low trip voltage (VA1).
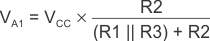
When VIN is greater than VA, the output voltage is low. In this case, the three network resistors can be presented as R2 || R3 in series with R1, as shown in Equation 2.
Use Equation 2 to define the low to high trip voltage (VA2).
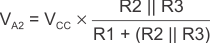
Equation 3 defines the total hysteresis provided by the network.