ZHCSHH1B January 2018 – November 2019 TLV6700
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
9.2.2.1 Resistor Divider Selection
Use Equation 1 through Equation 4 to calculate the resistor divider values and target threshold voltages.
Select a value for RT such that the current through the divider is approximately 100 times higher than the input current at the INA+ and INB– terminals. The resistors can have high values to minimize current consumption as a result of low-input bias current without adding significant error to the resistive divider. See the application note Optimizing Resistor Dividers at a Comparator Input (SLVA450) for details on sizing input resistors.
Use Equation 2 to calculate the value of R3.

where
Use Equation 3 or Equation 4 to calculate the value of R2.
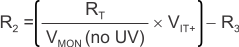
where
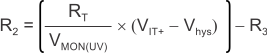
where
The worst-case tolerance can be calculated by referring to Equation 13 in application report SLVA450, Optimizing Resistor Dividers at a Comparator Input (available for download at www.ti.com). An example of the rising threshold error, VMON(OV), is given in Equation 5.