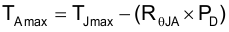ZHCS844D November 2011 – January 2025 TLV70012-Q1 , TLV70018-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.1.2.1 Thermal Calculations
Power dissipation depends on input voltage and load conditions. Power dissipation (PD) is equal to the product of the output current and the voltage drop across the output pass transistor, as shown in Equation 1.
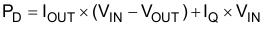
where
- PD is continuous power dissipation
- IOUT is output current
- VIN is input voltage
- VOUT is output voltage
Because IQ << IOUT, the term IQ × VIN is always ignored.
For a device under operation at a given ambient air temperature (TA), use Equation 2 to calculate the junction temperature (TJ).
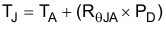
where:
- ZθJA is the junction-to-ambient air temperature thermal impedance
Use Equation 3 to calculate the rise in junction temperature due to power dissipation.
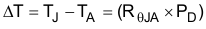
For a given maximum junction temperature (TJ(MAX), use Equation 4 to calculate the maximum ambient air temperature (TA(MAX) at which the device can operate.