ZHCSFV7 November 2016 TMP421-Q1 , TMP422-Q1 , TMP423-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1 Serial Interface
- 8.5.2 Bus Overview
- 8.5.3 Bus Definitions
- 8.5.4 Serial Bus Address
- 8.5.5 Two-Wire Interface Slave Device Addresses
- 8.5.6 Read and Write Operations
- 8.5.7 High-Speed Mode
- 8.5.8 One-Shot Conversion
- 8.5.9 η-Factor Correction Register
- 8.5.10 Software Reset
- 8.5.11 General Call Reset
- 8.5.12 Identification Registers
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Remote temperature sensing on the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 measures very small voltages using very low currents; therefore, noise at the device inputs must be minimized. Most applications using the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 have high digital content, with several clocks and logic level transitions creating a noisy environment. Layout must adhere to the following guidelines:
- Place the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 as close to the remote junction sensor as possible.
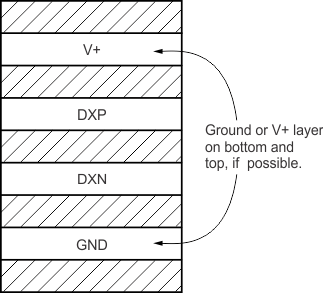
- Route the DXP and DXN traces next to each other and shield them from adjacent signals through the use of ground guard traces, as shown in Figure 23. If a multilayer PCB is used, bury these traces between ground or V+ planes to shield them from extrinsic noise sources. 5 mil (0.127 mm) PCB traces are recommended.
- Minimize additional thermocouple junctions caused by copper-to-solder connections. If these junctions are used, make the same number and approximate locations of copper-to-solder connections in both the DXP and DXN connections to cancel any thermocouple effects.
- Use a 0.1-μF local bypass capacitor directly between the V+ and GND of the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1; see Figure 24. Minimize filter capacitance between DXP and DXN to 1000 pF or less for optimum measurement performance. This capacitance includes any cable capacitance between the remote temperature sensor and the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1.
- If the connection between the remote temperature sensor and the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 is less than 8 in (20.32 cm) long, use a twisted-wire pair connection. Beyond 8 in, use a twisted, shielded pair with the shield grounded as close to the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 as possible. Leave the remote sensor connection end of the shield wire open to avoid ground loops and 60-Hz pickup.
- Thoroughly clean and remove all flux residue in and around the pins of the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 to avoid temperature offset readings as a result of leakage paths between DXP or DXN and GND, or between DXP or DXN and V+.
NOTE:
Use minimum 5 mil (0.127mm) traces with 5 mil spacing.11.2 Layout Example
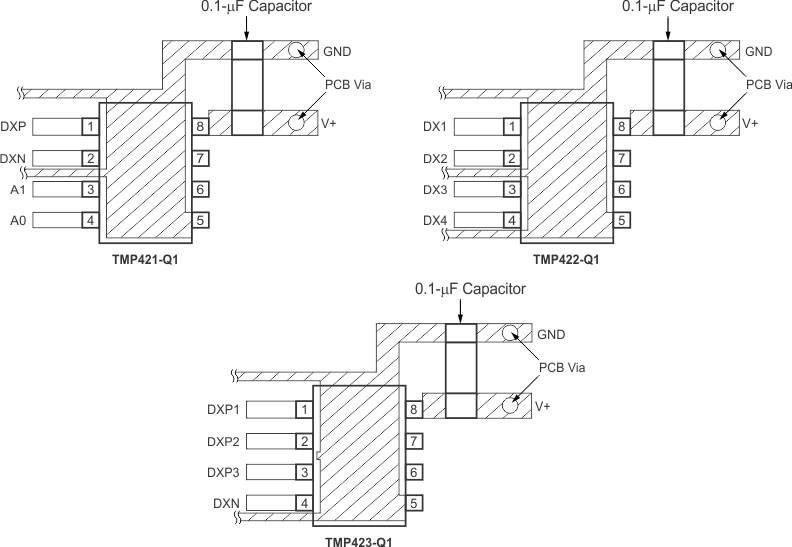 Figure 24. Suggested Bypass Capacitor Placement and Trace Shielding
Figure 24. Suggested Bypass Capacitor Placement and Trace Shielding
11.3 Measurement Accuracy and Thermal Considerations
The temperature measurement accuracy of the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 depends on the remote and local temperature sensor being at the same temperature as the system point being monitored. Clearly, if the temperature sensor is not in good thermal contact with the part of the system being monitored, then there is a delay in the response of the sensor to a temperature change in the system. For remote temperature-sensing applications using a substrate transistor (or a small, SOT-23 transistor) placed close to the device being monitored, this delay is usually not a concern.
The local temperature sensor inside the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 monitors the ambient air around the device. The thermal time constant for the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 is approximately two seconds. This constant implies that if the ambient air changes quickly by 100°C, then the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 requires approximately 10 seconds (that is, five thermal time constants) to settle to within 1°C of the final value. In most applications, the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 package is in electrical, and therefore thermal, contact with the printed circuit board (PCB), as well as subjected to forced airflow. The accuracy of the measured temperature directly depends on how accurately the PCB and forced airflow temperatures represent the temperature that the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 is measuring. Additionally, the internal power dissipation of the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 can cause the temperature to rise above the ambient or PCB temperature. The internal power dissipated as a result of exciting the remote temperature sensor is negligible because of the small currents used. For a 5.5-V supply and maximum conversion rate of eight conversions per second, the TMP421-Q1, TMP422-Q1, and TMP423-Q1 dissipate 2.3 mW (PDIQ = 5.5 V × 415 μA). A θJA of 100°C/W (for SOT-23 package) causes the junction temperature to rise approximately 0.23°C above the ambient.