ZHCSA18F March 2009 – February 2021 TMS320C28341 , TMS320C28342 , TMS320C28343 , TMS320C28343-Q1 , TMS320C28344 , TMS320C28345 , TMS320C28346 , TMS320C28346-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings (1) (1)
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 7.9.2 Power Sequencing
- 7.9.3 Clock Requirements and Characteristics
- 7.9.4
Peripherals
- 7.9.4.1
General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9.4.1.1 GPIO - Output Timing
- 7.9.4.1.2 GPIO - Input Timing
- 7.9.4.1.3 Sampling Window Width for Input Signals
- 7.9.4.1.4
Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- 7.9.4.1.4.1 IDLE Mode Timing Requirements (1)
- 7.9.4.1.4.2 IDLE Mode Switching Characteristics (1)
- 7.9.4.1.4.3 IDLE Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.1.4.4 STANDBY Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.4.1.4.5 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.4.1.4.6 STANDBY Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.1.4.7 HALT Mode Timing Requirements
- 7.9.4.1.4.8 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
- 7.9.4.1.4.9 HALT Mode Timing Diagram
- 7.9.4.2 Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 7.9.4.3 External Interrupt Timing
- 7.9.4.4 I2C Electrical Specification and Timing
- 7.9.4.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 7.9.4.6
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Timing
- 7.9.4.6.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 7.9.4.6.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- 7.9.4.6.2.1 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0) (1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.2 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.3 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0) (1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.4 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- 7.9.4.6.2.5 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1) (1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.6 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.7 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1) (1)
- 7.9.4.6.2.8 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1) (1)
- 7.9.4.1
General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 7.9.5 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 7.9.6
External Interface (XINTF) Timing
- 7.9.6.1 USEREADY = 0
- 7.9.6.2 Synchronous Mode (USEREADY = 1, READYMODE = 0)
- 7.9.6.3 Asynchronous Mode (USEREADY = 1, READYMODE = 1)
- 7.9.6.4 XINTF Signal Alignment to XCLKOUT
- 7.9.6.5 External Interface Read Timing
- 7.9.6.6 External Interface Write Timing
- 7.9.6.7
External Interface Ready-on-Read Timing With One External Wait State
- 7.9.6.7.1 External Interface Read Switching Characteristics (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.7.2 External Interface Read Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.7.3 Synchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State) (1)
- 7.9.6.7.4 Asynchronous XREADY Timing Requirements (Ready-on-Read, One Wait State)
- 7.9.6.8 External Interface Ready-on-Write Timing With One External Wait State
- 7.9.6.9 XHOLD and XHOLDA Timing
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1
Brief Descriptions
- 8.1.1 C28x CPU
- 8.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 8.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 8.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 8.1.5 External Interface (XINTF)
- 8.1.6 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 8.1.7 L0, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6, L7, H0, H1, H2, H3, H4, H5 SARAMs
- 8.1.8 Boot ROM
- 8.1.9 Security
- 8.1.10 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 8.1.11 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT7, XNMI)
- 8.1.12 Oscillator and PLL
- 8.1.13 Watchdog
- 8.1.14 Peripheral Clocking
- 8.1.15 Low-Power Modes
- 8.1.16 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 8.1.17 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 8.1.18 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 8.1.19 Control Peripherals
- 8.1.20 Serial Port Peripherals
- 8.2
Peripherals
- 8.2.1 DMA Overview
- 8.2.2 32-Bit CPU-Timer 0, CPU-Timer 1, CPU-Timer 2
- 8.2.3 Enhanced PWM Modules
- 8.2.4 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 8.2.5 Enhanced CAP Modules
- 8.2.6 Enhanced QEP Modules
- 8.2.7 External ADC Interface
- 8.2.8 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP) Module
- 8.2.9 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Modules (eCAN-A and eCAN-B)
- 8.2.10 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Modules (SCI-A, SCI-B, SCI-C)
- 8.2.11 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module (SPI-A, SPI-D)
- 8.2.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 8.2.13 GPIO MUX
- 8.2.14 External Interface (XINTF)
- 8.3 Memory Maps
- 8.4 Register Map
- 8.5 Interrupts
- 8.6 System Control
- 8.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 8.1
Brief Descriptions
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.13 GPIO MUX
On the 2834x devices, the GPIO MUX can multiplex up to three independent peripheral signals on a single GPIO pin in addition to providing individual pin bit-banging I/O capability. The GPIO MUX block diagram per pin is shown in Figure 8-16. Because of the open-drain capabilities of the I2C pins, the GPIO MUX block diagram for these pins differ. See the TMS320x2834x Delfino System Control and Interrupts Reference Guide for details.
There is a 2-SYSCLKOUT cycle delay from when the write to the GPxMUXn and GPxQSELn registers occurs to when the action is valid.
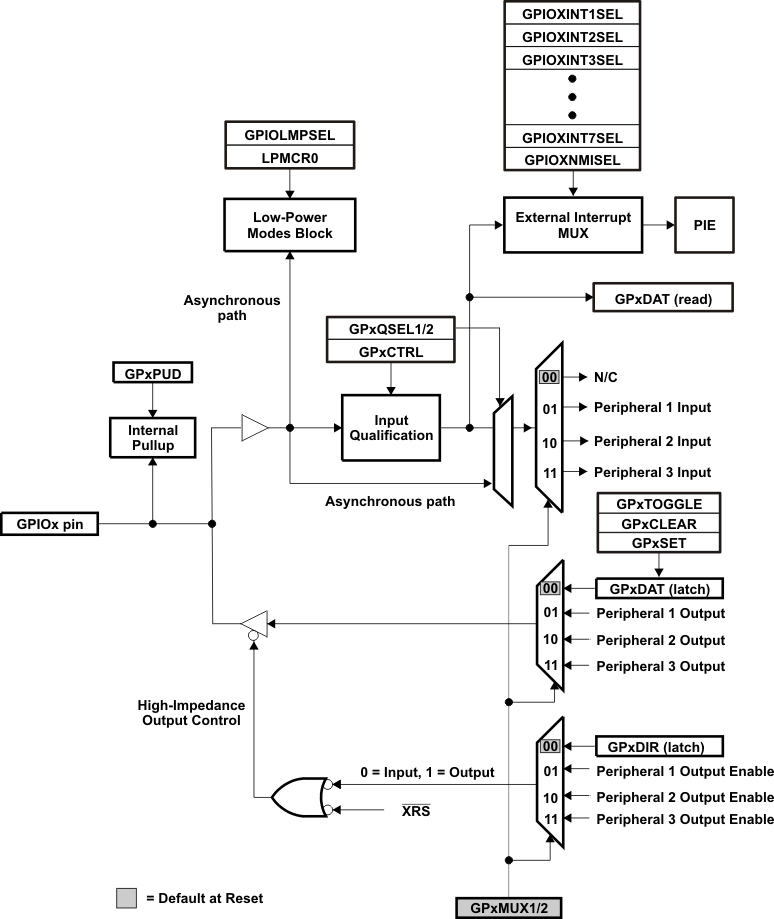
The device supports 88 GPIO pins. The GPIO control and data registers are mapped to Peripheral Frame 1 to enable 32-bit operations on the registers (along with 16-bit operations). Table 8-17 shows the GPIO register mapping.
| NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO CONTROL REGISTERS (EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPACTRL | 0x6F80 | 2 | GPIO A Control Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPAQSEL1 | 0x6F82 | 2 | GPIO A Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) |
| GPAQSEL2 | 0x6F84 | 2 | GPIO A Qualifier Select 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) |
| GPAMUX1 | 0x6F86 | 2 | GPIO A MUX 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) |
| GPAMUX2 | 0x6F88 | 2 | GPIO A MUX 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) |
| GPADIR | 0x6F8A | 2 | GPIO A Direction Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPAPUD | 0x6F8C | 2 | GPIO A Pullup Disable Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| Reserved | 0x6F8E – 0x6F8F | 2 | |
| GPBCTRL | 0x6F90 | 2 | GPIO B Control Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPBQSEL1 | 0x6F92 | 2 | GPIO B Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO32 to 47) |
| GPBQSEL2 | 0x6F94 | 2 | GPIOB Qualifier Select 2 Register (GPIO48 to 63) |
| GPBMUX1 | 0x6F96 | 2 | GPIO B MUX 1 Register (GPIO32 to 47) |
| GPBMUX2 | 0x6F98 | 2 | GPIO B MUX 2 Register (GPIO48 to 63) |
| GPBDIR | 0x6F9A | 2 | GPIO B Direction Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPBPUD | 0x6F9C | 2 | GPIO B Pullup Disable Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| Reserved | 0x6F9E – 0x6FA5 | 8 | |
| GPCMUX1 | 0x6FA6 | 2 | GPIO C MUX1 Register (GPIO64 to 79) |
| GPCMUX2 | 0x6FA8 | 2 | GPIO C MUX2 Register (GPIO80 to 87) |
| GPCDIR | 0x6FAA | 2 | GPIO C Direction Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| GPCPUD | 0x6FAC | 2 | GPIO C Pullup Disable Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| Reserved | 0x6FAE – 0x6FBF | 18 | |
| GPIO DATA REGISTERS (NOT EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPADAT | 0x6FC0 | 2 | GPIO A Data Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPASET | 0x6FC2 | 2 | GPIO A Data Set Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPACLEAR | 0x6FC4 | 2 | GPIO A Data Clear Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPATOGGLE | 0x6FC6 | 2 | GPIO A Data Toggle Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPBDAT | 0x6FC8 | 2 | GPIO B Data Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPBSET | 0x6FCA | 2 | GPIO B Data Set Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPBCLEAR | 0x6FCC | 2 | GPIO B Data Clear Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPBTOGGLE | 0x6FCE | 2 | GPIOB Data Toggle Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPCDAT | 0x6FD0 | 2 | GPIO C Data Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| GPCSET | 0x6FD2 | 2 | GPIO C Data Set Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| GPCCLEAR | 0x6FD4 | 2 | GPIO C Data Clear Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| GPCTOGGLE | 0x6FD6 | 2 | GPIO C Data Toggle Register (GPIO64 to 87) |
| Reserved | 0x6FD8 – 0x6FDF | 8 | |
| GPIO INTERRUPT AND LOW-POWER MODES SELECT REGISTERS (EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPIOXINT1SEL | 0x6FE0 | 1 | XINT1 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOXINT2SEL | 0x6FE1 | 1 | XINT2 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOXNMISEL | 0x6FE2 | 1 | XNMI GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOXINT3SEL | 0x6FE3 | 1 | XINT3 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPIOXINT4SEL | 0x6FE4 | 1 | XINT4 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPIOXINT5SEL | 0x6FE5 | 1 | XINT5 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPIOXINT6SEL | 0x6FE6 | 1 | XINT6 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPIOINT7SEL | 0x6FE7 | 1 | XINT7 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO32 to 63) |
| GPIOLPMSEL | 0x6FE8 | 2 | LPM GPIO Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| Reserved | 0x6FEA – 0x6FFF | 22 | |
| REGISTER BITS | PERIPHERAL SELECTION | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPADIR GPADAT GPASET GPACLR GPATOGGLE | GPAMUX1 GPAQSEL1 | GPIOx GPAMUX1 = 0,0 | PER1 GPAMUX1 = 0, 1 | PER2 GPAMUX1 = 1, 0 | PER3 GPAMUX1 = 1, 1 | |
| QUALPRD0 | 0 | 1, 0 | GPIO0 (I/O) | EPWM1A (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 1 | 3, 2 | GPIO1 (I/O) | EPWM1B (O) | ECAP6 (I/O) | MFSRB (I/O) | |
| 2 | 5, 4 | GPIO2 (I/O) | EPWM2A (O) | Reserved | Reserved | |
| 3 | 7, 6 | GPIO3 (I/O) | EPWM2B (O) | ECAP5 (I/O) | MCLKRB (I/O) | |
| 4 | 9, 8 | GPIO4 (I/O) | EPWM3A (O) | Reserved | Reserved | |
| 5 | 11, 10 | GPIO5 (I/O) | EPWM3B (O) | MFSRA (I/O) | ECAP1 (I/O) | |
| 6 | 13, 12 | GPIO6 (I/O) | EPWM4A (O) | EPWMSYNCI (I) | EPWMSYNCO (O) | |
| 7 | 15, 14 | GPIO7 (I/O) | EPWM4B (O) | MCLKRA (I/O) | ECAP2 (I/O) | |
| QUALPRD1 | 8 | 17, 16 | GPIO8 (I/O) | EPWM5A (O) | CANTXB (O) | ADCSOCAO (O) |
| 9 | 19, 18 | GPIO9 (I/O) | EPWM5B (O) | SCITXDB (O) | ECAP3 (I/O) | |
| 10 | 21, 20 | GPIO10 (I/O) | EPWM6A (O) | CANRXB (I) | ADCSOCBO (O) | |
| 11 | 23, 22 | GPIO11 (I/O) | EPWM6B (O) | SCIRXDB (I) | ECAP4 (I/O) | |
| 12 | 25, 24 | GPIO12 (I/O) | TZ1 (I) | CANTXB (O) | MDXB (O) | |
| 13 | 27, 26 | GPIO13 (I/O) | TZ2 (I) | CANRXB (I) | MDRB (I) | |
| 14 | 29, 28 | GPIO14 (I/O) | TZ3 (I)/ XHOLD (I) | SCITXDB (O) | MCLKXB (I/O) | |
| 15 | 31, 30 | GPIO15 (I/O) | TZ4 (I)/ XHOLDA (O) | SCIRXDB (I) | MFSXB (I/O) | |
| GPAMUX2 GPAQSEL2 | GPAMUX2 = 0, 0 | GPAMUX2 = 0, 1 | GPAMUX2 = 1, 0 | GPAMUX2 = 1, 1 | ||
| QUALPRD2 | 16 | 1, 0 | GPIO16 (I/O) | SPISIMOA (I/O) | CANTXB (O) | TZ5 (I) |
| 17 | 3, 2 | GPIO17 (I/O) | SPISOMIA (I/O) | CANRXB (I) | TZ6 (I) | |
| 18 | 5, 4 | GPIO18 (I/O) | SPICLKA (I/O) | SCITXDB (O) | CANRXA (I) | |
| 19 | 7, 6 | GPIO19 (I/O) | SPISTEA (I/O) | SCIRXDB (I) | CANTXA (O) | |
| 20 | 9, 8 | GPIO20 (I/O) | EQEP1A (I) | MDXA (O) | CANTXB (O) | |
| 21 | 11, 10 | GPIO21 (I/O) | EQEP1B (I) | MDRA (I) | CANRXB (I) | |
| 22 | 13, 12 | GPIO22 (I/O) | EQEP1S (I/O) | MCLKXA (I/O) | SCITXDB (O) | |
| 23 | 15, 14 | GPIO23 (I/O) | EQEP1I (I/O) | MFSXA (I/O) | SCIRXDB (I) | |
| QUALPRD3 | 24 | 17, 16 | GPIO24 (I/O) | ECAP1 (I/O) | EQEP2A (I) | MDXB (O) |
| 25 | 19, 18 | GPIO25 (I/O) | ECAP2 (I/O) | EQEP2B (I) | MDRB (I) | |
| 26 | 21, 20 | GPIO26 (I/O) | ECAP3 (I/O) | EQEP2I (I/O) | MCLKXB (I/O) | |
| 27 | 23, 22 | GPIO27 (I/O) | ECAP4 (I/O) | EQEP2S (I/O) | MFSXB (I/O) | |
| 28 | 25, 24 | GPIO28 (I/O) | SCIRXDA (I) | XZCS6 (O) | ||
| 29 | 27, 26 | GPIO29 (I/O) | SCITXDA (O) | XA19 (O) | ||
| 30 | 29, 28 | GPIO30 (I/O) | CANRXA (I) | XA18 (O) | ||
| 31 | 31, 30 | GPIO31 (I/O) | CANTXA (O) | XA17 (O) | ||
| REGISTER BITS | PERIPHERAL SELECTION | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPBDIR GPBDAT GPBSET GPBCLR GPBTOGGLE | GPBMUX1 GPBQSEL1 | GPIOx GPBMUX1 = 0, 0 | PER1 GPBMUX1 = 0, 1 | PER2 GPBMUX1 = 1, 0 | PER3 GPBMUX1 = 1, 1 | |
| QUALPRD0 | 0 | 1, 0 | GPIO32 (I/O) | SDAA (I/OC)(1) | EPWMSYNCI (I) | ADCSOCAO (O) |
| 1 | 3, 2 | GPIO33 (I/O) | SCLA (I/OC)(1) | EPWMSYNCO (O) | ADCSOCBO (O) | |
| 2 | 5, 4 | GPIO34 (I/O) | ECAP1 (I/O) | XREADY (I) | ||
| 3 | 7, 6 | GPIO35 (I/O) | SCITXDA (O) | XR/ W (O) | ||
| 4 | 9, 8 | GPIO36 (I/O) | SCIRXDA (I) | XZCS0 (O) | ||
| 5 | 11, 10 | GPIO37 (I/O) | ECAP2 (I/O) | XZCS7 (O) | ||
| 6 | 13, 12 | GPIO38 (I/O) | Reserved | XWE0 (O) | ||
| 7 | 15, 14 | GPIO39 (I/O) | XA16 (O) | |||
| QUALPRD1 | 8 | 17, 16 | GPIO40 (I/O) | XA0 (O) | ||
| 9 | 19, 18 | GPIO41 (I/O) | XA1 (O) | |||
| 10 | 21, 20 | GPIO42 (I/O) | XA2 (O) | |||
| 11 | 23, 22 | GPIO43 (I/O) | XA3 (O) | |||
| 12 | 25, 24 | GPIO44 (I/O) | XA4 (O) | |||
| 13 | 27, 26 | GPIO45 (I/O) | XA5 (O) | |||
| 14 | 29, 28 | GPIO46 (I/O) | XA6 (O) | |||
| 15 | 31, 30 | GPIO47 (I/O) | XA7 (O) | |||
| GPBMUX2 GPBQSEL2 | GPBMUX2 = 0, 0 | GPBMUX2 = 0, 1 | GPBMUX2 = 1, 0 | GPBMUX2 = 1, 1 | ||
| QUALPRD2 | 16 | 1, 0 | GPIO48 (I/O) | ECAP5 (I/O) | XD31 (I/O) | SPISIMOD (I/O) |
| 17 | 3, 2 | GPIO49 (I/O) | ECAP6 (I/O) | XD30 (I/O) | SPISOMID (I/O) | |
| 18 | 5, 4 | GPIO50 (I/O) | EQEP1A (I) | XD29 (I/O) | SPICLKD (I/O) | |
| 19 | 7, 6 | GPIO51 (I/O) | EQEP1B (I) | XD28 (I/O) | SPISTED (I/O) | |
| 20 | 9, 8 | GPIO52 (I/O) | EQEP1S (I/O) | XD27 (I/O) | Reserved | |
| 21 | 11, 10 | GPIO53 (I/O) | EQEP1I (I/O) | XD26 (I/O) | Reserved | |
| 22 | 13, 12 | GPIO54 (I/O) | SPISIMOA (I/O) | XD25 (I/O) | EQEP3A (I) | |
| 23 | 15, 14 | GPIO55 (I/O) | SPISOMIA (I/O) | XD24 (I/O) | EQEP3B (I) | |
| QUALPRD3 | 24 | 17, 16 | GPIO56 (I/O) | SPICLKA (I/O) | XD23 (I/O) | EQEP3S (I/O) |
| 25 | 19, 18 | GPIO57 (I/O) | SPISTEA (I/O) | XD22 (I/O) | EQEP3I (I/O) | |
| 26 | 21, 20 | GPIO58 (I/O) | MCLKRA (I/O) | XD21 (I/O) | EPWM7A (O) | |
| 27 | 23, 22 | GPIO59 (I/O) | MFSRA (I/O) | XD20 (I/O) | EPWM7B (O) | |
| 28 | 25, 24 | GPIO60 (I/O) | MCLKRB (I/O) | XD19 (I/O) | EPWM8A (O) | |
| 29 | 27, 26 | GPIO61 (I/O) | MFSRB (I/O) | XD18 (I/O) | EPWM8B (O) | |
| 30 | 29, 28 | GPIO62 (I/O) | SCIRXDC (I) | XD17 (I/O) | EPWM9A (O) | |
| 31 | 31, 30 | GPIO63 (I/O) | SCITXDC (O) | XD16 (I/O) | EPWM9B (O) | |
| REGISTER BITS | PERIPHERAL SELECTION | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCDIR GPCDAT GPCSET GPCCLR GPCTOGGLE | GPCMUX1 | GPIOx or PER1 GPCMUX1 = 0, 0 or 0, 1 | PER2 or PER3 GPCMUX1 = 1, 0 or 1, 1 | |
| no qual | 0 | 1, 0 | GPIO64 (I/O) | XD15 (I/O) |
| 1 | 3, 2 | GPIO65 (I/O) | XD14 (I/O) | |
| 2 | 5, 4 | GPIO66 (I/O) | XD13 (I/O) | |
| 3 | 7, 6 | GPIO67 (I/O) | XD12 (I/O) | |
| 4 | 9, 8 | GPIO68 (I/O) | XD11 (I/O) | |
| 5 | 11, 10 | GPIO69 (I/O) | XD10 (I/O) | |
| 6 | 13, 12 | GPIO70 (I/O) | XD9 (I/O) | |
| 7 | 15, 14 | GPIO71 (I/O) | XD8 (I/O) | |
| no qual | 8 | 17, 16 | GPIO72 (I/O) | XD7 (I/O) |
| 9 | 19, 18 | GPIO73 (I/O) | XD6 (I/O) | |
| 10 | 21, 20 | GPIO74 (I/O) | XD5 (I/O) | |
| 11 | 23, 22 | GPIO75 (I/O) | XD4 (I/O) | |
| 12 | 25, 24 | GPIO76 (I/O) | XD3 (I/O) | |
| 13 | 27, 26 | GPIO77 (I/O) | XD2 (I/O) | |
| 14 | 29, 28 | GPIO78 (I/O) | XD1 (I/O) | |
| 15 | 31, 30 | GPIO79 (I/O) | XD0 (I/O) | |
| GPCMUX2 | GPCMUX2 = 0, 0 or 0, 1 | GPCMUX2 = 1, 0 or 1, 1 | ||
| no qual | 16 | 1, 0 | GPIO80 (I/O) | XA8 (O) |
| 17 | 3, 2 | GPIO81 (I/O) | XA9 (O) | |
| 18 | 5, 4 | GPIO82 (I/O) | XA10 (O) | |
| 19 | 7, 6 | GPIO83 (I/O) | XA11 (O) | |
| 20 | 9, 8 | GPIO84 (I/O) | XA12 (O) | |
| 21 | 11, 10 | GPIO85 (I/O) | XA13 (O) | |
| 22 | 13, 12 | GPIO86 (I/O) | XA14 (O) | |
| 23 | 15, 14 | GPIO87 (I/O) | XA15 (O) | |
The user can select the type of input qualification for each GPIO pin through the GPxQSEL1/2 registers from four choices:
- Synchronization To SYSCLKOUT Only (GPxQSEL1/2 = 0, 0): This is the default mode of all GPIO pins at reset and it simply synchronizes the input signal to the system clock (SYSCLKOUT).
- Qualification Using Sampling Window (GPxQSEL1/2 = 0, 1 and 1, 0): In this mode the input signal, after synchronization to the system clock (SYSCLKOUT), is qualified by a specified number of cycles before the input is allowed to change.
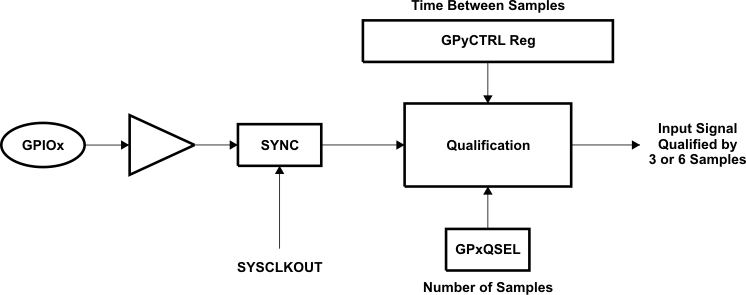 Figure 8-17 Qualification Using Sampling Window
Figure 8-17 Qualification Using Sampling Window - The sampling period is specified by the QUALPRD bits in the GPxCTRL register and is configurable in groups of 8 signals. It specifies a multiple of SYSCLKOUT cycles for sampling the input signal. The sampling window is either 3-samples or 6-samples wide and the output is only changed when all samples are the same (all 0s or all 1s) as shown in Figure 8-17 (for 6-sample mode).
- No Synchronization (GPxQSEL1/2 = 1,1): This mode is used for peripherals where synchronization is not required (synchronization is performed within the peripheral).
Due to the multilevel multiplexing that is required on the device, there may be cases where a peripheral input signal can be mapped to more then one GPIO pin. Also, when an input signal is not selected, the input signal will default to either a 0 or 1 state, depending on the peripheral.