ZHCSDR5B March 2012 – April 2015 TMS320C6654
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 C6654 特性和描述
- 2 修订历史记录
-
3 Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Characteristics
- 3.2 DSP Core Description
- 3.3 Memory Map Summary
- 3.4 Boot Sequence
- 3.5
Boot Modes Supported and PLL Settings
- 3.5.1 Boot Device Field
- 3.5.2 Device Configuration Field
- 3.5.3
Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.1 Sleep / XIP Mode Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.2 SRIO Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.3 Ethernet Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.4 NAND Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.5 PCIE Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.6 I2C Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.7 SPI Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.8 Hyperlink Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.5.3.9 UART Mode Boot Parameter Table
- 3.6 PLL Boot Configuration Settings
- 3.7 Second-Level Bootloaders
- 3.8 Terminals
- 3.9 Terminal Functions
-
4 Device Configuration
- 4.1 Device Configuration at Device Reset
- 4.2 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
- 4.3
Device State Control Registers
- 4.3.1 Device Status Register
- 4.3.2 Device Configuration Register
- 4.3.3 JTAG ID (JTAGID) Register Description
- 4.3.4 Kicker Mechanism (KICK0 and KICK1) Register
- 4.3.5 LRESETNMI PIN Status (LRSTNMIPINSTAT) Register
- 4.3.6 LRESETNMI PIN Status Clear (LRSTNMIPINSTAT_CLR) Register
- 4.3.7 Reset Status (RESET_STAT) Register
- 4.3.8 Reset Status Clear (RESET_STAT_CLR) Register
- 4.3.9 Boot Complete (BOOTCOMPLETE) Register
- 4.3.10 Power State Control (PWRSTATECTL) Register
- 4.3.11 NMI Event Generation to CorePac (NMIGRx) Register
- 4.3.12 IPC Generation (IPCGRx) Registers
- 4.3.13 IPC Acknowledgement (IPCARx) Registers
- 4.3.14 IPC Generation Host (IPCGRH) Register
- 4.3.15 IPC Acknowledgement Host (IPCARH) Register
- 4.3.16 Timer Input Selection Register (TINPSEL)
- 4.3.17 Timer Output Selection Register (TOUTPSEL)
- 4.3.18 Reset Mux (RSTMUXx) Register
- 4.3.19 Device Speed (DEVSPEED) Register
- 4.3.20 Pin Control 0 (PIN_CONTROL_0) Register
- 4.3.21 Pin Control 1 (PIN_CONTROL_1) Register
- 4.3.22 uPP Clock Source (UPP_CLOCK) Register
- 4.4 Pullup/Pulldown Resistors
- 5 System Interconnect
- 6 C66x CorePac
- 7 Device Operating Conditions
-
8 Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 8.1 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 8.2 Power Supplies
- 8.3 Power Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 8.4 Reset Controller
- 8.5
Main PLL and PLL Controller
- 8.5.1 Main PLL Controller Device-Specific Information
- 8.5.2
PLL Controller Memory Map
- 8.5.2.1 PLL Secondary Control Register (SECCTL)
- 8.5.2.2 PLL Controller Divider Register (PLLDIV2, PLLDIV5, PLLDIV8)
- 8.5.2.3 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register (ALNCTL)
- 8.5.2.4 PLLDIV Divider Ratio Change Status Register (DCHANGE)
- 8.5.2.5 SYSCLK Status Register (SYSTAT)
- 8.5.2.6 Reset Type Status Register (RSTYPE)
- 8.5.2.7 Reset Control Register (RSTCTRL)
- 8.5.2.8 Reset Configuration Register (RSTCFG)
- 8.5.2.9 Reset Isolation Register (RSISO)
- 8.5.3 Main PLL Control Register
- 8.5.4 Main PLL and PLL Controller Initialization Sequence
- 8.5.5 Main PLL Controller/PCIe Clock Input Electrical Data/Timing
- 8.6 DDR3 PLL
- 8.7 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller
- 8.8 Interrupts
- 8.9 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 8.10 DDR3 Memory Controller
- 8.11 I2C Peripheral
- 8.12 SPI Peripheral
- 8.13 UART Peripheral
- 8.14 PCIe Peripheral
- 8.15 EMIF16 Peripheral
- 8.16 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 8.17 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 8.18 Timers
- 8.19 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 8.20 Semaphore2
- 8.21 Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 8.22 Universal Parallel Port (uPP)
- 8.23 Emulation Features and Capability
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical Data
3 Device Overview
3.1 Device Characteristics
Table 3-1 Characteristics of the C6654 Processor
| HARDWARE FEATURES | TMS320C6654 | |
|---|---|---|
| Peripheral | DDR3 Memory Controller (32-bit bus width) [1.5 V I/O] (clock source = DDRREFCLKN|P) |
1 |
| DDR3 Maximum Data Rate | 1066 | |
| EDMA3 (64 independent channels) [DSP/3 clock rate] | 1 | |
| PCIe (2 lanes) | 1 | |
| 10/100/1000 Ethernet | 1 | |
| Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) | 1 | |
| EMIF16 | 1 | |
| McBSP | 2 | |
| SPI | 1 | |
| UART | 2 | |
| uPP | 1 | |
| I2C | 1 | |
| 64-Bit Timers (configurable) (internal clock source = CPU/6 clock frequency) | 8 (each configurable as two 32-bit timers) | |
| General-Purpose Input/Output port (GPIO) | 32 | |
| On-Chip Memory | CorePac Memory | 32KB L1 Program Memory [SRAM/Cache] 32KB L1 Data Memory [SRAM/Cache] 1024KB L2 Unified Memory/Cache |
| ROM Memory | 128KB L3 ROM | |
| C66x CorePac Revision ID | CorePac Revision ID Register (address location: 0181 2000h) | See Section 6.5 |
| JTAG BSDL_ID | JTAGID register (address location: 0262 0018h) | See Section 4.3.3 |
| Frequency | MHz | 850 (0.85 GHz) |
| Cycle Time | ns | 1.175 (0.85 GHz) |
| Voltage | Core (V) | SmartReflex variable supply |
| I/O (V) | 1.0 V, 1.5 V, and 1.8 V | |
| Process Technology | µm | 0.040 µm |
| BGA Package | 21 mm × 21mm | 625-Pin Flip-Chip Plastic BGA (CZH or GZH) |
| Product Status(1) | Product Preview (PP), Advance Information (AI), or Production Data (PD) |
PD |
3.2 DSP Core Description
The C66x Digital Signal Processor (DSP) extends the performance of the C64x+ and C674x DSPs through enhancements and new features. Many of the new features target increased performance for vector processing. The C64x+ and C674x DSPs support 2-way SIMD operations for 16-bit data and 4-way SIMD operations for 8-bit data. On the C66x DSP, the vector processing capability is improved by extending the width of the SIMD instructions. C66x DSPs can execute instructions that operate on 128-bit vectors. For example the QMPY32 instruction is able to perform the element-to-element multiplication between two vectors of four 32-bit data each. The C66x DSP also supports SIMD for floating-point operations. Improved vector processing capability (each instruction can process multiple data in parallel) combined with the natural instruction level parallelism of C6000 architecture (e.g execution of up to 8 instructions per cycle) results in a very high level of parallelism that can be exploited by DSP programmers through the use of TI's optimized C/C++ compiler.
The C66x DSP consists of eight functional units, two register files, and two data paths as shown in Figure 3-1. The two general-purpose register files (A and B) each contain 32 32-bit registers for a total of 64 registers. The general-purpose registers can be used for data or can be data address pointers. The data types supported include packed 8-bit data, packed 16-bit data, 32-bit data, 40-bit data, and 64-bit data. Multiplies also support 128-bit data. 40-bit-long or 64-bit-long values are stored in register pairs, with the 32 LSBs of data placed in an even register and the remaining 8 or 32 MSBs in the next upper register (which is always an odd-numbered register). 128-bit data values are stored in register quadruplets, with the 32 LSBs of data placed in a register that is a multiple of 4 and the remaining 96 MSBs in the next 3 upper registers.
The eight functional units (.M1, .L1, .D1, .S1, .M2, .L2, .D2, and .S2) are each capable of executing one instruction every clock cycle. The .M functional units perform all multiply operations. The .S and .L units perform a general set of arithmetic, logical, and branch functions. The .D units primarily load data from memory to the register file and store results from the register file into memory.
Each C66x .M unit can perform one of the following fixed-point operations each clock cycle: four 32 × 32 bit multiplies, sixteen 16 × 16 bit multiplies, four 16 × 32 bit multiplies, four 8 × 8 bit multiplies, four 8 × 8 bit multiplies with add operations, and four 16 × 16 multiplies with add/subtract capabilities. There is also support for Galois field multiplication for 8-bit and 32-bit data. Many communications algorithms such as FFTs and modems require complex multiplication. Each C66x .M unit can perform one 16 × 16 bit complex multiply with or without rounding capabilities, two 16 × 16 bit complex multiplies with rounding capability, and a 32 × 32 bit complex multiply with rounding capability. The C66x can also perform two 16 × 16 bit and one 32 × 32 bit complex multiply instructions that multiply a complex number with a complex conjugate of another number with rounding capability. Communication signal processing also requires an extensive use of matrix operations. Each C66x .M unit is capable of multiplying a [1 × 2] complex vector by a [2 × 2] complex matrix per cycle with or without rounding capability. A version also exists allowing multiplication of the conjugate of a [1 × 2] vector with a [2 × 2] complex matrix.
Each C66x .M unit also includes IEEE floating-point multiplication operations from the C674x DSP, which includes one single-precision multiply each cycle and one double-precision multiply every 4 cycles. There is also a mixed-precision multiply that allows multiplication of a single-precision value by a double-precision value and an operation allowing multiplication of two single-precision numbers resulting in a double-precision number. The C66x DSP improves the performance over the C674x double-precision multiplies by adding a instruction allowing one double-precision multiply per cycle and also reduces the number of delay slots from 10 down to 4. Each C66x .M unit can also perform one the following floating-point operations each clock cycle: one, two, or four single-precision multiplies or a complex single-precision multiply.
The .L and .S units can now support up to 64-bit operands. This allows for new versions of many of the arithmetic, logical, and data packing instructions to allow for more parallel operations per cycle. Additional instructions were added yielding performance enhancements of the floating point addition and subtraction instructions, including the ability to perform one double precision addition or subtraction per cycle. Conversion to/from integer and single-precision values can now be done on both .L and .S units on the C66x. Also, by taking advantage of the larger operands, instructions were also added to double the number of these conversions that can be done. The .L unit also has additional instructions for logical AND and OR instructions, as well as, 90 degree or 270 degree rotation of complex numbers (up to two per cycle). Instructions have also been added that allow for the computing the conjugate of a complex number.
The MFENCE instruction is a new instruction introduced on the C66x DSP. This instruction will create a DSP stall until the completion of all the DSP-triggered memory transactions, including:
- Cache line fills
- Writes from L1D to L2 or from the CorePac to MSMC and/or other system endpoints
- Victim write backs
- Block or global coherence operations
- Cache mode changes
- Outstanding XMC prefetch requests
This is useful as a simple mechanism for programs to wait for these requests to reach their endpoint. It also provides ordering guarantees for writes arriving at a single endpoint via multiple paths, multiprocessor algorithms that depend on ordering, and manual coherence operations.
For more details on the C66x DSP and its enhancements over the C64x+ and C674x architectures, see the following documents:
- C66x CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (SPRUGH7).
- C66x DSP Cache User's Guide (SPRUGY8).
- C66x CorePac User's Guide (SPRUGW0).
Figure 3-1 shows the DSP core functional units and data paths.
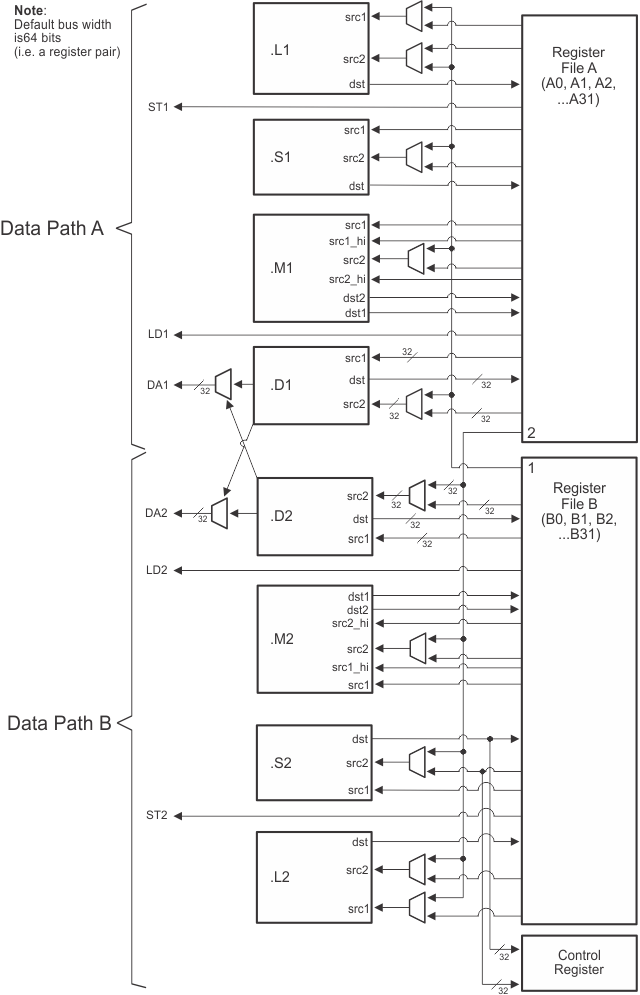 Figure 3-1 DSP Core Data Paths
Figure 3-1 DSP Core Data Paths
3.3 Memory Map Summary
Table 3-2 shows the memory map address ranges of the C6654 device.
Table 3-2 Memory Map Summary
| LOGICAL 32-BIT ADDRESS | PHYSICAL 36-BIT ADDRESS | BYTES | DESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| START | END | START | END | ||
| 00000000 | 007FFFFF | 0 00000000 | 0 007FFFFF | 8M | Reserved |
| 00800000 | 008FFFFF | 0 00800000 | 0 008FFFFF | 1M | Local L2 SRAM |
| 00900000 | 00DFFFFF | 0 00900000 | 0 00DFFFFF | 5M | Reserved |
| 00E00000 | 00E07FFF | 0 00E00000 | 0 00E07FFF | 32K | Local L1P SRAM |
| 00E08000 | 00EFFFFF | 0 00E08000 | 0 00EFFFFF | 1M-32K | Reserved |
| 00F00000 | 00F07FFF | 0 00F00000 | 0 00F07FFF | 32K | Local L1D SRAM |
| 00F08000 | 017FFFFF | 0 00F08000 | 0 017FFFFF | 9M-32K | Reserved |
| 01800000 | 01BFFFFF | 0 01800000 | 0 01BFFFFF | 4M | C66x CorePac Registers |
| 01C00000 | 01CFFFFF | 0 01C00000 | 0 01CFFFFF | 1M | Reserved |
| 01D00000 | 01D0007F | 0 01D00000 | 0 01D0007F | 128 | Tracer_MSMC_0 (Reserved) |
| 01D00080 | 01D07FFF | 0 01D00080 | 0 01D07FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D08000 | 01D0807F | 0 01D08000 | 0 01D0807F | 128 | Tracer_MSMC_1 (Reserved) |
| 01D08080 | 01D0FFFF | 0 01D08080 | 0 01D0FFFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D10000 | 01D1007F | 0 01D10000 | 0 01D1007F | 128 | Tracer_MSMC_2 (Reserved) |
| 01D10080 | 01D17FFF | 0 01D10080 | 0 01D17FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D18000 | 01D1807F | 0 01D18000 | 0 01D1807F | 128 | Tracer_MSMC_3 (Reserved) |
| 01D18080 | 01D1FFFF | 0 01D18080 | 0 01D1FFFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D20000 | 01D2007F | 0 01D20000 | 0 01D2007F | 128 | Tracer_QM_DMA |
| 01D20080 | 01D27FFF | 0 01D20080 | 0 01D27FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D28000 | 01D2807F | 0 01D28000 | 0 01D2807F | 128 | Tracer_DDR |
| 01D28080 | 01D2FFFF | 0 01D28080 | 0 01D2FFFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D30000 | 01D3007F | 0 01D30000 | 0 01D3007F | 128 | Tracer_SM |
| 01D30080 | 01D37FFF | 0 01D30080 | 0 01D37FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D38000 | 01D3807F | 0 01D38000 | 0 01D3807F | 128 | Tracer_QM_CFG |
| 01D38080 | 01D3FFFF | 0 01D38080 | 0 01D3FFFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D40000 | 01D4007F | 0 01D40000 | 0 01D4007F | 128 | Tracer_CFG |
| 01D40080 | 01D47FFF | 0 01D40080 | 0 01D47FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D48000 | 01D4807F | 0 01D48000 | 0 01D4807F | 128 | Tracer_L2_0 |
| 01D48080 | 01D4FFFF | 0 01D48080 | 0 01D4FFFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D50000 | 01D5007F | 0 01D50000 | 0 01D5007F | 128 | Reserved |
| 01D50080 | 01D57FFF | 0 01D50080 | 0 01D57FFF | 32K-128 | Reserved |
| 01D58000 | 01D5807F | 0 01D58000 | 0 01D5807F | 128 | Tracer_TNet_6P_A |
| 01D58080 | 021B3FFF | 0 01D58080 | 0 021B3FFF | 4464K -128 | Reserved |
| 021B4000 | 021B47FF | 0 021B4000 | 0 021B47FF | 2K | McBSP0 Registers |
| 021B4800 | 021B5FFF | 0 021B4800 | 0 021B5FFF | 6K | Reserved |
| 021B6000 | 021B67FF | 0 021B6000 | 0 021B67FF | 2K | McBSP0 FIFO Registers |
| 021B6800 | 021B7FFF | 0 021B6800 | 0 021B7FFF | 6K | Reserved |
| 021B8000 | 021B87FF | 0 021B8000 | 0 021B87FF | 2K | McBSP1 Registers |
| 021B8800 | 021B9FFF | 0 021B8800 | 0 021B9FFF | 6K | Reserved |
| 021BA000 | 021BA7FF | 0 021BA000 | 0 021BA7FF | 2K | McBSP1 FIFO Registers |
| 021BA800 | 021BFFFF | 0 021BA800 | 0 021BFFFF | 22K | Reserved |
| 021C0000 | 021C03FF | 0 021C0000 | 0 021C03FF | 1K | Reserved |
| 021C0400 | 021CFFFF | 0 021C0400 | 0 021CFFFF | 63K | Reserved |
| 021D0000 | 021D00FF | 0 021D0000 | 0 021D00FF | 256 | Reserved |
| 021D0100 | 021D3FFF | 0 021D0100 | 0 021D3FFF | 16K - 256 | Reserved |
| 021D4000 | 021D40FF | 0 021D4000 | 0 021D40FF | 256 | Reserved |
| 021D4100 | 021FFFFF | 0 021D4100 | 0 021FFFFF | 176K - 256 | Reserved |
| 02200000 | 0220007F | 0 02200000 | 0 0220007F | 128 | Timer0 |
| 02200080 | 0220FFFF | 0 02200080 | 0 0220FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02210000 | 0221007F | 0 02210000 | 0 0221007F | 128 | Reserved |
| 02210080 | 0221FFFF | 0 02210080 | 0 0221FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02220000 | 0222007F | 0 02220000 | 0 0222007F | 128 | Timer2 |
| 02220080 | 0222FFFF | 0 02220080 | 0 0222FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02230000 | 0223007F | 0 02230000 | 0 0223007F | 128 | Timer3 |
| 02230080 | 0223FFFF | 0 02230080 | 0 0223FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02240000 | 0224007F | 0 02240000 | 0 0224007F | 128 | Timer4 |
| 02240080 | 0224FFFF | 0 02240080 | 0 0224FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02250000 | 0225007F | 0 02250000 | 0 0225007F | 128 | Timer5 |
| 02250080 | 0225FFFF | 0 02250080 | 0 0225FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02260000 | 0226007F | 0 02260000 | 0 0226007F | 128 | Timer6 |
| 02260080 | 0226FFFF | 0 02260080 | 0 0226FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02270000 | 0227007F | 0 02270000 | 0 0227007F | 128 | Timer7 |
| 02270080 | 0230FFFF | 0 02270080 | 0 0230FFFF | 640K - 128 | Reserved |
| 02310000 | 023101FF | 0 02310000 | 0 023101FF | 512 | PLL Controller |
| 02310200 | 0231FFFF | 0 02310200 | 0 0231FFFF | 64K-512 | Reserved |
| 02320000 | 023200FF | 0 02320000 | 0 023200FF | 256 | GPIO |
| 02320100 | 0232FFFF | 0 02320100 | 0 0232FFFF | 64K-256 | Reserved |
| 02330000 | 023303FF | 0 02330000 | 0 023303FF | 1K | SmartReflex |
| 02330400 | 0234FFFF | 0 02330400 | 0 0234FFFF | 127K | Reserved |
| 02350000 | 02350FFF | 0 02350000 | 0 02350FFF | 4K | Power Sleep Controller (PSC) |
| 02351000 | 0235FFFF | 0 02351000 | 0 0235FFFF | 64K-4K | Reserved |
| 02360000 | 023603FF | 0 02360000 | 0 023603FF | 1K | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) 0 |
| 02360400 | 02367FFF | 0 02360400 | 0 02367FFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 02368000 | 023683FF | 0 02368000 | 0 023683FF | 1K | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) 1 |
| 02368400 | 0236FFFF | 0 02368400 | 0 0236FFFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 02370000 | 023703FF | 0 02370000 | 0 023703FF | 1K | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) 2 |
| 02370400 | 02377FFF | 0 02370400 | 0 02377FFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 02378000 | 023783FF | 0 02378000 | 0 023783FF | 1K | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) 3 |
| 02378400 | 0237FFFF | 0 02378400 | 0 0237FFFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 02380000 | 023803FF | 0 02380000 | 0 023803FF | 1K | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) 4 |
| 02380400 | 023FFFFF | 0 02380400 | 0 023FFFFF | 511K | Reserved |
| 02440000 | 02443FFF | 0 02440000 | 0 02443FFF | 16K | DSP trace formatter 0 |
| 02444000 | 0244FFFF | 0 02444000 | 0 0244FFFF | 48K | Reserved |
| 02450000 | 02453FFF | 0 02450000 | 0 02453FFF | 16K | Reserved |
| 02454000 | 02521FFF | 0 02454000 | 0 02521FFF | 824K | Reserved |
| 02522000 | 02522FFF | 0 02522000 | 0 02522FFF | 4K | Efuse |
| 02523000 | 0252FFFF | 0 02523000 | 0 0252FFFF | 52K | Reserved |
| 02530000 | 0253007F | 0 02530000 | 0 0253007F | 128 | I2C data & control |
| 02530080 | 0253FFFF | 0 02530080 | 0 0253FFFF | 64K-128 | Reserved |
| 02540000 | 0254003F | 0 02540000 | 0 0254003F | 64 | UART 0 |
| 02540400 | 0254FFFF | 0 02540400 | 0 0254FFFF | 64K-64 | Reserved |
| 02550000 | 0255003F | 0 02550000 | 0 0255003F | 64 | UART 1 |
| 02550040 | 0257FFFF | 0 02550040 | 0 0257FFFF | 192K-64 | Reserved |
| 02580000 | 02580FFF | 0 02580000 | 0 02580FFF | 4K | uPP |
| 02581000 | 025FFFFF | 0 02581000 | 0 025FFFFF | 508K | Reserved |
| 02600000 | 02601FFF | 0 02600000 | 0 02601FFF | 8K | Chip Interrupt Controller (CIC) 0 |
| 02602000 | 02603FFF | 0 02602000 | 0 02603FFF | 8K | Reserved |
| 02604000 | 02605FFF | 0 02604000 | 0 02605FFF | 8K | Chip Interrupt Controller (CIC) 1 |
| 02606000 | 02607FFF | 0 02606000 | 0 02607FFF | 8K | Reserved |
| 02608000 | 02609FFF | 0 02608000 | 0 02609FFF | 8K | Reserved |
| 0260A000 | 0261FFFF | 0 0260A000 | 0 0261FFFF | 88K | Reserved |
| 02620000 | 026207FF | 0 02620000 | 0 026207FF | 2K | Chip-Level Registers |
| 02620800 | 0263FFFF | 0 02620800 | 0 0263FFFF | 126K | Reserved |
| 02640000 | 026407FF | 0 02640000 | 0 026407FF | 2K | Semaphore |
| 02640800 | 0273FFFF | 0 02640800 | 0 0273FFFF | 1022K | Reserved |
| 02740000 | 02747FFF | 0 02740000 | 0 02747FFF | 32K | EDMA Channel Controller (EDMA3CC) |
| 02748000 | 0278FFFF | 0 02748000 | 0 0278FFFF | 288K | Reserved |
| 02790000 | 027903FF | 0 02790000 | 0 027903FF | 1K | EDMA3CC Transfer Controller EDMA3TC0 |
| 02790400 | 02797FFF | 0 02790400 | 0 02797FFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 02798000 | 027983FF | 0 02798000 | 0 027983FF | 1K | EDMA3CC Transfer Controller EDMA3TC1 |
| 02798400 | 0279FFFF | 0 02798400 | 0 0279FFFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 027A0000 | 027A03FF | 0 027A0000 | 0 027A03FF | 1K | EDMA3CC Transfer Controller EDMA3TC2 |
| 027A0400 | 027A7FFF | 0 027A0400 | 0 027A7FFF | 31K | Reserved |
| 027A8000 | 027A83FF | 0 027A8000 | 0 027A83FF | 1K | EDMA3CC Transfer Controller EDMA3TC3 |
| 027A8400 | 027CFFFF | 0 027A8400 | 0 027CFFFF | 159K | Reserved |
| 027D0000 | 027D0FFF | 0 027D0000 | 0 027D0FFF | 4K | TI embedded trace buffer (TETB) - CorePac0 |
| 027D1000 | 027DFFFF | 0 027D1000 | 0 027DFFFF | 60K | Reserved |
| 027E0000 | 027E0FFF | 0 027E0000 | 0 027E0FFF | 4K | Reserved |
| 027E1000 | 0284FFFF | 0 027E1000 | 0 0284FFFF | 444K | Reserved |
| 02850000 | 02857FFF | 0 02850000 | 0 02857FFF | 32K | TI embedded trace buffer (TETB) — system |
| 02858000 | 028FFFFF | 0 02858000 | 0 028FFFFF | 672K | Reserved |
| 02900000 | 02920FFF | 0 02900000 | 0 02920FFF | 132K | Reserved |
| 02921000 | 029FFFFF | 0 02921000 | 0 029FFFFF | 1M-132K | Reserved |
| 02A00000 | 02AFFFFF | 0 02A00000 | 0 02AFFFFF | 1M | Queue manager subsystem configuration |
| 02B00000 | 02C07FFF | 0 02B00000 | 0 02C07FFF | 1056K | Reserved |
| 02C08000 | 02C8BFFF | 0 02C08000 | 0 02C8BFFF | 16K | EMAC subsystem configuration |
| 02C0C000 | 07FFFFFF | 0 02C0C000 | 0 07FFFFFF | 84M - 48K | Reserved |
| 08000000 | 0800FFFF | 0 08000000 | 0 0800FFFF | 64K | Extended memory controller (XMC) configuration |
| 08010000 | 0BBFFFFF | 0 08010000 | 0 0BBFFFFF | 60M-64K | Reserved |
| 0BC00000 | 0BCFFFFF | 0 0BC00000 | 0 0BCFFFFF | 1M | Multicore shared memory controller (MSMC) config |
| 0BD00000 | 0BFFFFFF | 0 0BD00000 | 0 0BFFFFFF | 3M | Reserved |
| 0C000000 | 0C0FFFFF | 0 0C000000 | 0 0C0FFFFF | 1M | Reserved |
| 0C200000 | 107FFFFF | 0 0C100000 | 0 107FFFFF | 71 M | Reserved |
| 10800000 | 108FFFFF | 0 10800000 | 0 108FFFFF | 1M | CorePac0 L2 SRAM |
| 10900000 | 10DFFFFF | 0 10900000 | 0 10DFFFFF | 5M | Reserved |
| 10E00000 | 10E07FFF | 0 10E00000 | 0 10E07FFF | 32K | CorePac0 L1P SRAM |
| 10E08000 | 10EFFFFF | 0 10E08000 | 0 10EFFFFF | 1M-32K | Reserved |
| 10F00000 | 10F07FFF | 0 10F00000 | 0 10F07FFF | 32K | CorePac0 L1D SRAM |
| 10F08000 | 117FFFFF | 0 10F08000 | 0 117FFFFF | 9M-32K | Reserved |
| 11800000 | 118FFFFF | 0 11800000 | 0 118FFFFF | 1M | Reserved |
| 11900000 | 11DFFFFF | 0 11900000 | 0 11DFFFFF | 5M | Reserved |
| 11E00000 | 11E07FFF | 0 11E00000 | 0 11E07FFF | 32K | Reserved |
| 11E08000 | 11EFFFFF | 0 11E08000 | 0 11EFFFFF | 1M-32K | Reserved |
| 11F00000 | 11F07FFF | 0 11F00000 | 0 11F07FFF | 32K | Reserved |
| 11F08000 | 1FFFFFFF | 0 11F08000 | 0 1FFFFFFF | 225M-32K | Reserved |
| 20000000 | 200FFFFF | 0 20000000 | 0 200FFFFF | 1M | System trace manager (STM) configuration |
| 20100000 | 207FFFFF | 0 20100000 | 0 207FFFFF | 7M | Reserved |
| 20800000 | 208FFFFF | 0 20080000 | 0 208FFFFF | 1M | Reserved |
| 20900000 | 20AFFFFF | 0 20900000 | 0 20AFFFFF | 2M | Reserved |
| 20B00000 | 20B1FFFF | 0 20B00000 | 0 20B1FFFF | 128K | Boot ROM |
| 20B20000 | 20BEFFFF | 0 20B20000 | 0 20BEFFFF | 832K | Reserved |
| 20BF0000 | 20BF01FF | 0 20BF0000 | 0 20BF01FF | 512 | SPI |
| 20BF0400 | 20BFFFFF | 0 20BF0200 | 0 20BFFFFF | 64K -512 | Reserved |
| 20C00000 | 20C000FF | 0 20C00000 | 0 20C000FF | 256 | EMIF16 configuration |
| 20C00100 | 20FFFFFF | 0 20C00100 | 0 20FFFFFF | 4M - 256 | Reserved |
| 21000000 | 210001FF | 1 00000000 | 1 000001FF | 512 | DDR3 EMIF configuration |
| 21000200 | 213FFFFF | 0 21000200 | 0 213FFFFF | 4M-512 | Reserved |
| 21400000 | 214000FF | 0 21400000 | 0 214000FF | 256 | Reserved |
| 21400100 | 217FFFFF | 0 21400100 | 0 217FFFFF | 4M-256 | Reserved |
| 21800000 | 21807FFF | 0 21800000 | 0 21807FFF | 32K | PCIe config |
| 21808000 | 33FFFFFF | 0 21808000 | 0 33FFFFFF | 8M-32K | Reserved |
| 22000000 | 22000FFF | 0 22000000 | 0 22000FFF | 4K | McBSP0 FIFO Data |
| 22000100 | 223FFFFF | 0 22000100 | 0 223FFFFF | 4M-4K | Reserved |
| 22400000 | 22400FFF | 0 22400000 | 0 22400FFF | 4K | McBSP1 FIFO Data |
| 22400100 | 229FFFFF | 0 22400100 | 0 229FFFFF | 6M-4K | Reserved |
| 22A00000 | 22A0FFFF | 0 22A00000 | 0 22A0FFFF | 64K | Reserved |
| 22A01000 | 22AFFFFF | 0 22A01000 | 0 22AFFFFF | 1M-64K | Reserved |
| 22B00000 | 22B0FFFF | 0 22B00000 | 0 22B0FFFF | 64K | Reserved |
| 22B01000 | 33FFFFFF | 0 22B01000 | 0 33FFFFFF | 277M-64K | Reserved |
| 34000000 | 341FFFFF | 0 34000000 | 0 341FFFFF | 2M | Queue manager subsystem data |
| 34200000 | 3FFFFFFF | 0 34200000 | 0 3FFFFFFF | 190M | Reserved |
| 40000000 | 4FFFFFFF | 0 40000000 | 0 4FFFFFFF | 256M | Reserved |
| 50000000 | 5FFFFFFF | 0 50000000 | 0 5FFFFFFF | 256M | Reserved |
| 60000000 | 6FFFFFFF | 0 60000000 | 0 6FFFFFFF | 256M | PCIe data |
| 70000000 | 73FFFFFF | 0 70000000 | 0 73FFFFFF | 64M | EMIF16 CE0 data space, supports NAND, NOR, or SRAM memory(1) |
| 74000000 | 77FFFFFF | 0 74000000 | 0 77FFFFFF | 64M | EMIF16 CE1 data space, supports NAND, NOR, or SRAM memory(1) |
| 78000000 | 7BFFFFFF | 0 78000000 | 0 7BFFFFFF | 64M | EMIF16 CE2 data space, supports NAND, NOR, or SRAM memory(1) |
| 7C000000 | 7FFFFFFF | 0 7C000000 | 0 7FFFFFFF | 64M | EMIF16 CE3 data space, supports NAND, NOR or SRAM memory(1) |
| 80000000 | FFFFFFFF | 8 00000000 | 8 7FFFFFFF | 2G | DDR3 EMIF data(2) |
3.4 Boot Sequence
The boot sequence is a process by which the DSP's internal memory is loaded with program and data sections. The DSP's internal registers are programmed with predetermined values. The boot sequence is started automatically after each power-on reset, warm reset, and system reset. A local reset to an individual C66x CorePac should not affect the state of the hardware boot controller on the device. For more details on the initiators of the resets, see Section 8.4. The bootloader uses a section of the L2 SRAM (start address 0x008EFD00 and end address 0x008F FFFF) during initial booting of the device. For more details on the type of configurations stored in this reserved L2 section see the Bootloader for the C66x DSP User's Guide (SPRUGY5).
3.5 Boot Modes Supported and PLL Settings
The device supports several boot processes, which leverage the internal boot ROM. Most boot processes are software driven, using the BOOTMODE[2:0] device configuration inputs to determine the software configuration that must be completed. From a hardware perspective, there are two possible boot modes:
- ROM Boot - C66x CorePac0 is released from reset and begins executing from the L3 ROM base address. After performing the boot process (e.g., from I2C ROM, Ethernet, or RapidIO), C66x CorePac0 then begins execution from the provided boot entry point. See the Bootloader for the C66x DSP User's Guide (SPRUGY5) for more details.
The boot process performed by the C66x CorePac0 in ROM boot is determined by the BOOTMODE[12:0] value in the DEVSTAT register. The C66x CorePac0 reads this value, and then executes the associated boot process in software. Figure 3-2 shows the bits associated with BOOTMODE[12:0].
| 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| PLL Mult I2C /SPI Ext Dev Cfg | Device Configuration | Boot Device | ||||||||||
3.5.1 Boot Device Field
The Boot Device field BOOTMODE[2:0] defines the boot device that is chosen. Table 3-3 shows the supported boot modes.
Table 3-3 Boot Mode Pins: Boot Device Values
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2-0 | Boot Device | Device boot mode
|
3.5.2 Device Configuration Field
The device configuration fields BOOTMODE[9:3] are used to configure the boot peripheral and, therefore, the bit definitions depend on the boot mode.
3.5.2.1 EMIF16 / UART / No Boot Device Configuration
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Sub-Mode Specific Configuration | Sub-Mode | |||||
Table 3-4 EMIF16 / UART / No Boot Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9-6 | Sub-Mode Specific Configuration | Configures the selected sub-mode. See Section 3.5.2.1.1, Section 3.5.2.1.2, and Section 3.5.2.1.3 |
| 5-3 | Sub-Mode | Sub mode selection.
|
3.5.2.1.1 No Boot Mode
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Reserved |
Table 3-5 No Boot Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9-6 | Reserved |
|
3.5.2.1.2 UART Boot Mode
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Speed | Parity |
Table 3-6 UART Boot Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9-8 | Speed | UART interface speed.
|
| 7-6 | Parity | UART parity used during boot.
|
3.5.2.1.3 EMIF16 Boot Mode
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Wait Enable | Width Select | Chip Select | |
Table 3-7 EMIF16 Boot Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | Wait Enable | Extended Wait mode for EMIF16.
|
| 8 | Width Select | EMIF data width for EMIF16.
|
| 7-6 | Chip Select | EMIF Chip Select used during EMIF 16 boot.
|
3.5.2.2 Ethernet (SGMII) Boot Device Configuration
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| SerDes Clock Mult | Ext connection | Device ID | ||||
Table 3-8 Ethernet (SGMII) Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9-8 | SerDes Clock Mult | SGMII SerDes input clock. The output frequency of the PLL must be 1.25 GBs.
|
| 7-6 | Ext connection | External connection mode
|
| 5-3 | Device ID | This value can range from 0 to 7 is used in the device ID field of the Ethernet-ready frame. |
3.5.2.3 NAND Boot Device Configuration
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| 1st Block | I2C | Reserved | ||||
Table 3-9 NAND Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9-5 | 1st Block | NAND Block to be read first by the boot ROM.
|
| 4 | I2C | NAND parameters read from I2C EEPROM
|
| 3 | Reserved | Reserved |
3.5.2.4 PCI Boot Device Configuration
Extra device configuration is provided in the PCI bits in the DEVSTAT register.
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Ref Clock | BAR Config | Reserved | ||||
Table 3-10 PCI Device Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | Ref Clock | PCIe reference clock configuration
|
| 8-5 | BAR Config | PCIe BAR registers configuration This value can range from 0 to 0xf. See Table 3-11. |
| 4-3 | Reserved | Reserved |
Table 3-11 BAR Config / PCIe Window Sizes
| BAR CFG | BAR0 | 32-BIT ADDRESS TRANSLATION | 64-BIT ADDRESS TRANSLATION | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAR1 | BAR2 | BAR3 | BAR4 | BAR5 | BAR2/3 | BAR4/5 | ||
| 0b0000 | PCIe MMRs | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | Clone of BAR4 | ||
| 0b0001 | 16 | 16 | 32 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0010 | 16 | 32 | 32 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0011 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0100 | 16 | 16 | 64 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0101 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0110 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 64 | ||||
| 0b0111 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 128 | ||||
| 0b1000 | 64 | 64 | 128 | 256 | ||||
| 0b1001 | 4 | 128 | 128 | 128 | ||||
| 0b1010 | 4 | 128 | 128 | 256 | ||||
| 0b1011 | 4 | 128 | 256 | 256 | ||||
| 0b1100 | 256 | 256 | ||||||
| 0b1101 | 512 | 512 | ||||||
| 0b1110 | 1024 | 1024 | ||||||
| 0b1111 | 2048 | 2048 | ||||||
3.5.2.5 I2C Boot Device Configuration
3.5.2.5.1 I2C Master Mode
In master mode, the I2C device configuration uses ten bits of device configuration instead of seven as used in other boot modes. In this mode, the device will make the initial read of the I2C EEPROM while the PLL is in bypass mode. The initial read will contain the desired clock multiplier, which will be set up prior to any subsequent reads.
| 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Mode | Address | Speed | Parameter Index | ||||||
Table 3-12 I2C Master Mode Device Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Mode | I2C operation mode
|
| 11 - 10 | Address | I2C bus address configuration
|
| 9 | Speed | I2C data rate configuration
|
| 8-3 | Parameter Index | Identifies the index of the configuration table initially read from the I2C EEPROM This value can range from 0 to 31. |
3.5.2.5.2 I2C Passive Mode
In passive mode, the device does not drive the clock, but simply acks data received on the specified address.
| 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Mode | Address | Reserved | |||||||
Table 3-13 I2C Passive Mode Device Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Mode | I2C operation mode
|
| 11 - 5 | Address | I2C bus address accepted during boot. Value may range from 0x00 to 0x7F |
| 4 - 3 | Reserved | Reserved |
3.5.2.6 SPI Boot Device Configuration
In SPI boot mode, the SPI device configuration uses ten bits of device configuration instead of seven as used in other boot modes.
| 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Mode | 4, 5 Pin | Addr Width | Chip Select | Parameter Table Index | |||||
Table 3-14 SPI Device Configuration Field Descriptions
| Bit | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12-11 | Mode | Clk Pol / Phase
|
| 10 | 4, 5 Pin | SPI operation mode configuration
|
| 9 | Addr Width | SPI address width configuration
|
| 8-7 | Chip Select | The chip select field value |
| 6-3 | Parameter Table Index | Specifies which parameter table is loaded |
3.5.3 Boot Parameter Table
The ROM Bootloader (RBL) is guided by the boot parameter table to carry out the boot process. The boot parameter table is the most common format the RBL employs to determine the boot flow. These boot parameter tables have certain parameters common across all the boot modes, while the rest of the parameters are unique to the boot modes. The common entries in boot parameter table is are shown in table below.
Table 3-15 Boot Parameter Table Common Values
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Length | The length of this table, including this length field, in bytes. |
| 2 | Checksum | Identifies the device port number to boot from, if applicable. The value 0xFFFF indicates that all ports are configured (Ethernet, SRIO). |
| 4 | Boot Mode | See Table 3-16 |
| 6 | Port Num | Identifies the device port number to boot from, if applicable. The value 0xFFFF indicates that all ports are configured (Ethernet, SRIO). |
| 8 | PLL config, MSW | PLL configuration, MSW (see Figure 5-6) |
| 10 | PLL config, LSW | PLL configuration, LSW |
Table 3-16 Boot Parameter Table Boot Mode Field
| Value | Boot Mode |
|---|---|
| 10 | Ethernet (boot table) |
| 20 | Rapid I/O |
| 30 | PCIe |
| 40 | I2C Master |
| 41 | I2C Slave |
| 42 | I2C Master Write |
| 50 | SPI |
| 60 | Hyperlink |
| 70 | EMIF25 |
| 80 | NAND |
| 81 | NAND I2C |
| 100 | SLEEP, no PLL configuration |
| 110 | UART |
| 31 | 30 | 29 | 16 | 15 | 8 | 7 | 0 |
| PLL Config Ctl | PLL Multiplier | PLL Pre-Divider | PLL Post-Divider | ||||||||||
Table 3-17 PLL Configuration Field Description
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PLL Config Ctl | 0b00 | PLL is not configured |
| 0b01 | PLL is configured only if it is currently disabled or in bypass | |
| 0b10 | PLL is configured only if it is currently disabled or in bypass | |
| 0b11 | PLL is disabled and put into bypass | |
| Pre-divider | 0-255 | Input clock division. The value 0 is treated as pre-divide by 1 |
| Multiplier | 0-16383 | Multiplier. The value 0 is treated as multiply by 1 |
| Post-divider | 0-255 | PLL output division. The value 0 is treated as post divide by 1 |
3.5.3.1 Sleep / XIP Mode Parameter Table
The sleep mode parameter table has no fields in addition to the common fields described in Section 3.5.3.
Table 3-18 EMIF16 XIP Parameter Table Values
| Byte Offset | Name | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | Figure 3-14 |
| 14 | Type | Must be set to 0 for NOR flash |
| 16 | Branch Addr, MSW | Address to branch to |
| 18 | Branch Addr, LSW | |
| 20 | CsNum | The chip select number, valid values are 2-5 |
| 22 | memWidth | The bit width of the memory, valid values are 8 or 16 |
| 24 | waitEnable | Extended wait is enabled if this value is 1, otherwise disabled |
| 26 | Async config, MSW | EMIF16 async config register value, msw |
| 28 | Async config, LSW | EMIF16 async config register value, lsw |
| 15 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | async | ||||||||||||||
Table 3-19 EMIF16 XIP Option Field Descriptions
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Async | 0 | The async config register is not changed by the boot code |
| 1 | The async config value in the boot parameter table is programmed in the async config register (EMIF timing values) |
3.5.3.2 SRIO Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-20 SRIO Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | See Figure 3-15 |
| 14 | Lane Setup | See Table 3-22 |
| 16 | Reserved | Reserved |
| 18 | Node ID | The node ID value to set for this device |
| 20 | SERDES ref clk | The SERDES reference clock frequency, in 1/100 MHZ. Used only if PLL setup field in options is set. |
| 22 | Link Rate | Link rate, MHz. Used only if PLL setup field in options is set. |
| 24 | PF Low | Packet forward address range, low value |
| 26 | PF high | Packet forward address range, high value |
| 28 | Promiscuous Mask | A bit is set for each lane/port that is configured as promiscuous. |
| 30 | Serdes AUX, MSW | Serdes Auxillary Register Configuration, MSW |
| 32 | Serdes AUX, LSW | Serdes Auxillary Register Configuration, LSW |
| 34 | SERDES Rx Lane 0, MSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 0, MSW |
| 36 | SERDES Rx Lane 0, LSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 0, LSW |
| 38 | SERDES Rx Lane 1, MSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 1, MSW |
| 40 | SERDES Rx Lane 1, LSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 1, LSW |
| 42 | SERDES Rx Lane 2, MSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 2, MSW |
| 44 | SERDES Rx Lane 2, LSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 2, LSW |
| 46 | SERDES Rx Lane 3, MSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 3, MSW |
| 48 | SERDES Rx Lane 3, LSW | Serdes Rx Config, Lane 3, LSW |
| 50 | SERDES Tx Lane 0, MSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 0, MSW |
| 52 | SERDES Tx Lane 0, LSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 0, LSW |
| 54 | SERDES Tx Lane 1, MSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 1, MSW |
| 56 | SERDES Tx Lane 1, LSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 1, LSW |
| 58 | SERDES Tx Lane 2, MSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 2, MSW |
| 60 | SERDES Tx Lane 2, LSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 2, LSW |
| 62 | SERDES Tx Lane 3, MSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 3, MSW |
| 64 | SERDES Tx Lane 3, LSW | Serdes Tx Config, Lane 3, LSW |
| 15 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | PLL Setup | QM Bypass | Cfg Bypass | Mailbox En | Tx En | |||||||||
Table 3-21 SRIO Boot Options Description
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PLL Setup | 0 | Serdes Configuration registers taken without modification |
| 1 | Multiplier and rate fields are modified based on the reference clock and link rate fields. | |
| QM Bypass | 0 | Configure the QM (and cpdma) |
| 1 | Bypass QM configuration | |
| Cfg Bypass | 0 | Configure the SRIO |
| 1 | Bypass SRIO configuration | |
| Mailbox En | 0 | Mailbox mode disabled. SRIO boot is in Master mode |
| 1 | Mailbox mode enabled. SRIO boot is in message mode (master boot still works) | |
| Tx En | 0 | SRIO transmit disabled |
| 1 | SRIO transmit enabled |
Table 3-22 SRIO Lane Setup Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | SRIO configured as four 1x ports |
| 1 | SRIO configured as 3 ports (2x, 1x, 1x) |
| 2 | SRIO configured as 3 ports (1x, 1x, 2x) |
| 3 | SRIO configured as 2 ports (2x, 2x) |
| 4 | SRIO configured as 1 4x port |
| 5-0xFFFF | Reserved |
3.5.3.3 Ethernet Mode Boot Parameter Table
The default multi-cast Ethernet mac address is the broadcast address.
Table 3-23 Ethernet Boot Parameter Table Values
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | See Figure 3-16 |
| 14 | MAC High | The 16 MSBs of the MAC address to receive during boot |
| 16 | MAC Med | The 16 middle bits of the MAC address to receive during boot |
| 18 | MAC Low | The 16 LSBs of the MAC address to receive during boot |
| 20 | Multi MAC High | The 16 MSBs of the multi-cast MAC address to receive during boot |
| 22 | Multi MAC Med | The 16 middle bits of the multi-cast MAC address to receive during boot |
| 24 | Mulit MAC Low | The 16 LSBs of the multi-cast MAC address to receive during boot |
| 26 | Source Port | The source UDP port to accept boot packets from. A value of 0 will accept packets from any UDP port |
| 28 | Dest Port | The destination port to accept boot packets on. |
| 30 | Device ID 12 | The 1st two bytes of the device ID. This is typically a string value, and is sent in the Ethernet ready frame |
| 32 | Device ID 34 | The 2nd two bytes of the device ID. |
| 34 | Dest MAC High | The 16 MSBs of the MAC destination address used for the Ethernet ready frame. Default is broadcast. |
| 36 | Dest MAC Med | The 16 middle bits of the MAC destination address |
| 38 | DEST MAC Low | The 16 LSBs of the MAC destination address |
| 40 | Sgmii Config | See Figure 3-17 |
| 42 | Sgmii Control | The SGMII control register value (if table value not used) |
| 44 | Sgmii Adv Abilility | The SGMII ADV Ability register value (if table value not used) |
| 46 | Sgmii Tx Cfg High | The 16 MSBs of the sgmii Tx config register (if table value not used) |
| 48 | Sgmii Tx Cfg Low | The 16 LSBs of the sgmii Tx config register (if table value not used) |
| 50 | Sgmii Rx Cfg High | The 16 MSBs of the sgmii Rx config register (if table value not used) |
| 52 | Sgmii Rx Cfg Low | The 16 LSBs of the sgmii Rx config register (if table value not used) |
| 54 | Sgmii Aux Cfg High | The 16 MSBs of the sgmii Aux config register (if table value not used) |
| 56 | Sgmii Aux Cfg Low | The 16 LSBs of the sgmii Aux config register (if table value not used) |
| 58 | Pkt PLL Config, MSW | The packet subsystem PLL configuration, MSW (unused in gauss) |
| 60 | Packet PLL Config, LSW | The packet subsystem PLL configuration, LSW |
| 15 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Reserved | Init Config | Skip Tx | Reserved | ||||||||||||
Table 3-24 Ethernet Options Field Descriptions
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Init Config | 0b00 | SERDES and SGMII are configured. |
| 0b01 | SERDES and SGMII are NOT configured | |
| 0b10 | Reserved | |
| 0b11 | None of the Ethernet system hardware is configured. | |
| Skip tx | 0 | Ethernet ready frame is sent once when the system is first ready to receive packets, and then roughly every 3 seconds until the first boot packet is accepted. |
| 1 | Ethernet ready frame is not sent |
| 15 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 0 |
| Reserved | bypass | direct | Index | ||||||||||||
Table 3-25 SGMII Config Field Descriptions
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Index | 0 | Configure the SGMII as a master |
| 1 | Configure the SGMII as a slave, or connected to a Phy | |
| 2 | Configure the SGMII as a forced link | |
| 3 | Configure the SGMII as mac to fiber | |
| 4-15 | Reserved | |
| Direct | 0 | Configure the SGMII as directed in the index field |
| 1 | Configure the SGMII using the advise ability and control fields in the boot parameter table, not based on the index field | |
| Bypass | 0 | Configure the SGMII. |
| 1 | Do not configure the SGMII. |
3.5.3.4 NAND Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-26 NAND Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Decription |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | See Figure 3-18 |
| 14 | I2cClkFreqKhz | The I2C clock frequency to use when using I2C tables |
| 16 | I2cTargetAddr | The I2C bus address of the EEPROM |
| 18 | I2cLocalAddr | The I2C bus address of the Appleton device |
| 20 | I2cDataAddr | The address on the EEPROM of the NAND configuration table |
| 22 | I2cWtoRDelay | Delay between addres writes and data reads, in I2C clock periods |
| 24 | csNum | The NAND chip select region (0-3) |
| 26 | firstBlock | The first block of the boot image |
| 15 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | I2C | ||||||||||||||
Table 3-27 NAND Boot Parameter Options Bit Field Descriptions
| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| I2C | 0 | NAND configuration is NOT read from I2C |
| 1 | NAND configuration is read from the I2C |
3.5.3.5 PCIE Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-28 PCIe Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | options | PCI configuration options (see Figure 3-19) |
| 14 | Address Width | PCI address width, can be 32 or 64 |
| 16 | Serdes Frequency | Serdes frequency, in MBs. Currently only 2500 supported. |
| 18 | Reference clock | Reference clock frequency, in units of 10kHz. Valid values are 10000 (100MHz), 12500 (125MHz), 15625 (156.25Mhz), 25000 (250MHz) and 31250 (312.5 MHz), although other values should work. |
| 20 | Window 1 Size | Window 1 size, in Mbytes |
| 22 | Window 2 Size | Window 2 size, in Mbytes |
| 24 | Window 3 Size | Window 3 size, in Mbytes. Valid only if address width is 32. |
| 26 | Window 4 Size | Window 4 Size, in Mbytes Valid only if address width is 32. |
| 28 | Window 5 Size | Window 5 Size. Valid only if the address width is 32. |
| 30 | Vendor ID | Vendor ID field |
| 32 | Device ID | Device ID field (0xb006 by default for Gauss) |
| 34 | Class code Rev Id, MSW | Class code/revision ID field |
| 36 | Class code Rev Id, LSW | Class code/revision ID field |
| 38 | Serdes cfg msw | PCIe serdes config word, MSW |
| 40 | Serdes cfg lsw | PCIe serdes config word, LSW |
| 42 | Serdes lane 0 cfg msw | Serdes lane config word, msw lane 0 |
| 44 | Serdes lane 0 cfg lsw | Serdes lane config word, lsw, lane 0 |
| 46 | Serdes lane 1 cfg msw | Serdes lane config word, msw, lane 1 |
| 48 | Serdes lane 1 cfg lsw | Serdes lane config word, lsw, lane 1 |
| 15 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | Serdes Cfg | Cfg Disable | Reserved | |||||||||||
Table 3-29 PCIe Options Field Descriptions
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cfg disable | 0 | PCIe peripheral is configured by the boot rom |
| 1 | PCIe peripheral is not configured by the boot rom | |
| Serdes Cfg | 0 | Serdes PLL multiplier and rate fields in the table are used diretly |
| 1 | Serdes PLL multiplier and rate fields in the serdes registers will be overwritten based on the values in the serdes frequency and reference clock parameters. |
3.5.3.6 I2C Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-30 I2C Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | See Figure 3-20 |
| 14 | Boot Dev Addr | The I2C device address to boot from |
| 16 | Boot Dev Addr Ext | Extended boot device address, or I2C bus address (typically 0x50, 0x51) |
| 18 | Broadcast Addr | In master broadcast boot, this is the I2C address to send the boot data to |
| 20 | Local Address | The I2C address of this device. |
| 22 | Device Freq | The operating frequency of the device (MHz). Used to compute the divide down to the I2C module |
| 24 | Bus Frequency | The desired I2C data rate (kHz). |
| 26 | Next Dev Addr | The next device to boot from (used in boot config mode) |
| 28 | Next Dev Addr Ext | The extended next boot device address |
| 30 | Address Delay | The number of CPU cycles to delay between writing the address to an I2C eeprom and reading data. This allows the I2C eeprom time to load the data. |
| 15 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | Mode | ||||||||||||||
Table 3-31 Register Description
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | 0 | Load a boot parameter table from the I2C |
| 1 | Load boot records from the I2C (boot tables) | |
| 2 | Load boot config records from the I2C (boot config tables) | |
| 3 | Perform a slave mode boot, listening on the local address specified in the table. |
3.5.3.7 SPI Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-32 2.5.3.7 SPI Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | options | See Figure 3-21 |
| 14 | Address Width | The number of bytes in the SPI device address. Can be 2 or 3 (16 or 24 bit) |
| 16 | NPin | The operational mode, 4 or 5 pin |
| 18 | Chipsel | The chip select used. Can be 0-3. |
| 20 | Mode | SPI mode, 0-3 |
| 22 | C2T Delay | SPI chip select active to transmit start delay value (0-255) |
| 24 | CPU Freq MHz | The speed of the CPU, in MHz |
| 26 | Bus Freq, MHz | The MHz portion of the SPI bus frequency. Default = 5MHz |
| 28 | Bus Freq, kHz | The kHz portion of the SPI buf frequency. Default = 0 |
| 30 | Read Addr MSW | The first address to read from, MSW (valid for 24 bit address width only) |
| 32 | Read Addr LSW | The first address to read from, LSW |
| 34 | Next chipsel | Chipsel value used after boot config table processing is complete |
| 36 | Next read MSW | The next read address, MSW after config table processing is complete |
| 38 | Next read LSW | The next read address, LSW after config table processing is complete |
The bus frequency programmed into the SPI by the boot ROM is from the table: MHz.kHz. So for a 5.1 MHz bus frequency the MHz value is 5, the kHz value is 100.
| 15 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | Mode | ||||||||||||||
Table 3-33 SPI Options Field Description
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mode | 0 | Load a boot parameter table from the SPI |
| 1 | Load boot records from the SPI (boot tables) | |
| 2 | Load boot config records from the SPI (boot config tables) | |
| 3 | Reserved |
3.5.3.8 Hyperlink Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-34 Hyperlink Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Options | See Figure 3-22 |
| 14 | N lanes | The number of lanes to configure |
| 16 | Serdes Aux, MSW | SERDES Aux register config value, MSW |
| 18 | Serdes Aux, LSW | SERDES Aux register config value, LSW |
| 20 | Rx Lane 0, MSW | SERDES Rx Lane 0 register value, MSW |
| 22 | Rx Lane 0, LSW | SERDES Rx Lane 0 register value, LSW |
| 24 | Tx Lane 0, MSW | SERDES Tx Lane 0 register value, MSW |
| 26 | Tx Lane 0, LSW | SERDES Tx Lane 0 register value, LSW |
| 28 | Rx Lane 1, MSW | SERDES Rx Lane 1 register value, MSW |
| 30 | Rx Lane 1, LSW | SERDES Rx Lane 1 register value, LSW |
| 32 | Tx Lane 1, MSW | SERDES Tx Lane 1 register value, MSW |
| 34 | Tx Lane 1, LSW | SERDES Tx Lane 1 register value, LSW |
| 36 | Rx Lane 2, MSW | SERDES Rx Lane 2 register value, MSW |
| 38 | Rx Lane 2, LSW | SERDES Rx Lane 2 register value, LSW |
| 40 | Tx Lane 2, MSW | SERDES Tx Lane 2 register value, MSW |
| 42 | Tx Lane 2, LSW | SERDES Tx Lane 2 register value, LSW |
| 15 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Reserved | nonit | Rsvd | |||||||||||||
Table 3-35 Hyperlink Options Field Descriptions
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| nonit | 0 | Initialize hyperlink peripheral |
| 1 | Do not initialize hyperlink peripheral |
3.5.3.9 UART Mode Boot Parameter Table
Table 3-36 UART Mode Boot Parameter Table
| Byte Offset | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | Rsvd | Reserved |
| 14 | Data Format | Only value 1, boot table format is supported |
| 16 | Protocol | Only value 0, XMODEM is supported |
| 18 | Initial Ping Cnt | Number of initial pings without reply before the boot times out |
| 20 | Max Err Count | Number of consecutive errors before the boot fails |
| 22 | Nack timeout | Timeout period waiting for an ack/nack, in milli-seconds |
| 24 | Char timeout | Timeout period between characters |
| 26 | Data bits | Number of data bits. Only the value 8 is supported |
| 28 | Parity | 0 = none, 1 = odd, 2 = even |
| 30 | Stop bits x2 | Number of stop bits x2, (2 = 1 stop bit, 4 = 2 stop bits) |
| 32 | Oversample | The over-sample factor. Only 13 and 16 are valid |
| 34 | Flow Control | Only 0, no flow control is supported. |
| 36 | Data Rate, MSW | The Baud rate, MSW |
| 38 | Data Rate, LSW | The Baud rate, LSW |
| 40 | timerRefMhz | Timer reference frequency, in MHz. In Gauss this is the frequency the device is operating at after the PLL is programmed. |
3.6 PLL Boot Configuration Settings
The PLL default settings are determined by the BOOTMODE[12:10] bits. The following table shows settings for various input clock frequencies.
Table 3-37 C66x DSP System PLL Configuration(1)
| BOOTMODE [12:10] | INPUT CLOCK FREQ (MHz) | 850 MHz DEVICE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLLD | PLLM | DSP ƒ | ||
| 0b000 | 50.00 | 0 | 33 | 850 |
| 0b001 | 66.67 | 1 | 50 | 850.04 |
| 0b010 | 80.00 | 3 | 84 | 850 |
| 0b011 | 100.00 | 0 | 16 | 850 |
| 0b100 | 156.25 | 49 | 543 | 850 |
| 0b101 | 250.00 | 4 | 33 | 850 |
| 0b110 | 312.50 | 49 | 271 | 850 |
| 0b111 | 122.88 | 5 | 82 | 849.92 |
OUTPUT_DIVIDE is the value of the field of SECCTL[22:19]. This will set the PLL to the maximum clock setting for the device (with OUTPUT_DIVIDE=2, by default).
The Main PLL is controlled using a PLL controller and a chip-level MMR. The DDR3 PLL is controlled by chip level MMRs. For details on how to set up the PLL see Section 8.5. For details on the operation of the PLL controller module, see the Phase Locked Loop (PLL) for KeyStone Devices User's Guide (SPRUGV2).
3.7 Second-Level Bootloaders
Any of the boot modes can be used to download a second-level bootloader. A second-level bootloader allows for any level of customization to current boot methods as well as the definition of a completely customized boot.
3.8 Terminals
3.8.1 Package Terminals
Figure 3-23 shows the C6654 CZH and GZH ball grid area (BGA) packages (bottom view).
 Figure 3-23 CZH/GZH 625-Pin BGA Package (Bottom View)
Figure 3-23 CZH/GZH 625-Pin BGA Package (Bottom View)
3.8.2 Pin Map
Figure 3-25 through Figure 3-28 show the C6654 pin assignments in four quadrants (A, B, C, and D).
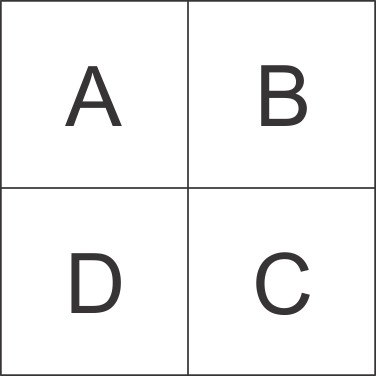 Figure 3-24 Pin Map Quadrants (Bottom View)
Figure 3-24 Pin Map Quadrants (Bottom View)
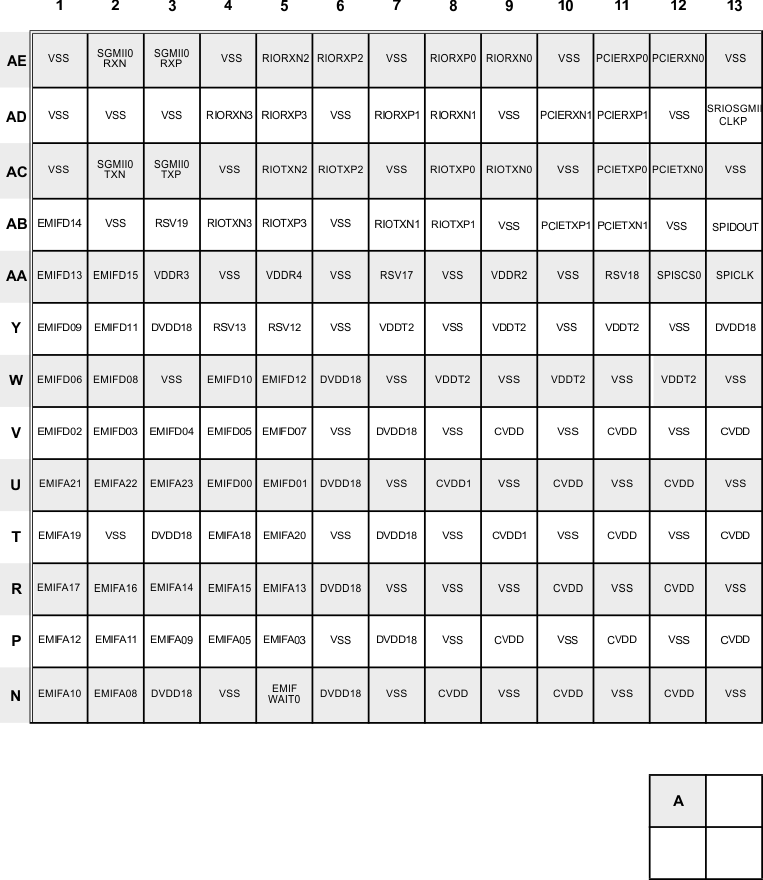 Figure 3-25 Upper Left Quadrant — A (Bottom View)
Figure 3-25 Upper Left Quadrant — A (Bottom View)
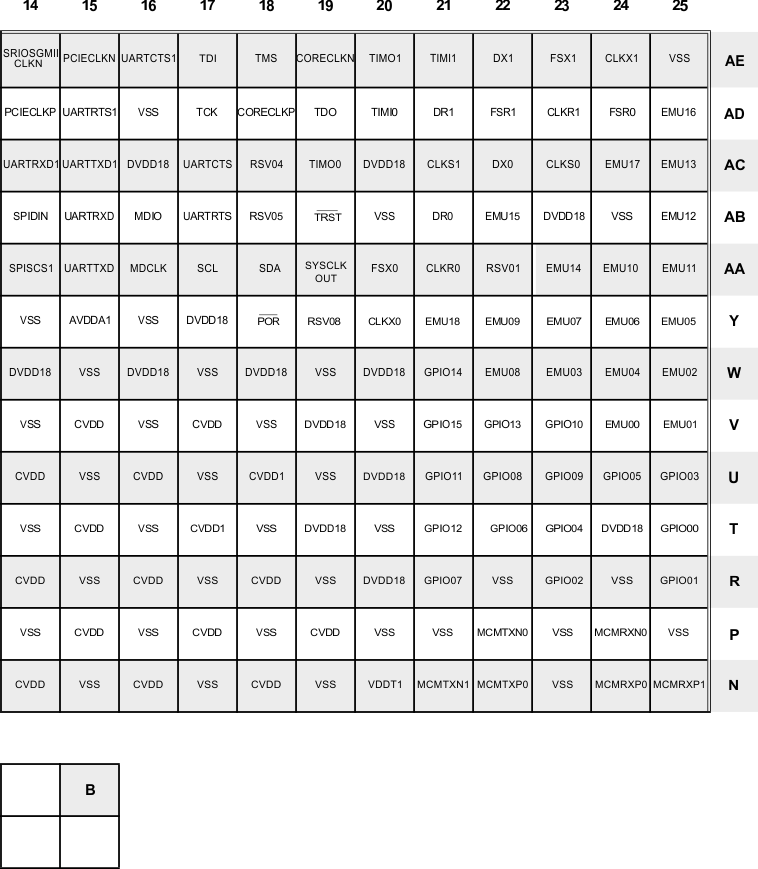 Figure 3-26 Upper Right Quadrant—B (Bottom View)
Figure 3-26 Upper Right Quadrant—B (Bottom View)
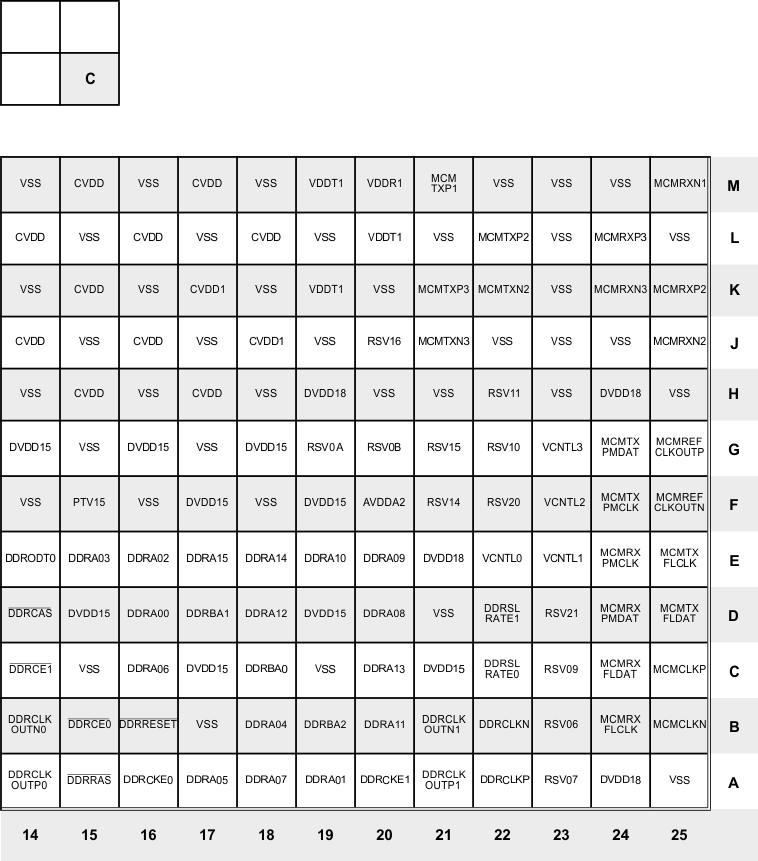 Figure 3-27 Lower Right Quadrant—C (Bottom View)
Figure 3-27 Lower Right Quadrant—C (Bottom View)
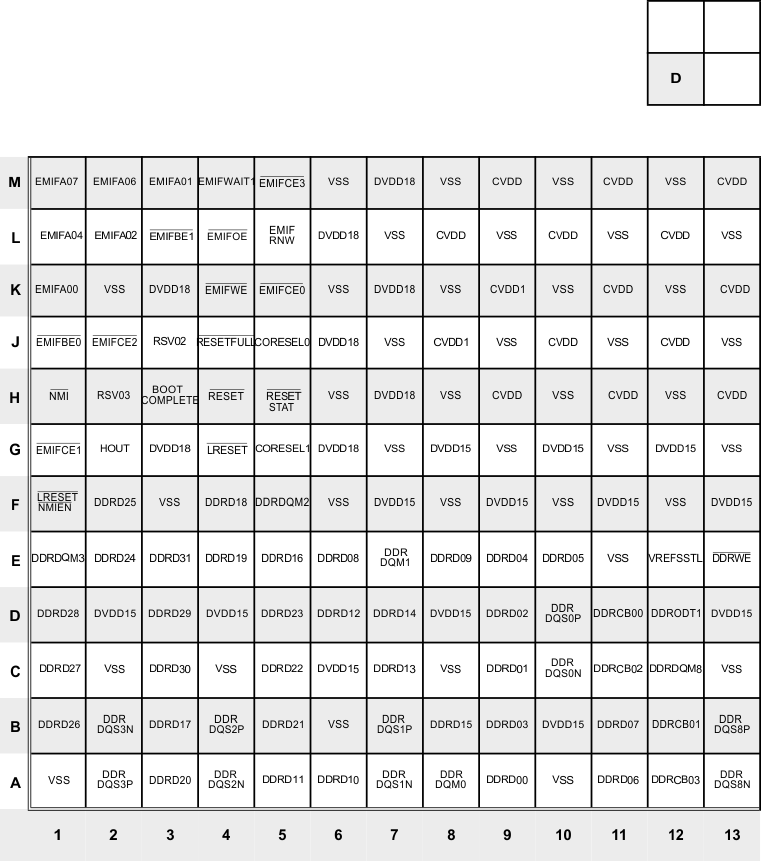 Figure 3-28 Lower Left Quadrant—D (Bottom View)
Figure 3-28 Lower Left Quadrant—D (Bottom View)
3.9 Terminal Functions
The terminal functions table (Table 3-39) identifies the external signal names, the associated pin (ball) numbers, the pin type (I, O/Z, or I/O/Z), whether the pin has any internal pullup/pulldown resistors, and gives functional pin descriptions. This table is arranged by function. The power terminal functions table (Table 3-40) lists the various power supply pins and ground pins and gives functional pin descriptions. Table 3-41 shows all pins arranged by signal name. Table 3-42 shows all pins arranged by ball number.
There are 73 pins that have a secondary function as well as a primary function. The secondary function is indicated with a dagger (†). There is one pin that has a tertiary function as well as primary and secondary functions. The tertiary function is indicated with a double dagger (‡).
For more detailed information on device configuration, peripheral selection, multiplexed/shared pins, and pullup/pulldown resistors, see Section 4.4.
Use the symbol definitions in Table 3-38 when reading Table 3-39.
Table 3-38 I/O Functional Symbol Definitions
| FUNCTIONAL SYMBOL | DEFINITION | Table 3-39
COLUMN HEADING |
|---|---|---|
| IPD or IPU | Internal 100-µA pulldown or pullup is provided for this terminal. In most systems, a 1-kΩ resistor can be used to oppose the IPD/IPU. For more detailed information on pulldown/pullup resistors and situations in which external pulldown/pullup resistors are required, see Hardware Design Guide for KeyStone Devices (SPRABI2). | IPD/IPU |
| A | Analog signal | Type |
| GND | Ground | Type |
| I | Input terminal | Type |
| O | Output terminal | Type |
| S | Supply voltage | Type |
| Z | Three-state terminal or high impedance | Type |
Table 3-39 Terminal Functions — Signals and Control by Function
| SIGNAL NAME | BALL NO. | TYPE | IPD/IPU | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boot Configuration Pins | ||||
| LENDIAN † | T25 | IOZ | UP | Endian configuration pin (Pin shared with GPIO[0]) |
| BOOTMODE00 † | R25 | IOZ | Down | See Section 3.5 for more details (Pins shared with GPIO[1:13]) |
| BOOTMODE01† | R23 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE02 † | U25 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE03 † | T23 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE04 † | U24 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE05 † | T22 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE06 † | R21 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE07 † | U22 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE08 † | U23 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE09 † | V23 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE10 † | U21 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE11 † | T21 | IOZ | Down | |
| BOOTMODE12 † | V22 | IOZ | Down | |
| PCIESSMODE0 † | W21 | IOZ | Down | PCIe Mode selection pins (Pins shared with GPIO[14:15]) |
| PCIESSMODE1 † | V21 | IOZ | Down | |
| PCIESSEN ‡ | AD20 | I | Down | PCIe module enable (Pin shared with TIMI0 and GPIO16) |
| Clock / Reset | ||||
| CORECLKP | AD18 | I | Core Clock Input to main PLL. | |
| CORECLKN | AE19 | I | ||
| SRIOSGMIICLKP | AD13 | I | SGMII Reference Clock to drive the SGMII SerDes | |
| SRIOSGMIICLKN | AE14 | I | ||
| DDRCLKP | A22 | I | DDR Reference Clock Input to DDR PLL | |
| DDRCLKN | B22 | I | ||
| PCIECLKP | AD14 | I | PCIe Clock Input to drive PCIe SerDes | |
| PCIECLKN | AE15 | I | ||
| MCMCLKP | C25 | I | Reserved | |
| MCMCLKN | B25 | I | ||
| AVDDA1 | Y15 | P | SYS_CLK PLL Power Supply Pin | |
| AVDDA2 | F20 | P | DDR_CLK PLL Power Supply Pin | |
| SYSCLKOUT | AA19 | OZ | Down | System Clock Output to be used as a general purpose output clock for debug purposes |
| HOUT | G2 | OZ | UP | Interrupt output pulse created by IPCGRH |
| NMI | H1 | I | UP | Non-maskable Interrupt |
| LRESET | G4 | I | UP | Warm Reset |
| LRESETNMIEN | F1 | I | UP | Enable for core selects |
| CORESEL0 | J5 | I | Down | Select for the target core for LRESET and NMI. For more details see Table 8-40 |
| CORESEL1 | G5 | I | Down | |
| RESETFULL | J4 | I | UP | Full Reset |
| RESET | H4 | I | UP | Warm Reset of non isolated portion on the IC |
| POR | Y18 | I | Power-on Reset | |
| RESETSTAT | H5 | O | UP | Reset Status Output |
| BOOTCOMPLETE | H3 | OZ | Down | Boot progress indication output |
| PTV15 | F15 | A | PTV Compensation NMOS Reference Input. A precision resistor placed between the PTV15 pin and ground is used to closely tune the output impedance of the DDR interface drivers to 50 Ohms. Presently, the recommended value for this 1% resistor is 45.3 Ohms. | |
| DDR | ||||
| DDRDQM0 | A8 | OZ | DDR EMIF Data Masks | |
| DDRDQM1 | E7 | OZ | ||
| DDRDQM2 | F5 | OZ | ||
| DDRDQM3 | E1 | OZ | ||
| DDRDQM8 | C12 | OZ | ||
| DDRDQS0P | D10 | IOZ | DDR EMIF Data Strobe | |
| DDRDQS0N | C10 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS1P | B7 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS1N | A7 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS2P | B4 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS2N | A4 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS3P | A2 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS3N | B2 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS8P | B13 | IOZ | ||
| DDRDQS8N | A13 | IOZ | ||
| DDRCB00 | D11 | IOZ | DDR EMIF Check Bits | |
| DDRCB01 | B12 | IOZ | ||
| DDRCB02 | C11 | IOZ | ||
| DDRCB03 | A12 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD00 | A9 | IOZ | DDR EMIF Data Bus | |
| DDRD01 | C9 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD02 | D9 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD03 | B9 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD04 | E9 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD05 | E10 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD06 | A11 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD07 | B11 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD08 | E6 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD09 | E8 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD10 | A6 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD11 | A5 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD12 | D6 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD13 | C7 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD14 | D7 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD15 | B8 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD16 | E5 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD17 | B3 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD18 | F4 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD19 | E4 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD20 | A3 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD21 | B5 | IOZ | DDR EMIF Data Bus | |
| DDRD22 | C5 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD23 | D5 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD24 | E2 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD25 | F2 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD26 | B1 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD27 | C1 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD28 | D1 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD29 | D3 | IOZ | ||
| DDRD30 | C3 | IOZ | DDR EMIF Data Bus | |
| DDRD31 | E3 | IOZ | ||
| DDRCE0 | B15 | OZ | DDR EMIF Chip Enables | |
| DDRCE1 | C14 | OZ | ||
| DDRBA0 | C18 | OZ | DDR EMIF Bank Address | |
| DDRBA1 | D17 | OZ | ||
| DDRBA2 | B19 | OZ | ||
| DDRA00 | D16 | OZ | DDR EMIF Address Bus | |
| DDRA01 | A19 | OZ | ||
| DDRA02 | E16 | OZ | ||
| DDRA03 | E15 | OZ | ||
| DDRA04 | B18 | OZ | ||
| DDRA05 | A17 | OZ | ||
| DDRA06 | C16 | OZ | ||
| DDRA07 | A18 | OZ | ||
| DDRA08 | D20 | OZ | ||
| DDRA09 | E20 | OZ | ||
| DDRA10 | E19 | OZ | ||
| DDRA11 | B20 | OZ | ||
| DDRA12 | D18 | OZ | ||
| DDRA13 | C20 | OZ | ||
| DDRA14 | E18 | OZ | ||
| DDRA15 | E17 | OZ | ||
| DDRCAS | D14 | OZ | DDR EMIF Column Address Strobe | |
| DDRRAS | A15 | OZ | DDR EMIF Row Address Strobe | |
| DDRWE | E13 | OZ | DDR EMIF Write Enable | |
| DDRCKE0 | A16 | OZ | DDR EMIF Clock Enable | |
| DDRCKE1 | A20 | OZ | DDR EMIF Clock Enable | |
| DDRCLKOUTP0 | A14 | OZ | DDR EMIF Output Clocks to drive SDRAMs (one clock pair per SDRAM) | |
| DDRCLKOUTN0 | B14 | OZ | ||
| DDRCLKOUTP1 | A21 | OZ | ||
| DDRCLKOUTN1 | B21 | OZ | ||
| DDRODT0 | E14 | OZ | DDR EMIF On Die Termination Outputs used to set termination on the SDRAMs | |
| DDRODT1 | D12 | OZ | DDR EMIF On Die Termination Outputs used to set termination on the SDRAMs | |
| DDRRESET | B16 | OZ | DDR Reset signal | |
| DDRSLRATE0 | C22 | I | Down | DDR Slew rate control |
| DDRSLRATE1 | D22 | I | Down | |
| VREFSSTL | E12 | P | Reference Voltage Input for SSTL15 buffers used by DDR EMIF (VDDS15 ÷ 2) | |
| EMIF16 | ||||
| EMIFRW | L5 | OZ | UP | EMIF16 Control Signals |
| EMIFCE0 | K5 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFCE1 | G1 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFCE2 | J2 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFCE3 | M5 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFOE | L4 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFWE | K4 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFBE0 | J1 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFBE1 | L3 | OZ | UP | |
| EMIFWAIT0 | N5 | I | Down | |
| EMIFWAIT1 | M4 | I | Down | EMIF16 Control Signal This EMIF16 pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see UPP). |
| EMIFA00 | K1 | OZ | Down | EMIF16 Address These EMIF16 pins have secondary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see uPP). |
| EMIFA01 | M3 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA02 | L2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA03 | P5 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA04 | L1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA05 | P4 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA06 | M2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA07 | M1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA08 | N2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA09 | P3 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA10 | N1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA11 | P2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA12 | P1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA13 | R5 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA14 | R3 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA15 | R4 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA16 | R2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA17 | R1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA18 | T4 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA19 | T1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA20 | T5 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA21 | U1 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA22 | U2 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFA23 | U3 | OZ | Down | |
| EMIFD00 | U4 | IOZ | Down | EMIF16 Data These EMIF16 pins have secondary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see uPP). |
| EMIFD01 | U5 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD02 | V1 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD03 | V2 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD04 | V3 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD05 | V4 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD06 | W1 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD07 | V5 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD08 | W2 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD09 | Y1 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD10 | W4 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD11 | Y2 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD12 | W5 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD13 | AA1 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD14 | AB1 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMIFD15 | AA2 | IOZ | Down | |
| uPP | ||||
| UPP_2XTXCLK † | M4 | I | Down | uPP Transmit Reference Clock (2x Transmit Rate) This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH0_CLK † | R2 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 0 Clock This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH0_START † | R1 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 0 Start This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH0_ENABLE † | T4 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 0 Enable This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH0_WAIT † | T1 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 0 Wait This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH1_CLK † | T5 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 1 Clock This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH1_START † | U1 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 1 Start This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH1_ENABLE † | U2 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 1 Enable This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPP_CH1_WAIT † | U3 | IOZ | Down | uPP Channel 1 Wait This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPPD00 † | U4 | IOZ | Down | uPP Data This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPPD01 † | U5 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD02 † | V1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD03 † | V2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD04 † | V3 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD05 † | V4 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD06 † | W1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD07 † | V5 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD08 † | W2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD09 † | Y1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD10 † | W4 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD11 † | Y2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD12 † | W5 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD13 † | AA1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD14 † | AB1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPD15 † | AA2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD00 † | K1 | IOZ | Down | uPP Extended Data This uPP pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see EMIF16). |
| UPPXD01 † | M3 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD02 † | L2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD03 † | P5 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD04 † | L1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD05 † | P4 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD06 † | M2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD07 † | M1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD08 † | N2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD09 † | P3 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD10 † | N1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD11 † | P2 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD12 † | P1 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD13 † | R5 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD14 † | R3 | IOZ | Down | |
| UPPXD15 † | R4 | IOZ | Down | |
| EMU | ||||
| EMU00 | V24 | IOZ | UP | Emulation and Trace Port |
| EMU01 | V25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU02 | W25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU03 | W23 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU04 | W24 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU05 | Y25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU06 | Y24 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU07 | Y23 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU08 | W22 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU09 | Y22 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU10 | AA24 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU11 | AA25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU12 | AB25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU13 | AC25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU14 | AA23 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU15 | AB22 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU16 | AD25 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU17 | AC24 | IOZ | UP | |
| EMU18 | Y21 | IOZ | UP | |
| General Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) | ||||
| GPIO00 | T25 | IOZ | UP | General Purpose Input/Output These GPIO pins have secondary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see Boot Configuration Pins). |
| GPIO01 | R25 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO02 | R23 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO03 | U25 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO04 | T23 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO05 | U24 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO06 | T22 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO07 | R21 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO08 | U22 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO09 | U23 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO10 | V23 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO11 | U21 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO12 | T21 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO13 | V22 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO14 | W21 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO15 | V21 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO16 † | AD20 | IOZ | Down | General Purpose Input/Output This GPIO pin has a primary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see Timer) and a tertiary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see Boot Configuration Pins). |
| GPIO17 † | AE21 | IOZ | Down | General Purpose Input/Output These GPIO pins have primary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see Timer). |
| GPIO18 † | AC19 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO19 † | AE20 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO20 † | AB15 | IOZ | Down | General Purpose Input/Output These GPIO pins have primary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see UART). |
| GPIO21 † | AA15 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO22 † | AC17 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO23 † | AB17 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO24 † | AC14 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO25 † | AC15 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO26 † | AE16 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO27 † | AD15 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO28 † | AA12 | IOZ | Up | General Purpose Input/Output These GPIO pins have primary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see SPI). |
| GPIO29 † | AA14 | IOZ | Up | |
| GPIO30 † | AB14 | IOZ | Down | |
| GPIO31 † | AB13 | IOZ | Down | |
| MCMRXN0 | P24 | I | Reserved — leave unconnected | |
| MCMRXP0 | N24 | I | ||
| MCMRXN1 | M25 | I | ||
| MCMRXP1 | N25 | I | ||
| MCMRXN2 | J25 | I | ||
| MCMRXP2 | K25 | I | ||
| MCMRXN3 | K24 | I | ||
| MCMRXP3 | L24 | I | ||
| MCMTXN0 | P22 | O | Reserved — leave unconnected | |
| MCMTXP0 | N22 | O | ||
| MCMTXN1 | N21 | O | ||
| MCMTXP1 | M21 | O | ||
| MCMTXN2 | K22 | O | ||
| MCMTXP2 | L22 | O | ||
| MCMTXN3 | J21 | O | ||
| MCMTXP3 | K21 | O | ||
| MCMRXFLCLK | B24 | O | Down | Reserved — leave unconnected |
| MCMRXFLDAT | C24 | O | Down | |
| MCMTXFLCLK | E25 | I | Down | |
| MCMTXFLDAT | D25 | I | Down | |
| MCMRXPMCLK | E24 | I | Down | |
| MCMRXPMDAT | D24 | I | Down | |
| MCMTXPMCLK | F24 | O | Down | |
| MCMTXPMDAT | G24 | O | Down | |
| MCMREFCLKOUTP | G25 | O | Reserved — leave unconnected | |
| MCMREFCLKOUTN | F25 | O | ||
| I2C | ||||
| SCL | AA17 | IOZ | I2C Clock | |
| SDA | AA18 | IOZ | I2C Data | |
| JTAG | ||||
| TCK | AD17 | I | Up | JTAG Clock Input |
| TDI | AE17 | I | Up | JTAG Data Input |
| TDO | AD19 | OZ | Up | JTAG Data Output |
| TMS | AE18 | I | Up | JTAG Test Mode Input |
| TRST | AB19 | I | Down | JTAG Reset |
| McBSP | ||||
| CLKR0 | AA21 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Receive Clock |
| CLKX0 | Y20 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Clock |
| CLKS0 | AC23 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Slow Clock |
| FSR0 | AD24 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Receive Frame Sync |
| FSX0 | AA20 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Frame Sync |
| DR0 | AB21 | I | Down | McBSP Receive Data |
| DX0 | AC22 | OZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Data |
| CLKR1 | AD23 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Receive Clock |
| CLKX1 | AE24 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Clock |
| CLKS1 | AC21 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Slow Clock |
| FSR1 | AD22 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Receive Frame Sync |
| FSX1 | AE23 | IOZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Frame Sync |
| DR1 | AD21 | I | Down | McBSP Receive Data |
| DX1 | AE22 | OZ | Down | McBSP Transmit Data |
| MDIO | ||||
| MDIO | AB16 | IOZ | Up | MDIO Data |
| MDCLK | AA16 | O | Down | MDIO Clock |
| PCIe | ||||
| PCIERXN0 | AE12 | I | PCIexpress Receive Data (2 links) | |
| PCIERXP0 | AE11 | I | ||
| PCIERXN1 | AD10 | I | ||
| PCIERXP1 | AD11 | I | ||
| PCIETXN0 | AC12 | O | PCIexpress Transmit Data (2 links) | |
| PCIETXP0 | AC11 | O | ||
| PCIETXN1 | AB11 | O | ||
| PCIETXP1 | AB10 | O | ||
| RIORXN0 | AE9 | I | Reserved — leave unconnected | |
| RIORXP0 | AE8 | I | ||
| RIORXN1 | AD8 | I | ||
| RIORXP1 | AD7 | I | ||
| RIORXN2 | AE5 | I | ||
| RIORXP2 | AE6 | I | ||
| RIORXN3 | AD4 | I | ||
| RIORXP3 | AD5 | I | ||
| RIOTXN0 | AC9 | O | Reserved — leave unconnected | |
| RIOTXP0 | AC8 | O | ||
| RIOTXN1 | AB7 | O | ||
| RIOTXP1 | AB8 | O | ||
| RIOTXN2 | AC5 | O | ||
| RIOTXP2 | AC6 | O | ||
| RIOTXN3 | AB4 | O | ||
| RIOTXP3 | AB5 | O | ||
| SGMII | ||||
| SGMII0RXN | AE2 | I | Ethernet MAC SGMII Receive Data | |
| SGMII0RXP | AE3 | I | ||
| SGMII0TXN | AC2 | O | Ethernet MAC SGMII Transmit Data | |
| SGMII0TXP | AC3 | O | ||
| SmartReflex | ||||
| VCNTL0 | E22 | OZ | Voltage Control Outputs to variable core power supply. These are open-drain output buffers. | |
| VCNTL1 | E23 | OZ | ||
| VCNTL2 | F23 | OZ | ||
| VCNTL3 | G23 | OZ | ||
| SPI | ||||
| SPISCS0 | AA12 | OZ | Up | SPI Interface Enable 0 This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| SPISCS1 | AA14 | OZ | Up | SPI Interface Enable 1 This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| SPICLK | AA13 | OZ | Down | SPI Clock |
| SPIDIN | AB14 | I | Down | SPI Data In This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| SPIDOUT | AB13 | OZ | Down | SPI Data Out This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| Timer | ||||
| TIMI0 | AD20 | I | Down | Timer Inputs This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| TIMI1 | AE21 | I | Down | |
| TIMO0 | AC19 | OZ | Down | Timer Outputs These Timer pins have secondary functions assigned to them as mentioned elsewhere in this table |
| TIMO1 | AE20 | OZ | Down | |
| UART | ||||
| UARTRXD | AB15 | I | Down | UART Serial Data In This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTTXD | AA15 | OZ | Down | UART Serial Data Out This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTCTS | AC17 | I | Down | UART Clear To Send This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTRTS | AB17 | OZ | Down | UART Request To Send This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTRXD1 | AC14 | I | Down | UART Serial Data In This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTTXD1 | AC15 | OZ | Down | UART Serial Data Out This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTCTS1 | AE16 | I | Down | UART Clear To Send This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| UARTRTS1 | AD15 | OZ | Down | UART Request To Send This SPI pin has a secondary function assigned to it as mentioned elsewhere in this table (see GPIO). |
| Reserved | ||||
| RSV01 | AA22 | IOZ | Up | Reserved - pullup to DVDD18 |
| RSV02 | J3 | OZ | Down | Reserved - leave unconnected |
| RSV03 | H2 | OZ | Down | Reserved - leave unconnected |
| RSV04 | AC18 | O | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV05 | AB18 | O | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV06 | B23 | O | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV07 | A23 | O | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV08 | Y19 | OZ | Down | Reserved - leave unconnected |
| RSV09 | C23 | OZ | Down | Reserved - leave unconnected |
| RSV10 | G22 | A | Reserved - connect to GND | |
| RSV11 | H22 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV12 | Y5 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV13 | Y4 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV14 | F21 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV15 | G21 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV16 | J20 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV17 | AA7 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV18 | AA11 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV19 | AB3 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV20 | F22 | IOZ | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV21 | D23 | IOZ | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV0A | G19 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
| RSV0B | G20 | A | Reserved - leave unconnected | |
Table 3-40 Terminal Functions — Power and Ground
| SUPPLY | BALL NO. | VOLTS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| AVDDA1 | Y15 | 1.8 | PLL Supply - CORE_PLL |
| AVDDA2 | F20 | 1.8 | PLL Supply - DDR3_PLL |
| CVDD | H9, H11, H13, H15, H17, J10, J12, J14, J16, K11, K13, K15, L8, L10, L12, L14, L16, L18, M9, M11, M13, M15, M17, N8, N10, N12, N14, N16, N18, P9, P11, P13, P15, P17, P19, R10, R12, R14, R16, R18, T11, T13, T15, U10, U12, U14, U16, V9, V11, V13, V15, V17 | 0.85 to 1.1 | SmartReflex core supply voltage |
| CVDD1 | J8, J18, K9, K17, T9, T17, U8, U18 | 1.0 | Fixed core supply voltage for memory array |
| DVDD15 | B10, C6, C17, C21, D2, D4, D8, D13, D15, D19, F7, F9, F11, F13, F17, F19, G8, G10, G12, G14, G16, G18 | 1.5 | DDR IO supply |
| DVDD18 | A24, E21, G3, G6, H7, H19, H24, J6, K3, K7, L6, M7, N3, N6, P7, R6, R20, T3, T7, T19, T24, U6, U20, V7, V19, W6, W14, W16, W18, W20, Y3, Y13, Y17, AB23, AC16, AC20 | 1.8 | IO supply |
| VDDR1 | M20 | 1.5 | Reserved — connect to DVDD15 |
| VDDR2 | AA9 | 1.5 | PCIe SerDes regulator supply |
| VDDR3 | AA3 | 1.5 | SGMII SerDes regulator supply |
| VDDR4 | AA5 | 1.5 | Reserved — connect to DVDD15 |
| VDDT1 | K19, L20, M19, N20 | 1.0 | Reserved — connect to CVDD1 |
| VDDT2 | W8, W10, W12, Y7, Y9, Y11 | 1.0 | SGMII/PCIe SerDes termination supply |
| VREFSSTL | E12 | 0.75 | DDR3 reference voltage |
| VSS | A1, A10, A25, B6, B17, C2, C4, C8, C13, C15, C19, D21, E11, F3, F6, F8, F10, F12, F14, F16, F18, G7, G9, G11, G13, G15, G17, H6, H8, H10, H12, H14, H16, H18, H20, H21, H23, H25, J7, J9, J11, J13, J15, J17, J19, J22, J23, J24, K2, K6, K8, K10, K12, K14, K16, K18, K20, K23, L7, L9, L11, L13, L15, L17, L19, L21, L23, L25, M6, M8, M10, M12, M14, M16, M18, M22, M23, M24, N4, N7, N9, N11, N13, N15, N17, N19, N23, P6, P8, P10, P12, P14, P16, P18, P20, P21, P23, P25, R7, R8, R9, R11, R13, R15, R17, R19, R22, R24, T2, T6, T8, T10, T12, T14, T16, T18, T20, U7, U9, U11, U13, U15, U17, U19, V6, V8, V10, V12, V14, V16, V18, V20, W3, W7, W9, W11, W13, W15, W17, W19, Y6, Y8, Y10, Y12, Y14, Y16, AA4, AA6, AA8, AA10, AB2, AB6, AB9, AB12, AB20, AB24, AC1, AC4, AC7, AC10, AC13, AD1, AD2, AD3, AD6, AD9, AD12, AD16, AE1, AE4, AE7, AE10, AE13, AE25 | GND | Ground |
Table 3-41 Terminal Functions — By Signal Name
| SIGNAL NAME | BALL NUMBER | SIGNAL NAME | BALL NUMBER | SIGNAL NAME | BALL NUMBER | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVDDA1 | Y15 | DDRA09 | E20 | DDRD22 | C5 | ||
| AVDDA2 | F20 | DDRA10 | E19 | DDRD23 | D5 | ||
| BOOTCOMPLETE | H3 | DDRA11 | B20 | DDRD24 | E2 | ||
| BOOTMODE00 † | R25 | DDRA12 | D18 | DDRD25 | F2 | ||
| BOOTMODE01 † | R23 | DDRA13 | C20 | DDRD26 | B1 | ||
| BOOTMODE02 † | U25 | DDRA14 | E18 | DDRD27 | C1 | ||
| BOOTMODE03 † | T23 | DDRA15 | E17 | DDRD28 | D1 | ||
| BOOTMODE04 † | U24 | DDRBA0 | C18 | DDRD29 | D3 | ||
| BOOTMODE05 † | T22 | DDRBA1 | D17 | DDRD30 | C3 | ||
| BOOTMODE06 † | R21 | DDRBA2 | B19 | DDRD31 | E3 | ||
| BOOTMODE07 † | U22 | DDRCAS | D14 | DDRDQM0 | A8 | ||
| BOOTMODE08 † | U23 | DDRCB00 | D11 | DDRDQM1 | E7 | ||
| BOOTMODE09 † | V23 | DDRCB01 | B12 | DDRDQM2 | F5 | ||
| BOOTMODE10 † | U21 | DDRCB02 | C11 | DDRDQM3 | E1 | ||
| BOOTMODE11 † | T21 | DDRCB03 | A12 | DDRDQM8 | C12 | ||
| BOOTMODE12 † | V22 | DDRCE0 | B15 | DDRDQS0N | C10 | ||
| CLKR0 | AA21 | DDRCE1 | C14 | DDRDQS0P | D10 | ||
| CLKR1 | AD23 | DDRCKE0 | A16 | DDRDQS1N | A7 | ||
| CLKS0 | AC23 | DDRCKE1 | A20 | DDRDQS1P | B7 | ||
| CLKS1 | AC21 | DDRCLKN | B22 | DDRDQS2N | A4 | ||
| CLKX0 | Y20 | DDRCLKOUTN0 | B14 | DDRDQS2P | B4 | ||
| CLKX1 | AE24 | DDRCLKOUTN1 | B21 | DDRDQS3N | B2 | ||
| CORECLKN | AE19 | DDRCLKOUTP0 | A14 | DDRDQS3P | A2 | ||
| CORECLKP | AD18 | DDRCLKOUTP1 | A21 | DDRDQS8N | A13 | ||
| CORESEL0 | J5 | DDRCLKP | A22 | DDRDQS8P | B13 | ||
| CORESEL1 | G5 | DDRD00 | A9 | DDRODT0 | E14 | ||
| CVDD | H9, H11, H13, H15, H17, J10, J12, J14, J16, K11, K13, K15, L8, L10, L12, L14, L16, L18, M9, M11, M13, M15, M17, N8, N10, N12, N14, N16, N18, P9, P11, P13, P15, P17, P19, R10, R12, R14, R16, R18, T11, T13, T15, U10, U12, U14, U16, V9, V11, V13, V15, V17 | DDRD01 | C9 | DDRODT1 | D12 | ||
| DDRD02 | D9 | DDRRAS | A15 | ||||
| DDRD03 | B9 | DDRRESET | B16 | ||||
| DDRD04 | E9 | DDRSLRATE0 | C22 | ||||
| DDRD05 | E10 | DDRSLRATE1 | D22 | ||||
| DDRD06 | A11 | DDRWE | E13 | ||||
| DDRD07 | B11 | DR0 | AB21 | ||||
| DDRD08 | E6 | DR1 | AD21 | ||||
| DDRD09 | E8 | DVDD15 | B10, C6, C17, C21, D2, D4, D8, D13, D15, D19, F7, F9, F11, F13, F17, F19, G8, G10, G12, G14, G16, G18 | ||||
| DDRD10 | A6 | ||||||
| CVDD1 | J8, J18, K9, K17, T9, T17, U8, U18 | DDRD11 | A5 | ||||
| DDRD12 | D6 | ||||||
| DDRA00 | D16 | DDRD13 | C7 | ||||
| DDRA01 | A19 | DDRD14 | D7 | DVDD18 | A24, E21, G3, G6, H7, H19, H24, J6, K3, K7, L6, M7, N3, N6, P7, R6, R20, T3, T7, T19, T24, U6, U20, V7, V19, W6, W14, W16, W18, W20, Y3, Y13, Y17, AB23, AC16, AC20 | ||
| DDRA02 | E16 | DDRD15 | B8 | ||||
| DDRA03 | E15 | DDRD16 | E5 | ||||
| DDRA04 | B18 | DDRD17 | B3 | ||||
| DDRA05 | A17 | DDRD18 | F4 | ||||
| DDRA06 | C16 | DDRD19 | E4 | ||||
| DDRA07 | A18 | DDRD20 | A3 | ||||
| DDRA08 | D20 | DDRD21 | B5 | ||||
| DX0 | AC22 | EMIFD15 | AA2 | GPIO18 † | AC19 | ||
| DX1 | AE22 | EMIFOE | L4 | GPIO19 † | AE20 | ||
| EMIFA00 | K1 | EMIFRNW | L5 | GPIO20 † | AB15 | ||
| EMIFA01 | M3 | EMIFWAIT0 | N5 | GPIO21 † | AA15 | ||
| EMIFA02 | L2 | EMIFWAIT1 | M4 | GPIO22 † | AC17 | ||
| EMIFA03 | P5 | EMIFWE | K4 | GPIO23 † | AB17 | ||
| EMIFA04 | L1 | EMU00 | V24 | GPIO24 † | AC14 | ||
| EMIFA05 | P4 | EMU01 | V25 | GPIO25 † | AC15 | ||
| EMIFA06 | M2 | EMU02 | W25 | GPIO26 † | AE16 | ||
| EMIFA07 | M1 | EMU03 | W23 | GPIO27 † | AD15 | ||
| EMIFA08 | N2 | EMU04 | W24 | GPIO28 † | AA12 | ||
| EMIFA09 | P3 | EMU05 | Y25 | GPIO29 † | AA14 | ||
| EMIFA10 | N1 | EMU06 | Y24 | GPIO30 † | AB14 | ||
| EMIFA11 | P2 | EMU07 | Y23 | GPIO31 † | AB13 | ||
| EMIFA12 | P1 | EMU08 | W22 | HOUT | G2 | ||
| EMIFA13 | R5 | EMU09 | Y22 | LENDIAN † | T25 | ||
| EMIFA14 | R3 | EMU10 | AA24 | LRESETNMIEN | F1 | ||
| EMIFA15 | R4 | EMU11 | AA25 | LRESET | G4 | ||
| EMIFA16 | R2 | EMU12 | AB25 | MCMCLKN | B25 | ||
| EMIFA17 | R1 | EMU13 | AC25 | MCMCLKP | C25 | ||
| EMIFA18 | T4 | EMU14 | AA23 | MCMREFCLKOUTN | F25 | ||
| EMIFA19 | T1 | EMU15 | AB22 | MCMREFCLKOUTP | G25 | ||
| EMIFA20 | T5 | EMU16 | AD25 | MCMRXFLCLK | B24 | ||
| EMIFA21 | U1 | EMU17 | AC24 | MCMRXFLDAT | C24 | ||
| EMIFA22 | U2 | EMU18 | Y21 | MCMRXN0 | P24 | ||
| EMIFA23 | U3 | FSR0 | AD24 | MCMRXN1 | M25 | ||
| EMIFBE0 | J1 | FSR1 | AD22 | MCMRXN2 | J25 | ||
| EMIFBE1 | L3 | FSX0 | AA20 | MCMRXN3 | K24 | ||
| EMIFCE0 | K5 | FSX1 | AE23 | MCMRXP0 | N24 | ||
| EMIFCE1 | G1 | GPIO00 | T25 | MCMRXP1 | N25 | ||
| EMIFCE2 | J2 | GPIO01 | R25 | MCMRXP2 | K25 | ||
| EMIFCE3 | M5 | GPIO02 | R23 | MCMRXP3 | L24 | ||
| EMIFD00 | U4 | GPIO03 | U25 | MCMRXPMCLK | E24 | ||
| EMIFD01 | U5 | GPIO04 | T23 | MCMRXPMDAT | D24 | ||
| EMIFD02 | V1 | GPIO05 | U24 | MCMTXFLCLK | E25 | ||
| EMIFD03 | V2 | GPIO06 | T22 | MCMTXFLDAT | D25 | ||
| EMIFD04 | V3 | GPIO07 | R21 | MCMTXN0 | P22 | ||
| EMIFD05 | V4 | GPIO08 | U22 | MCMTXN1 | N21 | ||
| EMIFD06 | W1 | GPIO09 | U23 | MCMTXN2 | K22 | ||
| EMIFD07 | V5 | GPIO10 | V23 | MCMTXN3 | J21 | ||
| EMIFD08 | W2 | GPIO11 | U21 | MCMTXP0 | N22 | ||
| EMIFD09 | Y1 | GPIO12 | T21 | MCMTXP1 | M21 | ||
| EMIFD10 | W4 | GPIO13 | V22 | MCMTXP2 | L22 | ||
| EMIFD11 | Y2 | GPIO14 | W21 | MCMTXP3 | K21 | ||
| EMIFD12 | W5 | GPIO15 | V21 | MCMTXPMCLK | F24 | ||
| EMIFD13 | AA1 | GPIO16 † | AD20 | MCMTXPMDAT | G24 | ||
| EMIFD14 | AB1 | GPIO17 † | AE21 | MDCLK | AA16 | ||
| MDIO | AB16 | RSV12 | Y5 | UPP_CH0_WAIT † | T1 | ||
| NMI | H1 | RSV13 | Y4 | UPP_CH1_CLK † | T5 | ||
| PCIECLKN | AE15 | RSV14 | F21 | UPP_CH1_ENABLE † | U2 | ||
| PCIECLKP | AD14 | RSV15 | G21 | UPP_CH1_START † | U1 | ||
| PCIERXN0 | AE12 | RSV16 | J20 | UPP_CH1_WAIT † | U3 | ||
| PCIERXN1 | AD10 | RSV17 | AA7 | UPPD00 † | U4 | ||
| PCIERXP0 | AE11 | RSV18 | AA11 | UPPD01 † | U5 | ||
| PCIERXP1 | AD11 | RSV19 | AB3 | UPPD02 † | V1 | ||
| PCIESSEN ‡ | AD20 | RSV20 | F22 | UPPD03 † | V2 | ||
| PCIETXN0 | AC12 | RSV21 | D23 | UPPD04 † | V3 | ||
| PCIETXN1 | AB11 | SCL | AA17 | UPPD05 † | V4 | ||
| PCIETXP0 | AC11 | SDA | AA18 | UPPD06 † | W1 | ||
| PCIETXP1 | AB10 | SGMII0RXN | AE2 | UPPD07 † | V5 | ||
| POR | Y18 | SGMII0RXP | AE3 | UPPD08 † | W2 | ||
| PTV15 | F15 | SGMII0TXN | AC2 | UPPD09 † | Y1 | ||
| RESETFULL | J4 | SGMII0TXP | AC3 | UPPD10 † | W4 | ||
| RESETSTAT | H5 | SPICLK | AA13 | UPPD11 † | Y2 | ||
| RESET | H4 | SPIDIN | AB14 | UPPD12 † | W5 | ||
| RIORXN0 | AE9 | SPIDOUT | AB13 | UPPD13 † | AA1 | ||
| RIORXN1 | AD8 | SPISCS0 | AA12 | UPPD14 † | AB1 | ||
| RIORXN2 | AE5 | SPISCS1 | AA14 | UPPD15 † | AA2 | ||
| RIORXN3 | AD4 | SRIOSGMIICLKN | AE14 | UPPXD00 † | K1 | ||
| RIORXP0 | AE8 | SRIOSGMIICLKP | AD13 | UPPXD01 † | M3 | ||
| RIORXP1 | AD7 | SYSCLKOUT | AA19 | UPPXD02 † | L2 | ||
| RIORXP2 | AE6 | TCK | AD17 | UPPXD03 † | P5 | ||
| RIORXP3 | AD5 | TDI | AE17 | UPPXD04 † | L1 | ||
| RIOTXN0 | AC9 | TDO | AD19 | UPPXD05 † | P4 | ||
| RIOTXN1 | AB7 | TIMI0 | AD20 | UPPXD06 † | M2 | ||
| RIOTXN2 | AC5 | TIMI1 | AE21 | UPPXD07 † | M1 | ||
| RIOTXN3 | AB4 | TIMO0 | AC19 | UPPXD08 † | N2 | ||
| RIOTXP0 | AC8 | TIMO1 | AE20 | UPPXD09 † | P3 | ||
| RIOTXP1 | AB8 | TMS | AE18 | UPPXD10 † | N1 | ||
| RIOTXP2 | AC6 | TRST | AB19 | UPPXD11 † | P2 | ||
| RIOTXP3 | AB5 | UARTCTS | AC17 | UPPXD12 † | P1 | ||
| RSV01 | AA22 | UARTCTS1 | AE16 | UPPXD13 † | R5 | ||
| RSV02 | J3 | UARTRTS | AB17 | UPPXD14 † | R3 | ||
| RSV03 | H2 | UARTRTS1 | AD15 | UPPXD15 † | R4 | ||
| RSV04 | AC18 | UARTRXD | AB15 | VCNTL0 | E22 | ||
| RSV05 | AB18 | UARTRXD1 | AC14 | VCNTL1 | E23 | ||
| RSV06 | B23 | UARTTXD | AA15 | VCNTL2 | F23 | ||
| RSV07 | A23 | UARTTXD1 | AC15 | VCNTL3 | G23 | ||
| RSV08 | Y19 | UPP_2XTXCLK † | M4 | VDDR1 | M20 | ||
| RSV09 | C23 | UPP_CH0_CLK † | R2 | VDDR2 | AA9 | ||
| RSV0A | G19 | UPP_CH0_ ENABLE † |
T4 | VDDR3 | AA3 | ||
| RSV0B | G20 | VDDR4 | AA5 | ||||
| RSV10 | G22 | UPP_CH0_ START † |
R1 | VDDT1 | K19, L20, M19, N20 | ||
| RSV11 | H22 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | W8, W10, W12, Y7, Y9, Y11 | ||||||
| VDDT1 | N20 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | W10 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | W12 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | Y7 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | Y9 | ||||||
| VDDT2 | Y11 | ||||||
| VREFSSTL | E12 | ||||||
| VSS | A1, A10, A25, B6, B17, C2, C4, C8, C13, C15, C19, D21, E11, F3, F6, F8, F10, F12, F14, F16, F18, G7, G9, G11, G13, G15, G17, H6, H8, H10, H12, H14, H16, H18, H20, H21, H23, H25, J7, J9, J11, J13, J15, J17, J19, J22, J23, J24, K2, K6, K8, K10, K12, K14, K16, K18, K20, K23, L7, L9, L11, L13, L15, L17, L19, L21, L23, L25, M6, M8, M10, M12, M14, M16, M18, M22, M23, M24, N4, N7, N9, N11, N13, N15, N17, N19, N23, P6, P8, P10, P12, P14, P16, P18, P20, P21, P23, P25, R7, R8, R9, R11, R13, R15, R17, R19, R22, R24, T2, T6, T8, T10, T12, T14, T16, T18, T20, U7, U9, U11, U13, U15, U17, U19, V6, V8, V10, V12, V14, V16, V18, V20, W3, W7, W9, W11, W13, W15, W17, W19, Y6, Y8, Y10, Y12, Y14, Y16, AA4, AA6, AA8, AA10, AB2, AB6, AB9, AB12, AB20, AB24, AC1, AC4, AC7, AC10, AC13, AD1, AD2, AD3, AD6, AD9, AD12, AD16, AE1, AE4, AE7, AE10, AE13, AE25 |
Table 3-42 Terminal Functions — By Ball Number
| BALL NUMBER | SIGNAL NAME | BALL NUMBER | SIGNAL NAME | BALL NUMBER | SIGNAL NAME | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | VSS | B23 | RSV06 | D20 | DDRA08 | ||
| A2 | DDRDQS3P | B24 | MCMRXFLCLK | D21 | VSS | ||
| A3 | DDRD20 | B25 | MCMCLKN | D22 | DDRSLRATE1 | ||
| A4 | DDRDQS2N | C1 | DDRD27 | D23 | RSV21 | ||
| A5 | DDRD11 | C2 | VSS | D24 | MCMRXPMDAT | ||
| A6 | DDRD10 | C3 | DDRD30 | D25 | MCMTXFLDAT | ||
| A7 | DDRDQS1N | C4 | VSS | E1 | DDRDQM3 | ||
| A8 | DDRDQM0 | C5 | DDRD22 | E2 | DDRD24 | ||
| A9 | DDRD00 | C6 | DVDD15 | E3 | DDRD31 | ||
| A10 | VSS | C7 | DDRD13 | E4 | DDRD19 | ||
| A11 | DDRD06 | C8 | VSS | E5 | DDRD16 | ||
| A12 | DDRCB03 | C9 | DDRD01 | E6 | DDRD08 | ||
| A13 | DDRDQS8N | C10 | DDRDQS0N | E7 | DDRDQM1 | ||
| A14 | DDRCLKOUTP0 | C11 | DDRCB02 | E8 | DDRD09 | ||
| A15 | DDRRAS | C12 | DDRDQM8 | E9 | DDRD04 | ||
| A16 | DDRCKE0 | C13 | VSS | E10 | DDRD05 | ||
| A17 | DDRA05 | C14 | DDRCE1 | E11 | VSS | ||
| A18 | DDRA07 | C15 | VSS | E12 | VREFSSTL | ||
| A19 | DDRA01 | C16 | DDRA06 | E13 | DDRWE | ||
| A20 | DDRCKE1 | C17 | DVDD15 | E14 | DDRODT0 | ||
| A21 | DDRCLKOUTP1 | C18 | DDRBA0 | E15 | DDRA03 | ||
| A22 | DDRCLKP | C19 | VSS | E16 | DDRA02 | ||
| A23 | RSV07 | C20 | DDRA13 | E17 | DDRA15 | ||
| A24 | DVDD18 | C21 | DVDD15 | E18 | DDRA14 | ||
| A25 | VSS | C22 | DDRSLRATE0 | E19 | DDRA10 | ||
| B1 | DDRD26 | C23 | RSV09 | E20 | DDRA09 | ||
| B2 | DDRDQS3N | C24 | MCMRXFLDAT | E21 | DVDD18 | ||
| B3 | DDRD17 | C25 | MCMCLKP | E22 | VCNTL0 | ||
| B4 | DDRDQS2P | D1 | DDRD28 | E23 | VCNTL1 | ||
| B5 | DDRD21 | D2 | DVDD15 | E24 | MCMRXPMCLK | ||
| B6 | VSS | D3 | DDRD29 | E25 | MCMTXFLCLK | ||
| B7 | DDRDQS1P | D4 | DVDD15 | F1 | LRESETNMIEN | ||
| B8 | DDRD15 | D5 | DDRD23 | F2 | DDRD25 | ||
| B9 | DDRD03 | D6 | DDRD12 | F3 | VSS | ||
| B10 | DVDD15 | D7 | DDRD14 | F4 | DDRD18 | ||
| B11 | DDRD07 | D8 | DVDD15 | F5 | DDRDQM2 | ||
| B12 | DDRCB01 | D9 | DDRD02 | F6 | VSS | ||
| B13 | DDRDQS8P | D10 | DDRDQS0P | F7 | DVDD15 | ||
| B14 | DDRCLKOUTN0 | D11 | DDRCB00 | F8 | VSS | ||
| B15 | DDRCE0 | D12 | DDRODT1 | F9 | DVDD15 | ||
| B16 | DDRRESET | D13 | DVDD15 | F10 | VSS | ||
| B17 | VSS | D14 | DDRCAS | F11 | DVDD15 | ||
| B18 | DDRA04 | D15 | DVDD15 | F12 | VSS | ||
| B19 | DDRBA2 | D16 | DDRA00 | F13 | DVDD15 | ||
| B20 | DDRA11 | D17 | DDRBA1 | F14 | VSS | ||
| B21 | DDRCLKOUTN1 | D18 | DDRA12 | F15 | PTV15 | ||
| B22 | DDRCLKN | D19 | DVDD15 | F16 | VSS | ||
| F17 | DVDD15 | H14 | VSS | K10 | VSS | ||
| F18 | VSS | H15 | CVDD | K11 | CVDD | ||
| F19 | DVDD15 | H16 | VSS | K12 | VSS | ||
| F20 | AVDDA2 | H17 | CVDD | K13 | CVDD | ||
| F21 | RSV14 | H18 | VSS | K14 | VSS | ||
| F22 | RSV20 | H19 | DVDD18 | K15 | CVDD | ||
| F23 | VCNTL2 | H20 | VSS | K16 | VSS | ||
| F24 | MCMTXPMCLK | H21 | VSS | K17 | CVDD1 | ||
| F25 | MCMREFCLKOUTN | H22 | RSV11 | K18 | VSS | ||
| G1 | EMIFCE1 | H23 | VSS | K19 | VDDT1 | ||
| G2 | HOUT | H24 | DVDD18 | K20 | VSS | ||
| G3 | DVDD18 | H25 | VSS | K21 | MCMTXP3 | ||
| G4 | LRESET | J1 | EMIFBE0 | K22 | MCMTXN2 | ||
| G5 | CORESEL1 | J2 | EMIFCE2 | K23 | VSS | ||
| G6 | DVDD18 | J3 | RSV02 | K24 | MCMRXN3 | ||
| G7 | VSS | J4 | RESETFULL | K25 | MCMRXP2 | ||
| G8 | DVDD15 | J5 | CORESEL0 | L1 | EMIFA04 | ||
| G9 | VSS | J6 | DVDD18 | L1 | UPPXD04 † | ||
| G10 | DVDD15 | J7 | VSS | L2 | EMIFA02 | ||
| G11 | VSS | J8 | CVDD1 | L2 | UPPXD02 † | ||
| G12 | DVDD15 | J9 | VSS | L3 | EMIFBE1 | ||
| G13 | VSS | J10 | CVDD | L4 | EMIFOE | ||
| G14 | DVDD15 | J11 | VSS | L5 | EMIFRNW | ||
| G15 | VSS | J12 | CVDD | L6 | DVDD18 | ||
| G16 | DVDD15 | J13 | VSS | L7 | VSS | ||
| G17 | VSS | J14 | CVDD | L8 | CVDD | ||
| G18 | DVDD15 | J15 | VSS | L9 | VSS | ||
| G19 | RSV0A | J16 | CVDD | L10 | CVDD | ||
| G20 | RSV0B | J17 | VSS | L11 | VSS | ||
| G21 | RSV15 | J18 | CVDD1 | L12 | CVDD | ||
| G22 | RSV10 | J19 | VSS | L13 | VSS | ||
| G23 | VCNTL3 | J20 | RSV16 | L14 | CVDD | ||
| G24 | MCMTXPMDAT | J21 | MCMTXN3 | L15 | VSS | ||
| G25 | MCMREFCLKOUTP | J22 | VSS | L16 | CVDD | ||
| H1 | NMI | J23 | VSS | L17 | VSS | ||
| H2 | RSV03 | J24 | VSS | L18 | CVDD | ||
| H3 | BOOTCOMPLETE | J25 | MCMRXN2 | L19 | VSS | ||
| H4 | RESET | K1 | EMIFA00 | L20 | VDDT1 | ||
| H5 | RESETSTAT | K1 | UPPXD00 † | L21 | VSS | ||
| H6 | VSS | K2 | VSS | L22 | MCMTXP2 | ||
| H7 | DVDD18 | K3 | DVDD18 | L23 | VSS | ||
| H8 | VSS | K4 | EMIFWE | L24 | MCMRXP3 | ||
| H9 | CVDD | K5 | EMIFCE0 | L25 | VSS | ||
| H10 | VSS | K6 | VSS | M1 | EMIFA07 | ||
| H11 | CVDD | K7 | DVDD18 | M1 | UPPXD07 † | ||
| H12 | VSS | K8 | VSS | M2 | EMIFA06 | ||
| H13 | CVDD | K9 | CVDD1 | M2 | UPPXD06 † | ||
| M3 | EMIFA01 | N21 | MCMTXN1 | R8 | VSS | ||
| M3 | UPPXD01 † | N22 | MCMTXP0 | R9 | VSS | ||
| M4 | EMIFWAIT1 | N23 | VSS | R10 | CVDD | ||
| M4 | UPP2XTXCLK † | N24 | MCMRXP0 | R11 | VSS | ||
| M5 | EMIFCE3 | N25 | MCMRXP1 | R12 | CVDD | ||
| M6 | VSS | P1 | EMIFA12 | R13 | VSS | ||
| M7 | DVDD18 | P1 | UPPXD12 † | R14 | CVDD | ||
| M8 | VSS | P2 | EMIFA11 | R15 | VSS | ||
| M9 | CVDD | P2 | UPPXD11 † | R16 | CVDD | ||
| M10 | VSS | P3 | EMIFA09 | R17 | VSS | ||
| M11 | CVDD | P3 | UPPXD09 † | R18 | CVDD | ||
| M12 | VSS | P4 | EMIFA05 | R19 | VSS | ||
| M13 | CVDD | P4 | UPPXD05 † | R20 | DVDD18 | ||
| M14 | VSS | P5 | EMIFA03 | R21 | GPIO07 | ||
| M15 | CVDD | P5 | UPPXD03 † | R21 | BOOTMODE06 † | ||
| M16 | VSS | P6 | VSS | R22 | VSS | ||
| M17 | CVDD | P7 | DVDD18 | R23 | GPIO02 | ||
| M18 | VSS | P8 | VSS | R23 | BOOTMODE01 † | ||
| M19 | VDDT1 | P9 | CVDD | R24 | VSS | ||
| M20 | VDDR1 | P10 | VSS | R25 | GPIO01 | ||
| M21 | MCMTXP1 | P11 | CVDD | R25 | BOOTMODE00 † | ||
| M22 | VSS | P12 | VSS | T1 | EMIFA19 | ||
| M23 | VSS | P13 | CVDD | T1 | UPP_CH0_WAIT † | ||
| M24 | VSS | P14 | VSS | T2 | VSS | ||
| M25 | MCMRXN1 | P15 | CVDD | T3 | DVDD18 | ||
| N1 | EMIFA10 | P16 | VSS | T4 | EMIFA18 | ||
| N1 | UPPXD10 † | P17 | CVDD | T4 | UPP_CH0_ENABLE † | ||
| N2 | EMIFA08 | P18 | VSS | T5 | EMIFA20 | ||
| N2 | UPPXD08 † | P19 | CVDD | T5 | UPP_CH1_CLK † | ||
| N3 | DVDD18 | P20 | VSS | T6 | VSS | ||
| N4 | VSS | P21 | VSS | T7 | DVDD18 | ||
| N5 | EMIFWAIT0 | P22 | MCMTXN0 | T8 | VSS | ||
| N6 | DVDD18 | P23 | VSS | T9 | CVDD1 | ||
| N7 | VSS | P24 | MCMRXN0 | T10 | VSS | ||
| N8 | CVDD | P25 | VSS | T11 | CVDD | ||
| N9 | VSS | R1 | EMIFA17 | T12 | VSS | ||
| N10 | CVDD | R1 | UPP_CH0_START † | T13 | CVDD | ||
| N11 | VSS | R2 | EMIFA16 | T14 | VSS | ||
| N12 | CVDD | R2 | UPP_CH0_CLK † | T15 | CVDD | ||
| N13 | VSS | R3 | EMIFA14 | T16 | VSS | ||
| N14 | CVDD | R3 | UPPXD14 † | T17 | CVDD1 | ||
| N15 | VSS | R4 | EMIFA15 | T18 | VSS | ||
| N16 | CVDD | R4 | UPPXD15 † | T19 | DVDD18 | ||
| N17 | VSS | R5 | EMIFA13 | T20 | VSS | ||
| N18 | CVDD | R5 | UPPXD13 † | T21 | GPIO12 | ||
| N19 | VSS | R6 | DVDD18 | T21 | BOOTMODE11 † | ||
| N20 | VDDT1 | R7 | VSS | T22 | GPIO06 | ||
| T22 | BOOTMODE05 † | V3 | UPPD04 † | W16 | DVDD18 | ||
| T23 | GPIO04 | V4 | EMIFD05 | W17 | VSS | ||
| T23 | BOOTMODE03 † | V4 | UPPD05 † | W18 | DVDD18 | ||
| T24 | DVDD18 | V5 | EMIFD07 | W19 | VSS | ||
| T25 | GPIO00 | V5 | UPPD07 † | W20 | DVDD18 | ||
| T25 | LENDIAN † | V6 | VSS | W21 | GPIO14 † | ||
| U1 | EMIFA21 | V7 | DVDD18 | W21 | PCIESSMODE0 † | ||
| U1 | UPP_CH1_START † | V8 | VSS | W22 | EMU08 | ||
| U2 | EMIFA22 | V9 | CVDD | W23 | EMU03 | ||
| U2 | UPP_CH1_ENABLE † | V10 | VSS | W24 | EMU04 | ||
| V11 | CVDD | W25 | EMU02 | ||||
| U3 | EMIFA23 | V12 | VSS | Y1 | EMIFD09 | ||
| U3 | UPP_CH1_WAIT † | V13 | CVDD | Y1 | UPPD09 † | ||
| U4 | EMIFD00 | V14 | VSS | Y2 | EMIFD11 | ||
| U4 | UPPD00 † | V15 | CVDD | Y2 | UPPD11 † | ||
| U5 | EMIFD01 | V16 | VSS | Y3 | DVDD18 | ||
| U5 | UPPD01 † | V17 | CVDD | Y4 | RSV13 | ||
| U6 | DVDD18 | V18 | VSS | Y5 | RSV12 | ||
| U7 | VSS | V19 | DVDD18 | Y6 | VSS | ||
| U8 | CVDD1 | V20 | VSS | Y7 | VDDT2 | ||
| U9 | VSS | V21 | GPIO15 | Y8 | VSS | ||
| U10 | CVDD | V21 | PCIESSMODE1 † | Y9 | VDDT2 | ||
| U11 | VSS | V22 | GPIO13 | Y10 | VSS | ||
| U12 | CVDD | V22 | BOOTMODE12 † | Y11 | VDDT2 | ||
| U13 | VSS | V23 | GPIO10 | Y12 | VSS | ||
| U14 | CVDD | V23 | BOOTMODE09 † | Y13 | DVDD18 | ||
| U15 | VSS | V24 | EMU00 | Y14 | VSS | ||
| U16 | CVDD | V25 | EMU01 | Y15 | AVDDA1 | ||
| U17 | VSS | W1 | EMIFD06 | Y16 | VSS | ||
| U18 | CVDD1 | W1 | UPPD06 † | Y17 | DVDD18 | ||
| U19 | VSS | W2 | EMIFD08 | Y18 | POR | ||
| U20 | DVDD18 | W2 | UPPD08 † | Y19 | RSV08 | ||
| U21 | GPIO11 | W3 | VSS | Y20 | CLKX0 | ||
| U21 | BOOTMODE10 † | W4 | EMIFD10 | Y21 | EMU18 | ||
| U22 | GPIO08 | W4 | UPPD10 † | Y22 | EMU09 | ||
| U22 | BOOTMODE07 † | W5 | EMIFD12 | Y23 | EMU07 | ||
| U23 | GPIO09 | W5 | UPPD12 † | Y24 | EMU06 | ||
| U23 | BOOTMODE08 † | W6 | DVDD18 | Y25 | EMU05 | ||
| U24 | GPIO05 | W7 | VSS | AA1 | EMIFD13 | ||
| U24 | BOOTMODE04 † | W8 | VDDT2 | AA1 | UPPD13 † | ||
| U25 | GPIO03 | W9 | VSS | AA2 | EMIFD15 | ||
| U25 | BOOTMODE02 † | W10 | VDDT2 | AA2 | UPPD15 † | ||
| V1 | EMIFD02 | W11 | VSS | AA3 | VDDR3 | ||
| V1 | UPPD02 † | W12 | VDDT2 | AA4 | VSS | ||
| V2 | EMIFD03 | W13 | VSS | AA5 | VDDR4 | ||
| V2 | UPPD03 † | W14 | DVDD18 | AA6 | VSS | ||
| V3 | EMIFD04 | W15 | VSS | AA7 | RSV17 | ||
| AA8 | VSS | AB22 | EMU15 | AD15 | UARTRTS1 | ||
| AA9 | VDDR2 | AB23 | DVDD18 | AD15 | GPIO27 † | ||
| AA10 | VSS | AB24 | VSS | AD16 | VSS | ||
| AA11 | RSV18 | AB25 | EMU12 | AD17 | TCK | ||
| AA12 | SPISCS0 | AC1 | VSS | AD18 | CORECLKP | ||
| AA12 | GPIO28 † | AC2 | SGMII0TXN | AD19 | TDO | ||
| AA13 | SPICLK | AC3 | SGMII0TXP | AD20 | TIMI0 | ||
| AA14 | SPISCS1 | AC4 | VSS | AD20 | GPIO16 † | ||
| AA14 | GPIO29 † | AC5 | RIOTXN2 | AD20 | PCIESSEN ‡ | ||
| AA15 | UARTTXD | AC6 | RIOTXP2 | AD21 | DR1 | ||
| AA15 | GPIO21 † | AC7 | VSS | AD22 | FSR1 | ||
| AA16 | MDCLK | AC8 | RIOTXP0 | AD23 | CLKR1 | ||
| AA17 | SCL | AC9 | RIOTXN0 | AD24 | FSR0 | ||
| AA18 | SDA | AC10 | VSS | AD25 | EMU16 | ||
| AA19 | SYSCLKOUT | AC11 | PCIETXP0 | AE1 | VSS | ||
| AA20 | FSX0 | AC12 | PCIETXN0 | AE2 | SGMII0RXN | ||
| AA21 | CLKR0 | AC13 | VSS | AE3 | SGMII0RXP | ||
| AA22 | RSV01 | AC14 | UARTRXD1 | AE4 | VSS | ||
| AA23 | EMU14 | AC14 | GPIO24 † | AE5 | RIORXN2 | ||
| AA24 | EMU10 | AC15 | UARTTXD1 | AE6 | RIORXP2 | ||
| AA25 | EMU11 | AC15 | GPIO25 † | AE7 | VSS | ||
| AB1 | EMIFD14 | AC16 | DVDD18 | AE8 | RIORXP0 | ||
| AB1 | UPPD14 † | AC17 | UARTCTS | AE9 | RIORXN0 | ||
| AB2 | VSS | AC17 | GPIO22 † | AE10 | VSS | ||
| AB3 | RSV19 | AC18 | RSV04 | AE11 | PCIERXP0 | ||
| AB4 | RIOTXN3 | AC19 | TIMO0 | AE12 | PCIERXN0 | ||
| AB5 | RIOTXP3 | AC19 | GPIO18 † | AE13 | VSS | ||
| AB6 | VSS | AC20 | DVDD18 | AE14 | SRIOSGMIICLKN | ||
| AB7 | RIOTXN1 | AC21 | CLKS1 | AE15 | PCIECLKN | ||
| AB8 | RIOTXP1 | AC22 | DX0 | AE16 | UARTCTS1 | ||
| AB9 | VSS | AC23 | CLKS0 | AE16 | GPIO26 † | ||
| AB10 | PCIETXP1 | AC24 | EMU17 | AE17 | TDI | ||
| AB11 | PCIETXN1 | AC25 | EMU13 | AE18 | TMS | ||
| AB12 | VSS | AD1 | VSS | AE19 | CORECLKN | ||
| AB13 | SPIDOUT | AD2 | VSS | AE20 | TIMO1 | ||
| AB13 | GPIO31 † | AD3 | VSS | AE20 | GPIO19 † | ||
| AB14 | SPIDIN | AD4 | RIORXN3 | AE21 | TIMI1 | ||
| AB14 | GPIO30 † | AD5 | RIORXP3 | AE21 | GPIO17 † | ||
| AB15 | UARTRXD | AD6 | VSS | AE22 | DX1 | ||
| AB15 | GPIO20 † | AD7 | RIORXP1 | AE23 | FSX1 | ||
| AB16 | MDIO | AD8 | RIORXN1 | AE24 | CLKX1 | ||
| AB17 | UARTRTS | AD9 | VSS | AE25 | VSS | ||
| AB17 | GPIO23 † | AD10 | PCIERXN1 | ||||
| AB18 | RSV05 | AD11 | PCIERXP1 | ||||
| AB19 | TRST | AD12 | VSS | ||||
| AB20 | VSS | AD13 | SRIOSGMIICLKP | ||||
| AB21 | DR0 | AD14 | PCIECLKP |