ZHCSAH6F November 2012 – September 2021 TMS320F28050 , TMS320F28051 , TMS320F28052 , TMS320F28052F , TMS320F28052M , TMS320F28053 , TMS320F28054 , TMS320F28054F , TMS320F28054M , TMS320F28055
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 7.3 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 7.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for PN Package
- 7.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 7.9 JTAG Debug Probe Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 7.10 Parameter Information
- 7.11 Test Load Circuit
- 7.12 Power Sequencing
- 7.13 Clock Specifications
- 7.14 Flash Timing
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1
Overview
- 8.1.1 CPU
- 8.1.2 Control Law Accelerator
- 8.1.3 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 8.1.4 Peripheral Bus
- 8.1.5 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 8.1.6 Flash
- 8.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 8.1.8 L0 SARAM, and L1, L2, and L3 DPSARAMs
- 8.1.9 Boot ROM
- 8.1.10 Security
- 8.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion Block
- 8.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1 to XINT3)
- 8.1.13 Internal Zero-Pin Oscillators, Oscillator, and PLL
- 8.1.14 Watchdog
- 8.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 8.1.16 Low-power Modes
- 8.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 8.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output Multiplexer
- 8.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 8.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 8.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 8.2 Memory Maps
- 8.3 Register Map
- 8.4 Device Emulation Registers
- 8.5 VREG, BOR, POR
- 8.6 System Control
- 8.7 Low-power Modes Block
- 8.8 Interrupts
- 8.9
Peripherals
- 8.9.1 Control Law Accelerator
- 8.9.2
Analog Block
- 8.9.2.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 8.9.2.1.1 ADC Device-Specific Information
- 8.9.2.1.2 ADC Electrical Data/Timing
- 8.9.2.2 Analog Front End
- 8.9.2.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 8.9.3 Detailed Descriptions
- 8.9.4 Serial Peripheral Interface
- 8.9.5 Serial Communications Interface
- 8.9.6 Enhanced Controller Area Network
- 8.9.7 Inter-Integrated Circuit
- 8.9.8 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator
- 8.9.9 Enhanced Capture Module
- 8.9.10 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse
- 8.9.11 JTAG Port
- 8.9.12 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 8.1
Overview
- 9 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.9.2.1.1 ADC Device-Specific Information
The core of the ADC contains a single 12-bit converter fed by two sample-and-hold circuits. The sample-and-hold circuits can be sampled simultaneously or sequentially. These, in turn, are fed by a total of up to 16 analog input channels. The converter can be configured to run with an internal bandgap reference to create true-voltage-based conversions or with a pair of external voltage references (VREFHI/VREFLO) to create ratiometric-based conversions.
Contrary to previous ADC types, this ADC is not sequencer-based. The user can easily create a series of conversions from a single trigger. However, the basic principle of operation is centered around the configurations of individual conversions, called SOCs, or Start-Of-Conversions.
Functions of the ADC module include:
- 12-bit ADC core with built-in dual sample-and-hold (S/H)
- Simultaneous sampling or sequential sampling modes
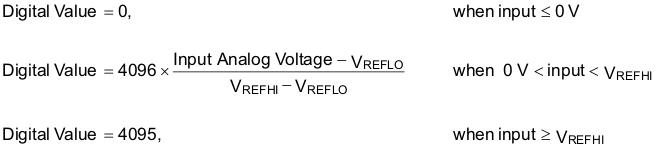
- Full range analog input: 0 V to 3.3 V fixed, or VREFHI/VREFLO ratiometric. The digital value of the input analog voltage is derived by:
- Internal Reference (VREFLO = VSSA. VREFHI must not exceed VDDA when using either internal or external reference modes.)

- External Reference (VREFHI/VREFLO connected to external references. VREFHI must not exceed VDDA when using either internal or external reference modes.)
- Internal Reference (VREFLO = VSSA. VREFHI must not exceed VDDA when using either internal or external reference modes.)
- Up to 16-channel, multiplexed inputs
- 16 SOCs, configurable for trigger, sample window, and channel
- 16 result registers (individually addressable) to store conversion values
- Multiple trigger sources
- S/W – software immediate start
- ePWM 1–7
- GPIO XINT2
- CPU-Timer 0, CPU-Timer 1, CPU-Timer 2
- ADCINT1, ADCINT2
- 9 flexible PIE interrupts, can configure interrupt request after any conversion
| REGISTER NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (×16) | EALLOW PROTECTED | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADCCTL1 | 0x7100 | 1 | Yes | Control 1 register |
| ADCCTL2 | 0x7101 | 1 | Yes | Control 2 register |
| ADCINTFLG | 0x7104 | 1 | No | Interrupt Flag register |
| ADCINTFLGCLR | 0x7105 | 1 | No | Interrupt Flag Clear register |
| ADCINTOVF | 0x7106 | 1 | No | Interrupt Overflow register |
| ADCINTOVFCLR | 0x7107 | 1 | No | Interrupt Overflow Clear register |
| INTSEL1N2 | 0x7108 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt 1 and 2 Selection register |
| INTSEL3N4 | 0x7109 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt 3 and 4 Selection register |
| INTSEL5N6 | 0x710A | 1 | Yes | Interrupt 5 and 6 Selection register |
| INTSEL7N8 | 0x710B | 1 | Yes | Interrupt 7 and 8 Selection register |
| INTSEL9N10 | 0x710C | 1 | Yes | Interrupt 9 Selection register (reserved Interrupt 10 Selection) |
| SOCPRICTL | 0x7110 | 1 | Yes | SOC Priority Control register |
| ADCSAMPLEMODE | 0x7112 | 1 | Yes | Sampling Mode register |
| ADCINTSOCSEL1 | 0x7114 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt SOC Selection 1 register (for 8 channels) |
| ADCINTSOCSEL2 | 0x7115 | 1 | Yes | Interrupt SOC Selection 2 register (for 8 channels) |
| ADCSOCFLG1 | 0x7118 | 1 | No | SOC Flag 1 register (for 16 channels) |
| ADCSOCFRC1 | 0x711A | 1 | No | SOC Force 1 register (for 16 channels) |
| ADCSOCOVF1 | 0x711C | 1 | No | SOC Overflow 1 register (for 16 channels) |
| ADCSOCOVFCLR1 | 0x711E | 1 | No | SOC Overflow Clear 1 register (for 16 channels) |
| ADCSOC0CTL to ADCSOC15CTL | 0x7120 to 0x712F | 1 | Yes | SOC0 Control Register to SOC15 Control register |
| ADCREFTRIM | 0x7140 | 1 | Yes | Reference Trim register |
| ADCOFFTRIM | 0x7141 | 1 | Yes | Offset Trim register |
| ADCREV | 0x714F | 1 | No | Revision register |
| REGISTER NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (×16) | EALLOW PROTECTED | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADCRESULT0 to ADCRESULT15 | 0xB00 to 0xB0F | 1 | No | ADC Result 0 register to ADC Result 15 register |
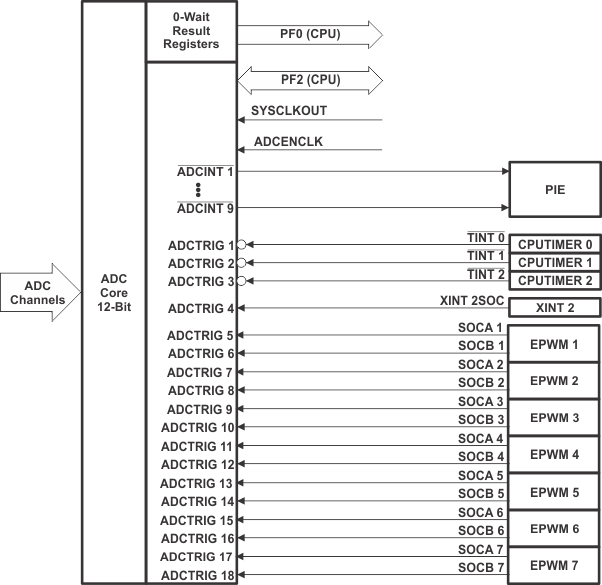 Figure 8-16 ADC Connections
Figure 8-16 ADC ConnectionsADC Connections if the ADC is Not Used
TI recommends keeping the connections for the analog power pins, even if the ADC is not used. Following is a summary of how the ADC pins should be connected, if the ADC is not used in an application:
- VDDA – Connect to VDDIO
- VSSA – Connect to VSS
- VREFLO – Connect to VSS
- ADCINAn, ADCINBn, VREFHI – Connect to VSSA
When the ADC module is used in an application, unused ADC input pins should be connected to analog ground (VSSA).
When the ADC is not used, be sure that the clock to the ADC module is not turned on to realize power savings.