ZHCSHE0 December 2017 TMS320F28377D-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.7
System
- 4.7.1 Power Sequencing
- 4.7.2 Reset Timing
- 4.7.3
Clock Specifications
- 4.7.3.1 Clock Sources
- 4.7.3.2 Clock Frequencies, Requirements, and Characteristics
- 4.7.3.3 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 4.7.3.4 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.7.3.5 Internal Oscillators
- 4.7.4 Flash Parameters
- 4.7.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 4.7.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.7.7 Interrupts
- 4.7.8
Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.1 Clock-Gating Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.2 Power-Gating Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.3
Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- Table 4-29 IDLE Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-30 IDLE Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-31 STANDBY Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-32 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-33 HALT Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-34 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-35 HIBERNATE Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-36 HIBERNATE Mode Switching Characteristics
- 4.7.9 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.8
Analog Peripherals
- 4.8.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 4.8.1.1
ADC Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 4-41 ADC Operating Conditions (16-Bit Differential Mode)
- Table 4-42 ADC Characteristics (16-Bit Differential Mode)
- Table 4-43 ADC Operating Conditions (12-Bit Single-Ended Mode)
- Table 4-44 ADC Characteristics (12-Bit Single-Ended Mode)
- Table 4-45 ADCEXTSOC Timing Requirements
- 4.8.1.1.1 ADC Input Models
- 4.8.1.1.2 ADC Timing Diagrams
- 4.8.1.2 Temperature Sensor Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.8.1.1
ADC Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.8.2 Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 4.8.3 Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 4.8.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 4.9
Control Peripherals
- 4.9.1 Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 4.9.2 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 4.9.3 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 4.9.4 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 4.9.5 Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
- 4.10
Communications Peripherals
- 4.10.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 4.10.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 4.10.3
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.10.3.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.10.3.1.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 4.10.3.1.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- Table 4-69 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-70 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-71 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-72 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-73 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-74 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-75 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-76 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 4.10.3.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.10.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 4.10.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.10.6 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 4.10.7 Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Interface
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Memory
- 5.4 Identification
- 5.5 Bus Architecture – Peripheral Connectivity
- 5.6 C28x Processor
- 5.7 Control Law Accelerator
- 5.8 Direct Memory Access
- 5.9 Interprocessor Communication Module
- 5.10 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 5.11 Dual Code Security Module
- 5.12 Timers
- 5.13 Nonmaskable Interrupt With Watchdog Timer (NMIWD)
- 5.14 Watchdog
- 5.15 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7器件和文档支持
- 8机械封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PTP|176
订购信息
4.10.7 Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Interface
The uPP interface is a high-speed parallel interface with dedicated data lines and minimal control signals. The uPP interface is designed to interface cleanly with high-speed ADCs or DACs with 8-bit data width. It can also be interconnected with field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) or other uPP devices to achieve high-speed digital data transfer. It can operate in receive mode or transmit mode (simplex mode).
The uPP interface includes an internal DMA controller to maximize throughput and minimize CPU overhead during high-speed data transmission. All uPP transactions use internal DMA to feed data to or retrieve data from the I/O channels. Even though there is only one I/O channel, the DMA controller includes two DMA channels to support data interleave mode, in which all DMA resources service a single I/O channel.
On this device, the uPP interface is the dedicated resource for the CPU1 subsystem. CPU1, CPU1.CLA1, and CPU1.DMA have access to this module. Two dedicated 512-byte data RAMs (also known as MSG RAMs) are tightly coupled with the uPP module (one for each, TX and RX). These data RAMs are used to store the bulk of data to avoid frequent interruptions to the CPU. Only CPU1 and CPU1.CLA1 have access to these data RAMs. Figure 4-78 shows the integration of the uPP on this device.
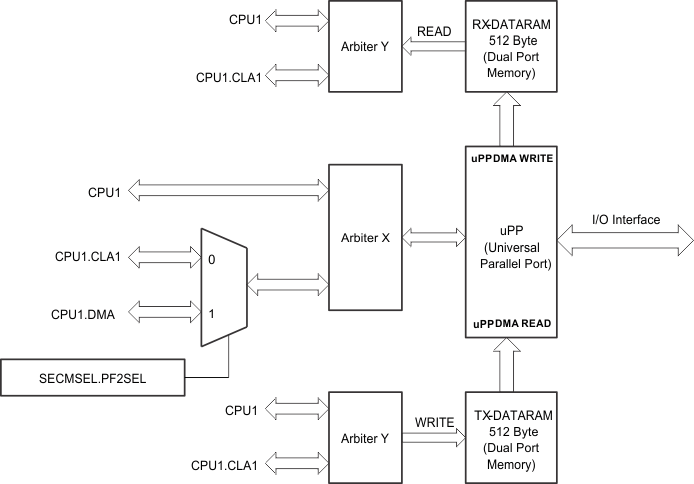 Figure 4-78 uPP Integration
Figure 4-78 uPP IntegrationNOTE
On some TI devices, the uPP module is also called the Radio Peripheral Interface (RPI) module.
The uPP interface supports the following:
- Mainstream high-speed data converters with parallel conversion interface.
- Mainstream high-speed streaming interface with frame START indication.
- Mainstream high-speed streaming interface with data ENABLE indication.
- Mainstream high-speed streaming interface with synchronization WAIT signal.
- SDR (single-data-rate) or DDR (double-data-rate, interleaved) interface.
- Multiplexing of interleaved data in SDR transmit case.
- Demultiplexing and multiplexing of interleaved data in DDR case.
- I/O interface clock frequency up to 50 MHz for SDR, and 25 MHz for DDR.
- Single-channel 8-bit input receive or output transmit mode.
- Max throughput is 50MB/s for pure read or pure write.
- Available as a DSP to FPGA general-purpose streaming interface.
Figure 4-79 shows the uPP functional block diagram.
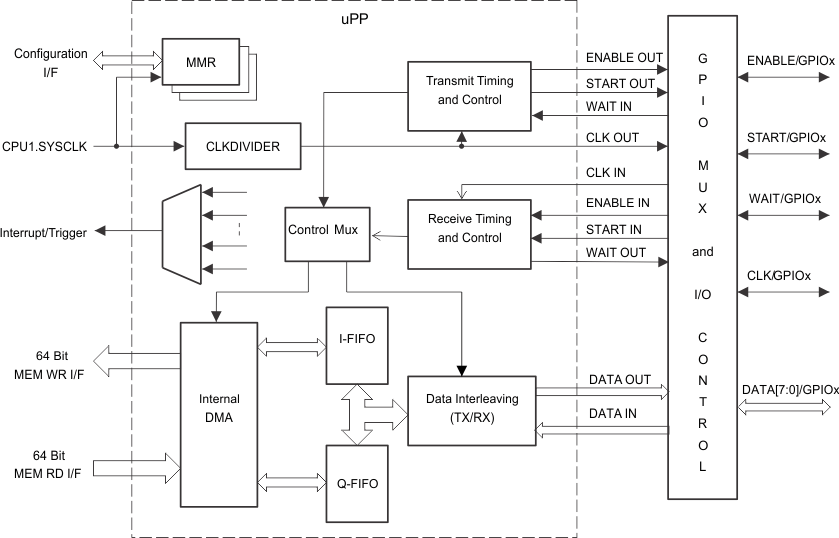 Figure 4-79 uPP Functional Block Diagram
Figure 4-79 uPP Functional Block Diagram