ZHCSHE0 December 2017 TMS320F28377D-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.6 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.7
System
- 4.7.1 Power Sequencing
- 4.7.2 Reset Timing
- 4.7.3
Clock Specifications
- 4.7.3.1 Clock Sources
- 4.7.3.2 Clock Frequencies, Requirements, and Characteristics
- 4.7.3.3 Input Clocks and PLLs
- 4.7.3.4 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.7.3.5 Internal Oscillators
- 4.7.4 Flash Parameters
- 4.7.5 Emulation/JTAG
- 4.7.6 GPIO Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.7.7 Interrupts
- 4.7.8
Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.1 Clock-Gating Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.2 Power-Gating Low-Power Modes
- 4.7.8.3
Low-Power Mode Wakeup Timing
- Table 4-29 IDLE Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-30 IDLE Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-31 STANDBY Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-32 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-33 HALT Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-34 HALT Mode Switching Characteristics
- Table 4-35 HIBERNATE Mode Timing Requirements
- Table 4-36 HIBERNATE Mode Switching Characteristics
- 4.7.9 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.8
Analog Peripherals
- 4.8.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 4.8.1.1
ADC Electrical Data and Timing
- Table 4-41 ADC Operating Conditions (16-Bit Differential Mode)
- Table 4-42 ADC Characteristics (16-Bit Differential Mode)
- Table 4-43 ADC Operating Conditions (12-Bit Single-Ended Mode)
- Table 4-44 ADC Characteristics (12-Bit Single-Ended Mode)
- Table 4-45 ADCEXTSOC Timing Requirements
- 4.8.1.1.1 ADC Input Models
- 4.8.1.1.2 ADC Timing Diagrams
- 4.8.1.2 Temperature Sensor Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.8.1.1
ADC Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.8.2 Comparator Subsystem (CMPSS)
- 4.8.3 Buffered Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
- 4.8.1
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 4.9
Control Peripherals
- 4.9.1 Enhanced Capture (eCAP)
- 4.9.2 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulator (ePWM)
- 4.9.3 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 4.9.4 High-Resolution Pulse Width Modulator (HRPWM)
- 4.9.5 Sigma-Delta Filter Module (SDFM)
- 4.10
Communications Peripherals
- 4.10.1 Controller Area Network (CAN)
- 4.10.2 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 4.10.3
Multichannel Buffered Serial Port (McBSP)
- 4.10.3.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.10.3.1.1 McBSP Transmit and Receive Timing
- 4.10.3.1.2
McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing
- Table 4-69 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-70 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-71 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-72 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 0)
- Table 4-73 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-74 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 10b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-75 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Timing Requirements (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- Table 4-76 McBSP as SPI Master or Slave Switching Characteristics (CLKSTP = 11b, CLKXP = 1)
- 4.10.3.1
McBSP Electrical Data and Timing
- 4.10.4 Serial Communications Interface (SCI)
- 4.10.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.10.6 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Controller
- 4.10.7 Universal Parallel Port (uPP) Interface
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3 Memory
- 5.4 Identification
- 5.5 Bus Architecture – Peripheral Connectivity
- 5.6 C28x Processor
- 5.7 Control Law Accelerator
- 5.8 Direct Memory Access
- 5.9 Interprocessor Communication Module
- 5.10 Boot ROM and Peripheral Booting
- 5.11 Dual Code Security Module
- 5.12 Timers
- 5.13 Nonmaskable Interrupt With Watchdog Timer (NMIWD)
- 5.14 Watchdog
- 5.15 Configurable Logic Block (CLB)
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7器件和文档支持
- 8机械封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PTP|176
订购信息
Table 4-32 STANDBY Mode Switching Characteristics
over recommended operating conditions (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| td(IDLE-XCOS) | Delay time, IDLE instruction executed to XCLKOUT stop | 16tc(INTOSC1) | cycles | ||
| td(WAKE-STBY) | Delay time, external wake signal to program execution resume(1) | cycles | |||
|
175tc(SYSCLK) + tw(WAKE-INT) | ||||
|
6700tc(SYSCLK)(2) + tw(WAKE-INT) | ||||
|
3tc(OSC) + 15tc(SYSCLK) + tw(WAKE-INT) | ||||
(1) This is the time taken to begin execution of the instruction that immediately follows the IDLE instruction. Execution of an ISR (triggered by the wake-up signal) involves additional latency.
(2) This value is based on the flash power-up time, which is a function of the SYSCLK frequency, flash wait states (RWAIT), and FPAC1[PSLEEP]. For more information, see the Flash and OTP Power-Down Modes and Wakeup section of the TMS320F2837xD Dual-Core Delfino Microcontrollers Technical Reference Manual. This value can be realized when SYSCLK is 200 MHz, RWAIT is 3, and FPAC1[PSLEEP] is 0x860.
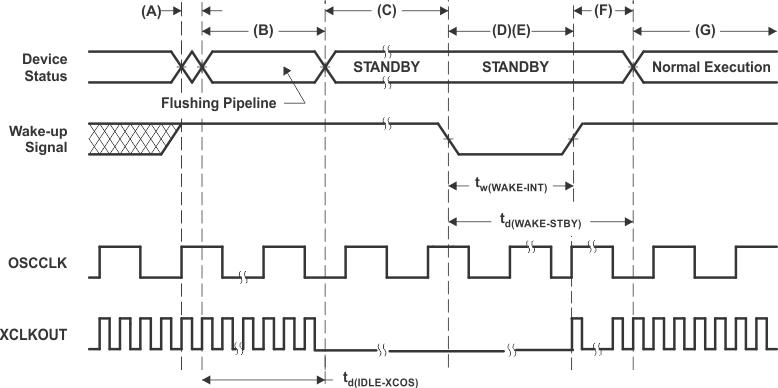
A. IDLE instruction is executed to put the device into STANDBY mode.
B. The LPM block responds to the STANDBY signal, SYSCLK is held for a maximum 16 INTOSC1 clock cycles before being turned off. This delay enables the CPU pipeline and any other pending operations to flush properly.
C. Clock to the peripherals are turned off. However, the PLL and watchdog are not shut down. The device is now in STANDBY mode. After the IDLE instruction is executed, a delay of five OSCCLK cycles (minimum) is needed before the wake-up signal could be asserted.
D. The external wake-up signal is driven active.
E. The wake-up signal fed to a GPIO pin to wake up the device must meet the minimum pulse width requirement. Furthermore, this signal must be free of glitches. If a noisy signal is fed to a GPIO pin, the wakeup behavior of the device will not be deterministic and the device may not exit low-power mode for subsequent wakeup pulses.
F. After a latency period, the STANDBY mode is exited.
G. Normal execution resumes. The device will respond to the interrupt (if enabled).
Figure 4-19 STANDBY Entry and Exit Timing DiagramTable 4-33 shows the HALT mode timing requirements, Table 4-34 shows the switching characteristics, and Figure 4-20 shows the timing diagram for HALT mode.