ZHCSIV1F September 2018 – February 2023 TPS1663
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 9.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.3 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.4 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 9.3.5 Output Power Limiting, PLIM (TPS16632 Only)
- 9.3.6 Current Monitoring Output (IMON)
- 9.3.7 FAULT Response (FLT)
- 9.3.8 Power Good Output (PGOOD)
- 9.3.9 IN, P_IN, OUT and GND Pins
- 9.3.10 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.3.11 Low Current Shutdown Control (SHDN)
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.2.2.2 Undervoltage Lockout and Overvoltage Set Point
The undervoltage lockout (UVLO) and overvoltage trip point are adjusted using an external voltage divider network of R1, R2 and R3 connected between IN, UVLO, OVP and GND pins of the device. The values required for setting the undervoltage and overvoltage are calculated by solving Equation 8 and Equation 9.
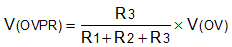
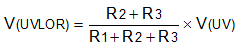
For minimizing the input current drawn from the power supply [I(R123) = V(IN) / (R1 + R2 + R3)], TI recommends to use higher value resistance for R1, R2 and R3.
However, the leakage current due to external active components connected at resistor string can add error to these calculations. So, the resistor string current, I(R123), must be chosen to be 20 times greater than the leakage current of UVLO and OVP pins.
From the device electrical specifications, V(OVPR) = 1.2 V and V(UVLOR) = 1.2 V. From the design requirements, V(OV) is 55 V and V(UV) is 18 V. To solve the equation, first choose the value of R3 = 20.5 kΩ and use Equation 8 to solve for (R1 + R2) = 930 kΩ. Use Equation 9 and value of (R1 + R2) to solve for R2 = 43 kΩ and finally R1 = 887 kΩ.
Choose the closest standard 1% resistor values: R1 = 887 kΩ, R2 = 43 kΩ, and R3 = 20.5 kΩ.