ZHCSGV1C June 2017 – March 2018 TPS25740B
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 ENSRC
- 8.3.2 USB Type-C CC Logic (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.3 USB PD BMC Transmission (CC1, CC2, VTX)
- 8.3.4 USB PD BMC Reception (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.5 Discharging (DSCG, VPWR)
- 8.3.6 Configuring Voltage Capabilities (HIPWR)
- 8.3.7 Configuring Power Capabilities (PSEL, PCTRL, HIPWR)
- 8.3.8 Gate Driver (GDNG, GDNS)
- 8.3.9 Fault Monitoring and Protection
- 8.3.10 Voltage Control (CTL1, CTL2,CTL3)
- 8.3.11 Sink Attachment Indicator (DVDD)
- 8.3.12 Power Supplies (VAUX, VDD, VPWR, DVDD)
- 8.3.13 Grounds (AGND, GND)
- 8.3.14 Output Power Supply (DVDD)
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Application Information
- 9.1.1 System-Level ESD Protection
- 9.1.2 Using ENSRC to Enable the Power Supply upon Sink Attachment
- 9.1.3 Use of GD Internal Clamp
- 9.1.4 Resistor Divider on GD for Programmable Start Up
- 9.1.5 Selection of the CTL1, CTL2, and CTL3 Resistors (R(FBL1), R(FBL2), and R(FBL3))
- 9.1.6 Voltage Transition Requirements
- 9.1.7 VBUS Slew Control using GDNG C(SLEW)
- 9.1.8 Tuning OCP using RF and CF
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.3 System Examples
- 9.1
Application Information
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.3.7 Configuring Power Capabilities (PSEL, PCTRL, HIPWR)
The power advertised to non-PD Type-C Sinks is always 15 W. However, the device only advertises Type-C default current until it debounces the Sink attachment for tCcDeb and the VBUS voltage has been given tVP to stabilize.
The device does not communicate with the cable to determine its capabilities. Therefore, unless the device is in a system with a captive cable able to support 5 A, the HIPWR pin should be used to limit the advertised current to 3 A.
PCTRL is an input pin used to control how much of the maximum allowed power the port will advertise. This pin may be changed dynamically in the system and the device automatically updates any existing USB PD contract. If the PCTRL pin is pulled below V(PCTRL_TH), then the source capabilities offers half of the maximum power specified by the PSEL pin.
The devices read the PSEL and HIPWR pins after a reset and latches the result, but the PCTRL pin is read dynamically by the device and if its state changes new capabilities are calculated and then transmitted.
While USB PD allows advertising a power of 100 W, UL certification for Class 2 power units (UL 1310) requires the maximum power remain below 100 W. The device only advertises up to 4.65 A for a 20-V contract, this allows the VBUS overshoot to reach 21.5 V as allowed by USB PD while remaining within the UL certification limits. Therefore, the device allows delivering 100 W of power without adding additional voltage tolerance constraints on the power supply.
The PSEL pin offers four possible maximum power settings, but the devices can actually advertise more power settings depending upon the state of the HIPWR and PCTRL pins. Table 2 summarizes the four maximum power settings that are available via PSEL, again note this is not necessarily the maximum power that is advertised.
Table 2. PSEL Configurations
| MAXIMUM POWER
(PSEL) [W] |
PSEL |
|---|---|
| P(SEL) = 36 | Direct to GND |
| P(SEL) = 45 | DVDD via R(SEL) |
| P(SEL) = 65 | GND via R(SEL) |
| P(SEL) = 93 | Direct to DVDD |
Equation 2 provides a quick reference which applies to device to see how the HIPWR, PSEL and PCTRL pins affect what current is advertised with each voltage in the source capabilities message:
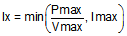
Where:
- For a voltage Vx, the advertised current is Ix
- If the PCTRL pin is low, then Pmax = P(SEL) / 2
- If the PCTRL pin is high, then Pmax = P(SEL).
- If the HIPWR pin is pulled high, then Imax = 3 A.
- If the HIPWR pin is pulled low, then Imax = 5 A.
Table 3 provides a comprehensive list of the currents and voltages that are advertised for each voltage.
Table 3. Maximum Current Advertised in the Power Data Object for a Given Voltage
| PSEL | VOLTAGE [V] | HIPWR | MAXIMUM CURRENT
PCTRL = LOW [A] |
MAXIMUM CURRENT
PCTRL = HIGH [A] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct to GND | 5 | Max = 3 A
DVDD through R(SEL) or Direct to DVDD |
3 | 3 |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 3 | 3 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to GND | 9 | 2 | 3 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 2.5 | 3 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to GND | 12 | 1.5 | 3 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 1.87 | 3 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 2.7 | 3 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to GND | 15 | 1.2 | 2.4 | |
| 100kΩ to DVDD | 1.5 | 3 | ||
| 100kΩ to GND | 2.17 | 3 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 3 | 3 | ||
| Direct to GND | 20 | 0.9 | 1.8 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 1.12 | 2.24 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 1.62 | 3 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 2.32 | 3 | ||
| Direct to GND | 5 | Max = 5 A
GND through R(SEL) or Direct to GND |
3.6 | 5 |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 4.5 | 5 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 5 | 5 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 5 | 5 | ||
| Direct to GND | 9 | 2 | 4 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 2.5 | 5 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 3.61 | 5 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 5 | 5 | ||
| Direct to GND | 12 | 1.5 | 3 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 1.87 | 3.74 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 2.7 | 5 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 4.16 | 5 | ||
| Direct to GND | 15 | 1.2 | 2.4 | |
| 100kΩ to DVDD | 1.5 | 3 | ||
| 100kΩ to GND | 2.17 | 4.33 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 3.1 | 5 | ||
| Direct to GND | 20 | 0.9 | 1.8 | |
| DVDD via R(SEL) | 1.12 | 2.24 | ||
| GND via R(SEL) | 1.62 | 3.24 | ||
| Direct to DVDD | 2.32 | 4.64 |