ZHCSTM4A October 2023 – March 2024 TPS25751
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Recommended Capacitance
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Power Supply Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Consumption
- 6.8 PP_5V Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.9 PPHV Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25751D
- 6.10 PP_EXT Power Switch Characteristics - TPS25751S
- 6.11 Power Path Supervisory
- 6.12 CC Cable Detection Parameters
- 6.13 CC VCONN Parameters
- 6.14 CC PHY Parameters
- 6.15 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.16 ADC Characteristics
- 6.17 Input/Output (I/O) Characteristics
- 6.18 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.19 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.20 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Power Paths
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Overvoltage Protection (CC1, CC2)
- 8.3.6 Default Behavior Configuration (ADCIN1, ADCIN2)
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 BC 1.2 (USB_P, USB_N)
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 Digital Core
- 8.3.11 I2C Interface
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Thermal Shutdown
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4
Layout
- 9.4.1 TPS25751D - Layout
- 9.4.2 TPS25751S - Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RSM|32
订购信息
8.3.1.2 USB-PD Bi-Phase Marked Coding
The USB-PD physical layer implemented in the TPS25751 is compliant to the USB-PD Specifications. The encoding scheme used for the baseband PD signal is a version of Manchester coding called Biphase Mark Coding (BMC). In this code, there is a transition at the start of every bit time and there is a second transition in the middle of the bit cell when a 1 is transmitted. This coding scheme is nearly DC balanced with limited disparity (limited to 1/2 bit over an arbitrary packet, so a very low DC level). Figure 8-6 illustrates Biphase Mark Coding.
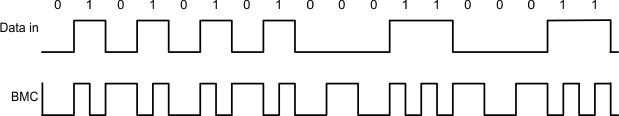 Figure 8-6 Biphase Mark Coding Example
Figure 8-6 Biphase Mark Coding ExampleThe USB PD baseband signal is driven onto the CC1 or CC2 pin with a tri-state driver. The tri-state driver is slew rate to limit coupling to D+/D– and to other signal lines in the Type-C fully featured cables. When sending the USB-PD preamble, the transmitter starts by transmitting a low level. The receiver at the other end tolerates the loss of the first edge. The transmitter terminates the final bit by an edge to ensure the receiver clocks the final bit of EOP.