ZHCSK92E September 2019 – March 2022 TPS25840-Q1 , TPS25842-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Buck Regulator
- 10.3.2 Enable/UVLO
- 10.3.3 Switching Frequency and Synchronization (RT/SYNC)
- 10.3.4 Spread-Spectrum Operation
- 10.3.5 VCC, VCC_UVLO
- 10.3.6 Minimum ON-time, Minimum OFF-time
- 10.3.7 Internal Compensation
- 10.3.8 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 10.3.9 RSNS, RSET, RILIMIT and RIMON
- 10.3.10 Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 10.3.11 Overvoltage, IEC and Short-to-Battery Protection
- 10.3.12 Cable Compensation
- 10.3.13 USB Port Control
- 10.3.14 FAULT Response
- 10.3.15 USB Specification Overview
- 10.3.16 Device Power Pins (IN, CSN/OUT, and PGND)
- 10.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Application
- 11.2.1 Design Requirements
- 11.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 11.2.2.1 Output Voltage
- 11.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 11.2.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 11.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 11.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 11.2.2.6 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 11.2.2.7 VCC Capacitor Selection
- 11.2.2.8 Enable and Under Voltage Lockout Set-Point
- 11.2.2.9 Current Limit Set-Point
- 11.2.2.10 Cable Compensation Set-Point
- 11.2.2.11 FAULT Resistor Selection
- 11.2.3 Application Curves
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14Device and Documentation Support
- 15Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.3.10.4 Cycle-by-Cycle Buck Current Limit
The buck regulator cycle-by-cycle current limit on both the peak and valley of the inductor current. Hiccup mode is activated if a fault condition persists to prevent over-heating.
High-side MOSFET overcurrent protection is implemented by the nature of the Peak Current Mode control. The HS switch current is sensed when the HS is turned on after a set blanking time. The HS switch current is compared to the output of the Error Amplifier (EA) minus slope compensation every switching cycle. for more details, refer to the Functional Block Diagram. The peak current of HS switch is limited by a clamped maximum peak current threshold IHS_LIMIT which is constant. So the peak current limit of the high-side switch is not affected by the slope compensation and remains constant over the full duty cycle range.
The current going through LS MOSFET is also sensed and monitored. When the LS switch turns on, the inductor current begins to ramp down. The LS switch is not turned OFF at the end of a switching cycle if its current is above the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. The LS switch is kept ON so that the inductor current keeps ramping down, until the inductor current ramps below the LS current limit ILS_LIMIT. Then the LS switch is turned OFF and the HS switch is turned on after a dead time. This is somewhat different than the more typical peak current limit, and results in Equation 8 for the maximum load current.
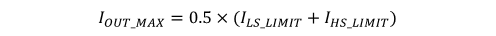
If VCSN/OUT < 2-V typical due to a short circuit for 128 consecutive cycles, hiccup current protection mode is activated. In hiccup mode, the regulator is shut down and kept off for 118 ms typically, then TPS2583x-Q1 go through a normal re-start with soft start again. If the short-circuit condition remains, hiccup repeats until the fault condition is removed. Hiccup mode reduces power dissipation under severe overcurrent conditions, prevents over-heating and potential damage to the device and serves as a backup to the programmable current limit. See Current Limit Setting Using RILIMIT. After the output short is removed, the hiccup delay is passed and the output voltage recovers normally as shown in Figure 11-21.