ZHCSFF5G July 2016 – December 2019 TPS2660
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.3 Reverse Input Supply Protection
- 9.3.4 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
- 9.3.5 Overload and Short Circuit Protection
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 System Examples
- 10.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RHF|24
- PWP|16
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PWP|16
订购信息
9.3.4 Hot Plug-In and In-Rush Current Control
The devices are designed to control the in-rush current upon insertion of a card into a live backplane or other "hot" power source. This limits the voltage sag on the backplane’s supply voltage and prevents unintended resets of the system power. The controlled start-up also helps to eliminate conductive and radiative interferences. An external capacitor connected from the dVdT pin to RTN defines the slew rate of the output voltage at power-on as shown in Figure 37 and Figure 38.
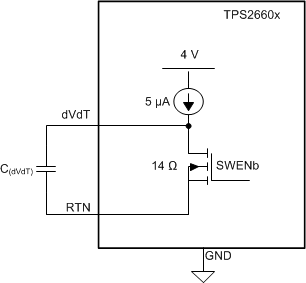 Figure 37. Output Ramp Up Time tdVdT is Set by C(dVdT)
Figure 37. Output Ramp Up Time tdVdT is Set by C(dVdT) The dVdT pin can be left floating to obtain a predetermined slew rate (tdVdT) on the output. When the terminal is left floating, the devices set an internal output voltage ramp rate of 23.9 V/1.6 ms. A capacitor can be connected from dVdT pin to RTN to program the output voltage slew rate slower than 23.9 V/1.6 ms. Use Equation 1 and Equation 2 to calculate the external C(dVdT) capacitance.
Equation 1 governs slew rate at start-up.
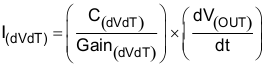
where
- I(dVdT) = 4.7 µA (typical)
- Gain(dVdT) = dVdT to VOUT gain = 24.6
The total ramp time (tdVdT) of V(OUT) for 0 to V(IN) can be calculated using Equation 2.
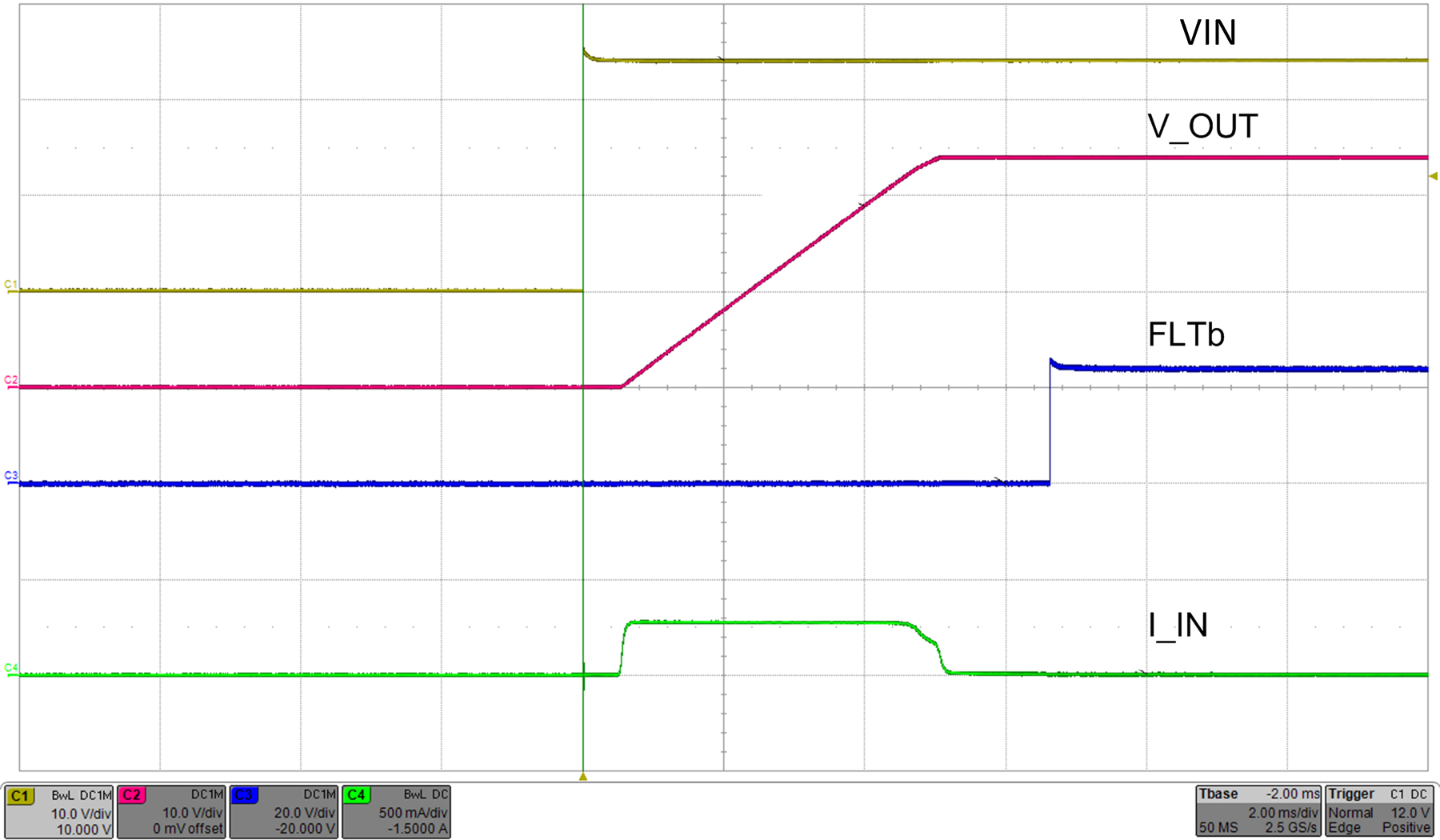
| CdVdT = 22 nF | COUT = 47 µF | RILIM = 5.36 kΩ |