ZHCSME3 November 2020 TPS27SA08
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Summary Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Protection Mechanisms
- 9.3.2 Diagnostic Mechanisms
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.2.1.2 Detection With Switch Disabled
While the switch is disabled, if DIA_EN is high, an internal comparator will detect the condition of VOUT. If the load is disconnected (open load condition) or there is a short to supply theOUT voltage will be higher than the open load threshold (VOL,off) and a fault is indicated on the SNS pin. An internal pull-up of 1 MΩ is in series with an internal MOSFET switch, so no external component is required if only a completely open load needs to be detected. However, if there is significant leakage or other current draw even when the load is disconnected, a lower value pull-up resistor and switch can be added externally to set the VOUT voltage above the VOL,off during open load conditions.
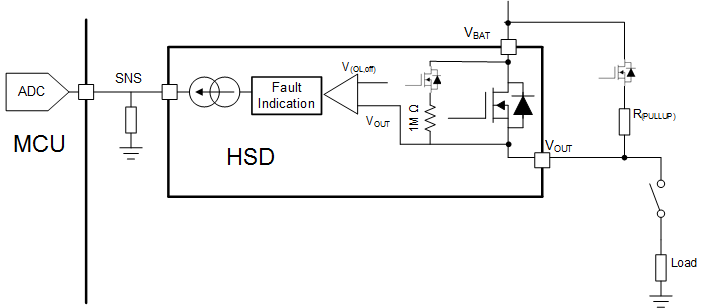
The detection circuitry is only enabled when DIA_EN = HIGH and EN = LOW.
If VOUT > VOL, the SNS pin will go to the fault level.
If VOUT < VOL, then there is no fault indication.
The fault indication will only occur if the SEL1 pin is set to diagnose the channel.
While the switch is disabled and DIA_EN is high, the fault indication mechanisms will continuously represent the present status. For example, if VOUT decreases from >VOL to <VOL, the fault indication is reset. Additionally, the fault indication is reset upon the falling edge of DIA_EN or the rising edge of EN.
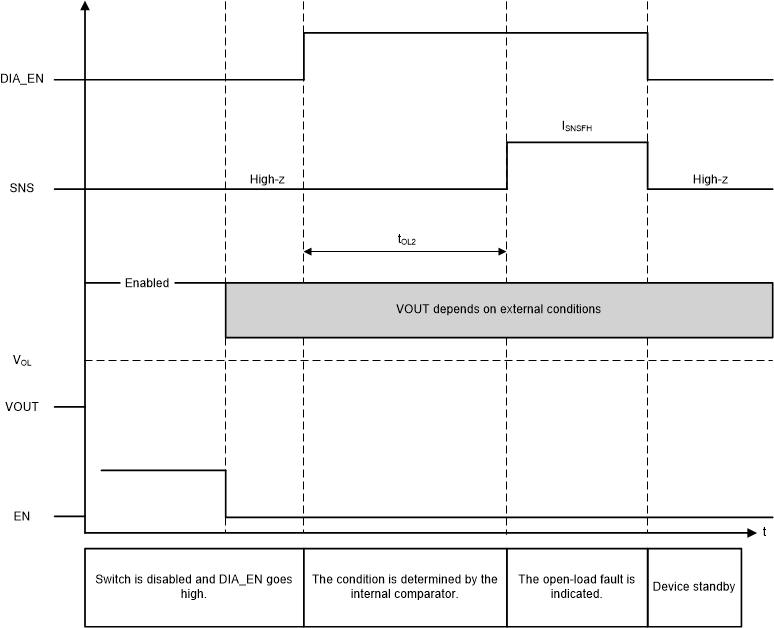 Figure 9-8 Open
Load
Figure 9-8 Open
Load