ZHCSF57 June 2016 TPS51200-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Sink and Source Regulator (VO Pin)
- 7.3.2 Reference Input (REFIN Pin)
- 7.3.3 Reference Output (REFOUT Pin)
- 7.3.4 Soft-Start Sequencing
- 7.3.5 Enable Control (EN Pin)
- 7.3.6 Powergood Function (PGOOD Pin)
- 7.3.7 Current Protection (VO Pin)
- 7.3.8 UVLO Protection (VIN Pin)
- 7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.10 Tracking Start-up and Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
8.1 Application Information
The TPS51200-EP device is specifically designed to power up the memory termination rail (as shown in Figure 19). The DDR memory termination structure determines the main characteristics of the VTT rail, which is to be able to sink and source current while maintaining acceptable VTT tolerance. See Figure 20 for typical characteristics for a single memory cell.
8.2 Typical VTT DIMM Applications
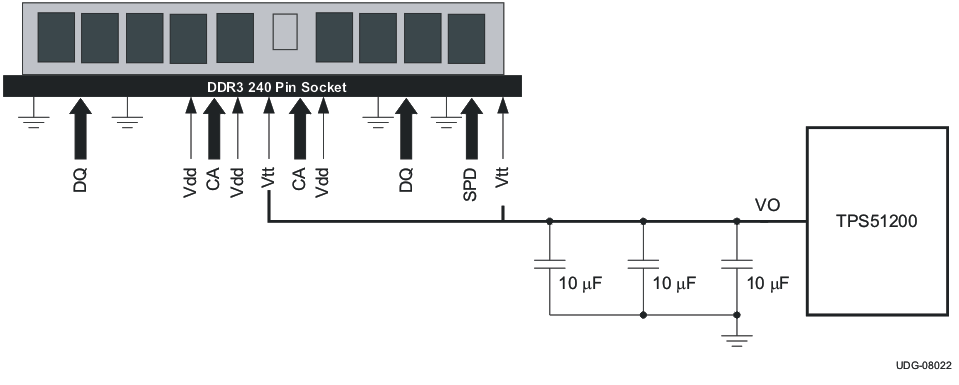 Figure 19. Typical Application Diagram for DDR3 VTT DIMM Using TPS51200-EP
Figure 19. Typical Application Diagram for DDR3 VTT DIMM Using TPS51200-EP
8.2.1 Design Requirements
Use the information listed in Table 1 as the design parameters.
Table 1. DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and LP DDR3 Termination Technology and Differences
| PARAMETER | DDR | DDR2 | DR3 | LOW-POWER DDR3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSB data rates | 200, 266, 333 and 400 MHz | 400, 533, 677 and 800 MHz | 800, 1066, 1330 and 1600 MHz | Same as DDR3 | ||
| Termination | Motherboard termination to VTT for all signals | On-die termination for data group. VTT termination for address, command and control signals. | On-die termination for data group. VTT termination for address, command and control signals. | Same as DDR3 | ||
| Termination current demand | Max sink and source transient currents of up to 2.6 A to 2.9 A | Not as demanding
|
Not as demanding
|
Same as DDR3 | ||
| Voltage level | 2.5-V core and I/O 1.25-V VTT | 1.8-V core and I/O 0.9-V VTT | 1.5-V core and I/O 0.75-V VTT | 1.2-V core and I/O 0.6-V VTT | ||
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
8.2.2.1 Input Voltage Capacitor
Add a ceramic capacitor, with a value between 1-μF and 4.7-μF, placed close to the VIN pin, to stabilize the bias supply (2.5-V rail or 3.3-V rail) from any parasitic impedance from the supply.
8.2.2.2 VLDO Input Capacitor
Depending on the trace impedance between the VLDOIN bulk power supply to the device, a transient increase of source current is supplied mostly by the charge from the VLDOIN input capacitor. Use a 10-μF (or greater) ceramic capacitor to supply this transient charge. Provide more input capacitance as more output capacitance is used at the VO pin. In general, use one-half of the COUT value for input.
8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
For stable operation, the total capacitance of the VO output pin must be greater than 20 μF. Attach 3 × 10-μF ceramic capacitors in parallel to minimize the effect of equivalent series resistance (ESR) and equivalent series inductance (ESL). If the ESR is greater than 2 mΩ, insert an RC filter between the output and the VOSNS input to achieve loop stability. The RC filter time constant should be almost the same as or slightly lower than the time constant of the output capacitor and its ESR.
8.2.2.4 Output Tolerance Consideration for VTT DIMM Applications
Figure 20 shows the typical characteristics for a single memory cell.
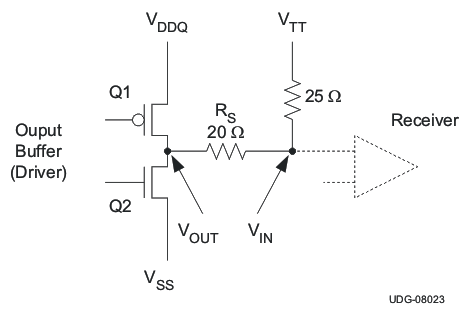 Figure 20. DDR Physical Signal System Bi-Directional SSTL Signaling
Figure 20. DDR Physical Signal System Bi-Directional SSTL Signaling
In Figure 20, when Q1 is on and Q2 is off:
- Current flows from VDDQ via the termination resistor to VTT
- VTT sinks current
In Figure 20, when Q2 is on and Q1 is off:
- Current flows from VTT via the termination resistor to GND
- VTT sources current
Because VTT accuracy has a direct impact on the memory signal integrity, it is imperative to understand the tolerance requirement on VTT. Equation 1 applies to both DC and AC conditions and is based on JEDEC VTT specifications for DDR and DDR2 (JEDEC standard: DDR JESD8-9B May 2002; DDR2 JESD8-15A Sept 2003).
The specification itself indicates that VTT must keep track of VTTREF for proper signal conditioning.
The TPS51200-EP ensures the regulator output voltage to be as shown in Equation 2, which applies to both DC and AC conditions.
where
- –2 A < IVTT < 2 A
The regulator output voltage is measured at the regulator side, not the load side. The tolerance is applicable to DDR, DDR2, DDR3, Low Power DDR3, and DDR4 applications (see Table 1 for detailed information). To meet the stability requirement, a minimum output capacitance of 20 μF is needed. Considering the actual tolerance on the MLCC capacitors, 3 × 10-μF ceramic capacitors sufficiently meet the VTT accuracy requirement.
The TPS51200-EP device uses transconductance (gM) to drive the LDO. The transconductance and output current of the device determine the voltage droop between the reference input and the output regulator. The typical transconductance level is 250 S at 2 A and changes with respect to the load in order to conserve the quiescent current (that is, the transconductance is very low at no load condition). The (gM) LDO regulator is a single pole system. Only the output capacitance determines the unity gain bandwidth for the voltage loop, as a result of the bandwidth nature of the transconductance (see Equation 3).
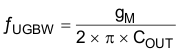
where
- ƒUGBW is the unity gain bandwidth
- gM is transconductance
- COUT is the output capacitance
Consider these two limitations to this type of regulator that come from the output bulk capacitor requirement. In order to maintain stability, the zero location contributed by the ESR of the output capacitors must be greater than the –3-dB point of the current loop. This constraint means that higher ESR capacitors should not be used in the design. In addition, the impedance characteristics of the ceramic capacitor should be well understood in order to prevent the gain peaking effect around the transconductance (gM) –3-dB point because of the large ESL, the output capacitor, and the parasitic inductance of the VO pin voltage trace.
8.2.3 Application Curves
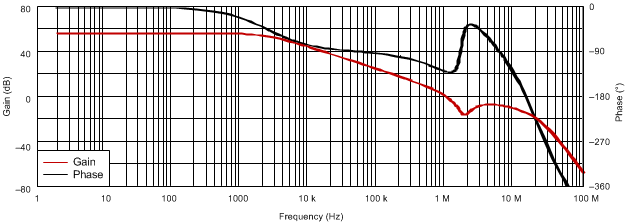
Figure 21 shows the bode plot simulation for this DDR3 design example of the TPS51200-EP device.
The unity-gain bandwidth is approximately 1 MHz and the phase margin is 52°. When the 0-dB level is crossed, the gain peaks because of the ESL effect. However, the peaking maintains a level well below 0 dB.
Figure 22 shows the load regulation and Figure 23 shows the transient response for a typical DDR3 configuration. When the regulator is subjected to ±1.5-A load step and release, the output voltage measurement shows no difference between the DC and AC conditions.
| VIN = 3.3 V | VVLDOIN = 1.5 V | VVO = 0.75 V | |
| IIO = 2 A | 3 × 10-μF capacitors | ESR = 2.5 mΩ | |
| ESL = 800 pH |
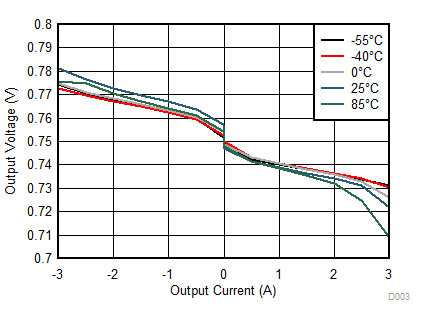
| VVIN = 3.3 V | DDR3 |
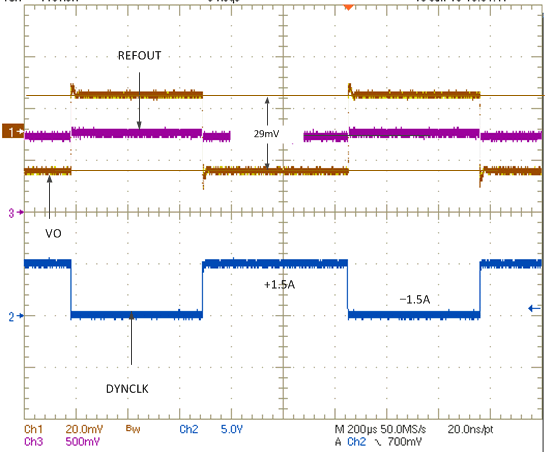 Figure 23. Transient Waveform
Figure 23. Transient Waveform
8.3 System Examples
8.3.1 3.3-VIN, DDR2 Configuration
This design example describes a 3.3-VIN, DDR2 configuration application.
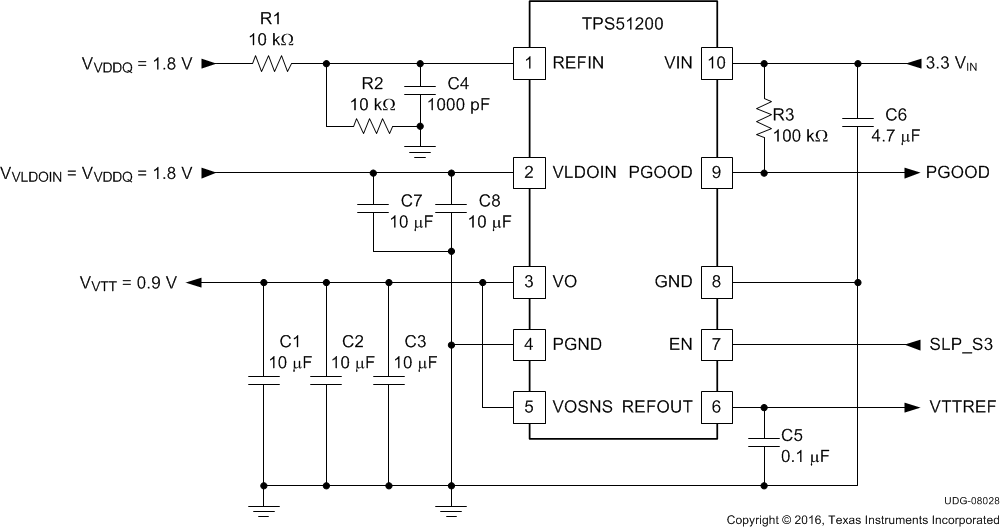 Figure 24. 3.3-VIN, DDR2 Configuration
Figure 24. 3.3-VIN, DDR2 Configuration
Table 2. 3.3-VIN, DDR2 Configuration List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 10 kΩ | ||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
8.3.2 2.5-VIN, DDR3 Configuration
This design example describes a 2.5-VIN, DDR3 configuration application.
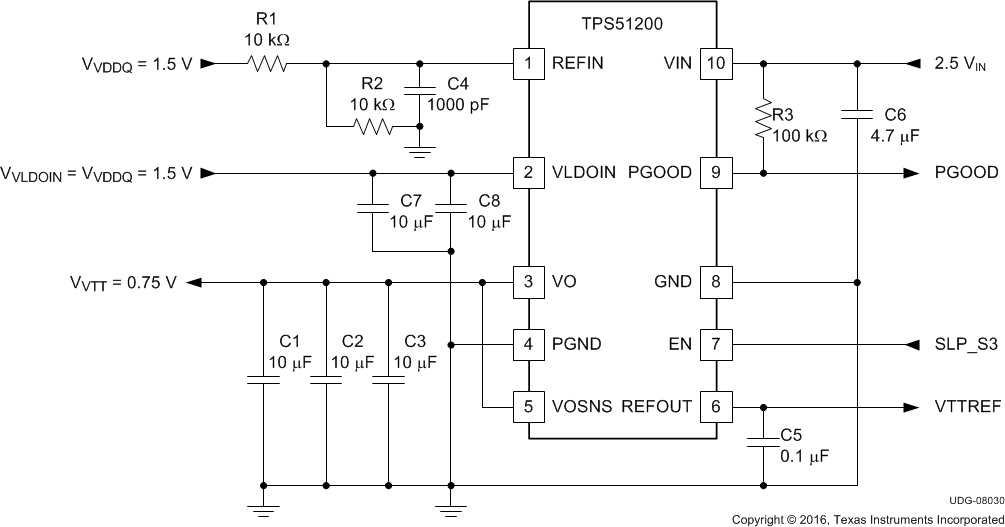 Figure 25. 2.5-VIN, DDR3 Configuration
Figure 25. 2.5-VIN, DDR3 Configuration
Table 3. 2.5-VIN, DDR3 Configuration List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 10 kΩ | ||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
8.3.3 3.3-VIN, LP DDR3 or DDR4 Configuration
This design example describes a 3.3-VIN, LP DDR3 or DDR4 configuration application.
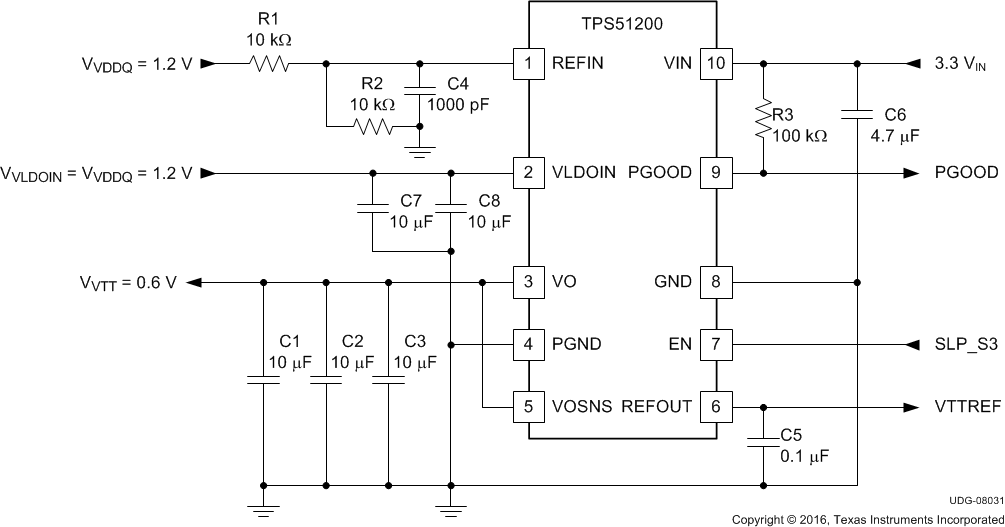 Figure 26. 3.3-VIN, LP DDR3 or DDR4 Configuration
Figure 26. 3.3-VIN, LP DDR3 or DDR4 Configuration
Table 4. 3.3-VIN, LP DDR3 or DDR4 Configuration List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 10 kΩ | ||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
8.3.4 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Tracking Configuration
This design example describes a 3.3-VIN, DDR3 tracking configuration application.
Table 5. 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Tracking Configuration List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 10 kΩ | ||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
8.3.5 3.3-VIN, LDO Configuration
This design example describes a 3.3-VIN, LDO configuration application.
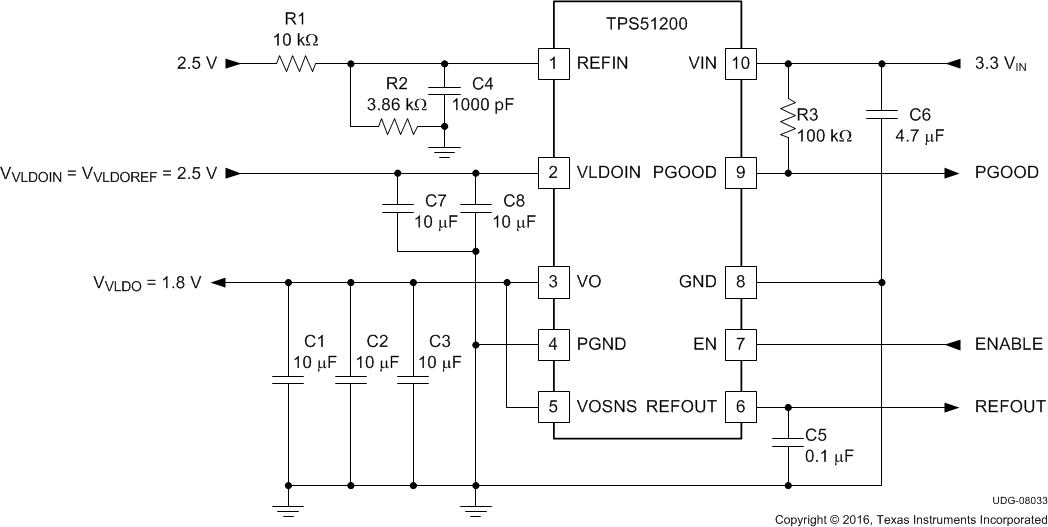 Figure 28. 3.3-VIN, LDO Configuration
Figure 28. 3.3-VIN, LDO Configuration
Table 6. 3.3-VIN, LDO Configuration List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Resistor | 3.86 kΩ | ||
| R2 | 10 kΩ | |||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
8.3.6 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Configuration with LFP
This design example describes a 3.3-VIN, DDR3 configuration with LFP application.
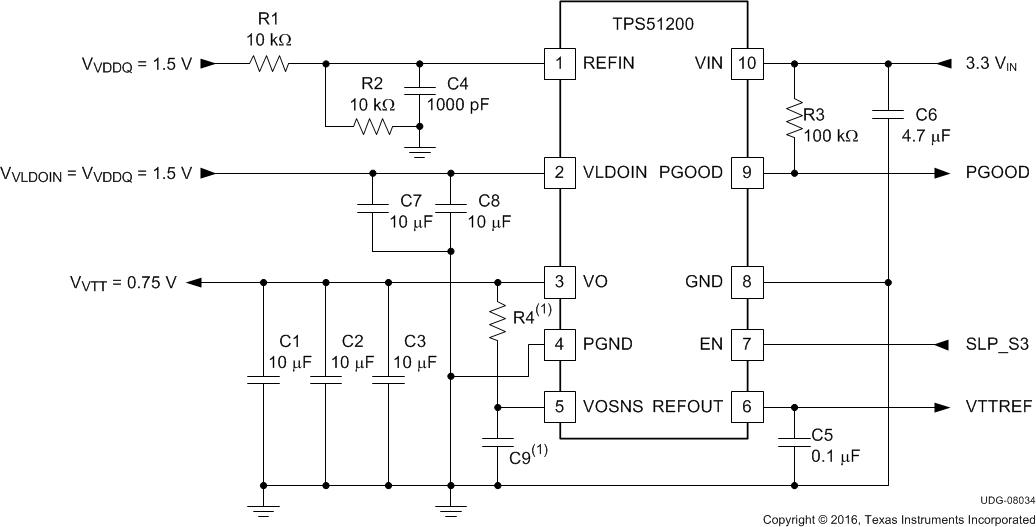 Figure 29. 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Configuration with LFP
Figure 29. 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Configuration with LFP
Table 7. 3.3-VIN, DDR3 Configuration with LFP List of Materials
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | SPECIFICATION | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1, R2 | Resistor | 10 kΩ | ||
| R3 | 100 kΩ | |||
| R4(1) | ||||
| C1, C2, C3 | Capacitor | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata |
| C4 | 1000 pF | |||
| C5 | 0.1 μF | |||
| C6 | 4.7 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR60J475KA11L | Murata | |
| C7, C8 | 10 μF, 6.3 V | GRM21BR70J106KE76L | Murata | |
| C9(1) |