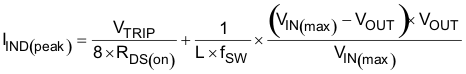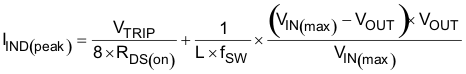ZHCSTR3B December 2010 – November 2023 TPS53315
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 D-CAP™ Integrated Circuit with Adaptive On-Time
- 6.3.2 Small Signal Model
- 6.3.3 Ramp Signal
- 6.3.4 Auto-Skip Eco-mode Light Load Operation
- 6.3.5 Adaptive Zero Crossing
- 6.3.6 Forced Continuous Conduction Mode
- 6.3.7 Power Good
- 6.3.8 Current Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 6.3.9 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 6.3.10 UVLO Protection
- 6.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1
Typical Application Circuit Diagram
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Step 1: Select Operation Mode and Soft-Start Time
- 7.2.1.2.2 Step 2: Select Switching Frequency
- 7.2.1.2.3 Step 3: Select the Inductance
- 7.2.1.2.4 Step 4: Select Output Capacitors
- 7.2.1.2.5 Step 5: Determine the Voltage-Divider Resistance (R1 and R2)
- 7.2.1.2.6 Step 6: Select the Overcurrent Resistance (RTRIP)
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 7.2.2 Typical Application Circuit Diagram With Ceramic Output Capacitors
- 7.2.1
Typical Application Circuit Diagram
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.1.2.3 Step 3: Select the Inductance
The inductance value must be determined to give the ripple current of approximately 1/4 to 1/2 of maximum output current. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage and improves signal-to-noise ratio and helps make sure of stable operation, but increases inductor core loss. Using 1/3 ripple current to maximum output current ratio, the inductance can be determined by Equation 6.
The inductor requires a low DCR to achieve good efficiency. It also requires enough room above peak inductor current before saturation. The peak inductor current can be estimated in Equation 7.
Equation 6. 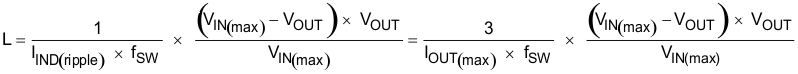
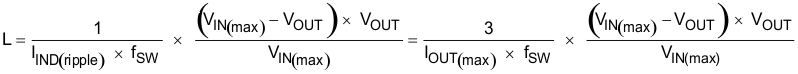
Equation 7.