ZHCS453D August 2011 – April 2021 TPS53353
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 5-V LDO and VREG Start-Up
- 7.3.2 Adaptive On-Time D-CAP™ Control and Frequency Selection
- 7.3.3 Ramp Signal
- 7.3.4 Adaptive Zero Crossing
- 7.3.5 Power-Good
- 7.3.6 Current Sense, Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection
- 7.3.7 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.8 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
8.2.2.2.1 External Component Selection
Refer to Section 8.2.2.2.2 for guidelines for this design with all ceramic output capacitors.
The external components selection is a simple process when using organic semiconductors or special polymer output capacitors.
- Select Operation Mode and Soft-Start Time
Select operation mode and soft-start time using Table 7-3.
- Select Switching Frequency
Select the switching frequency from 250 kHz to 1 MHz using Table 7-1.
- Choose The Inductor
The inductance value should be determined to give the ripple current of approximately 1/4 to 1/2 of maximum output current. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage and improves signal-to-noise ratio and helps ensure stable operation, but increases inductor core loss. Using 1/3 ripple current to maximum output current ratio, the inductance can be determined by Equation 8.
Equation 13.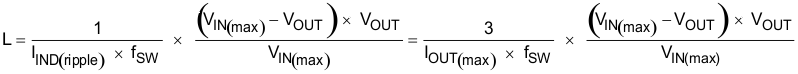
The inductor requires a low DCR to achieve good efficiency. It also requires enough room above peak inductor current before saturation. The peak inductor current can be estimated in Equation 9.
Equation 14.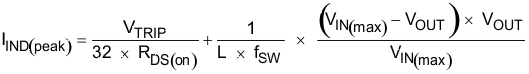
- External Component Selection with All Ceramic
Output Capacitors
Refer to Section 8.2.2.2.2 to select external components because ceramic output capacitors are used in this design.
- Choose the Overcurrent Setting Resistor
The overcurrent setting resistor, RTRIP, can be determined by Equation 15.
Equation 15.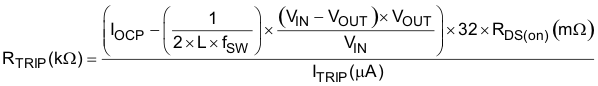
where
- ITRIP is the TRIP pin sourcing current (10 µA).
- RDS(on) is the thermally compensated on-time resistance value of the low-side MOSFET.
Use an RDS(on) value of 1.6 mΩ for an overcurrent level of approximately 20 A. Use an RDS(on) value of
1.7 mΩ for overcurrent level of approximately 10 A. - BST Resistor Selection
The recommended BST resistor value is 2 Ω and anything larger than 5.1 Ω is not recommended. Note that when the gate drive turns on, the voltage on the boot-strap capacitor splits between the internal pull-up resistance and the boot-strap resistance, with the internal circuits only seeing the portion across the internal pull-up resistance. Therefore, when the external resistor gets larger than the pull-up resistance, it crashes the head-room of the SW to BOOT logic, which can cause logic issues with the high-side gate driver.