ZHCSF14D March 2010 – October 2018 TPS54260
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse-Skip Eco-Mode
- 7.3.4 Low-Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.7 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.8 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.9 Slow-Start / Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 7.3.10 Overload Recovery Circuit
- 7.3.11 Sequencing
- 7.3.12 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.13 Overcurrent Protection and Frequency Shift
- 7.3.14 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 7.3.15 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.16 Powergood (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.17 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.18 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.20 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.21 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
3.3-V Output Application
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.7 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.9 Undervoltage Lock Out Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.10 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.1.2.12 Discontinuous Mode and Eco-Mode Boundary
- 8.2.1.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Inverting Power Supply
- 8.2.3 Split-Rail Power Supply
- 8.2.4 12-V to 3.8-V GSM Power Supply
- 8.2.5 24-V to 4.2-V GSM Power Supply
- 8.2.1
3.3-V Output Application
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.3.8 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
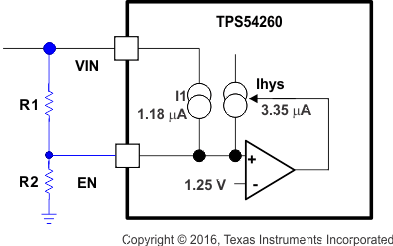
The TPS54260 is disabled when the VIN pin voltage falls below 2.5 V. If an application requires a higher undervoltage lockout (UVLO), use the EN pin as shown in Figure 27 to adjust the input voltage UVLO by using the two external resistors. Though it is not necessary to use the UVLO adjust registers, for operation it is highly recommended to provide consistent power-up behavior. The EN pin has an internal pullup current source, I1, of 0.9μA that provides the default condition of the TPS54260 operating when the EN pin floats. Once the EN pin voltage exceeds 1.25 V, an additional 2.9 μA of hysteresis, Ihys, is added. This additional current facilitates input voltage hysteresis. Use Equation 2 to set the external hysteresis for the input voltage. Use Equation 3 to set the input start voltage.

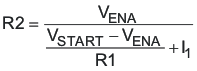
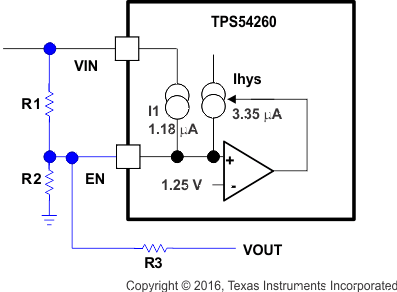
Another technique to add input voltage hysteresis is shown in Figure 28. This method may be used, if the resistance values are high from the previous method and a wider voltage hysteresis is needed. The resistor R3 sources additional hysteresis current into the EN pin.
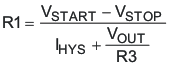
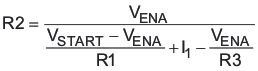
Do not place a low-impedance voltage source with greater than 5 V directly on the EN pin. Do not place a capacitor directly on the EN pin if VEN > 5 V when using a voltage divider to adjust the start and stop voltage. The node voltage, (see Figure 29) must remain equal to or less than 5.8 V. The zener diode can sink up to
100 µA. The EN pin voltage can be greater than 5 V if the VIN voltage source has a high impedance and does not source more than 100 µA into the EN pin.
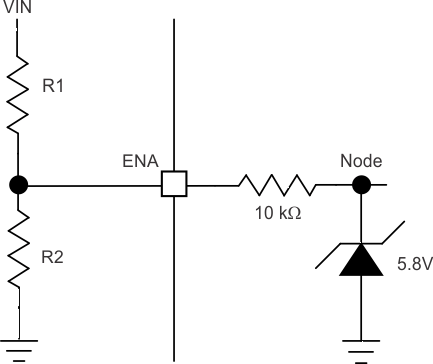 Figure 29. Node Voltage
Figure 29. Node Voltage