ZHCSI26C August 2010 – April 2018 TPS54320
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Current Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN and Power VIN Pins (VIN and PVIN)
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.6 Safe Start-up into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.7 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.9 Enable and Adjusting UVLO
- 7.3.10 Slow Start (SS/TR)
- 7.3.11 Power Good (PWRGD)
- 7.3.12 Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.13 Sequencing (SS/TR)
- 7.3.14 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Operating Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Slow-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 UVLO Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage Feedback Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation Component Selection
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.3.18 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
Figure 29 is a simple small signal model that can be used to understand how to design the frequency compensation. The device's power stage can be approximated to a voltage controlled current source (duty cycle modulator) supplying current to the output capacitor and load resistor. The control to output transfer function is shown in Equation 9 and consists of a dc gain, one dominant pole, and one equivalent series resistance (ESR) zero. The quotient of the change in switch current and the change in COMP pin voltage (node c in Figure 28) is the power stage transconductance (gmps), which is 12 A/V for the device. The DC gain of the power stage is the product of gmps and the load resistance (RL), as shown in Equation 10 with resistive loads. As the load current increases, the DC gain decreases. This variation with load may seem problematic at first glance, but fortunately the dominant pole moves with load current (see Equation 11). The combined effect is highlighted by the dashed line in Figure 30. As the load current decreases, the gain increases and the pole frequency lowers, keeping the 0-dB crossover frequency the same for the varying load conditions, which makes it easier to design the frequency compensation.
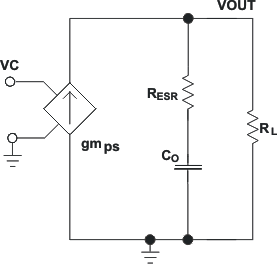 Figure 29. Simplified Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
Figure 29. Simplified Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
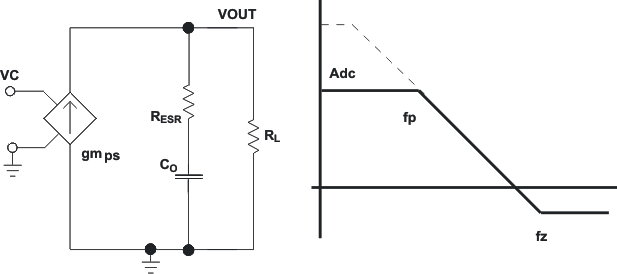 Figure 30. Simplified Frequency Response for Peak Current Mode Control
Figure 30. Simplified Frequency Response for Peak Current Mode Control
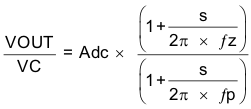
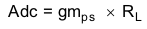
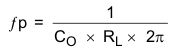
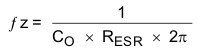
where
- gmea is the GM amplifier gain (1300 μA/V).
- gmps is the power stage gain (12 A/V).
- RL is the load resistance.
- CO is the output capacitance.
- RESR is the equivalent series resistance of the output capacitor.