ZHCSC58C March 2013 – March 2017 TPS54560
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Pulse Skip Eco-mode
- 7.3.4 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Internal Soft-Start
- 7.3.9 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK) Terminal)
- 7.3.10 Accurate Current Limit Operation and Maximum Switching Frequency
- 7.3.11 Synchronization to RT/CLK Terminal
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.14 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.15 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 7.3.16 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Minimum Input Voltage, VIN
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.2.12 Discontinuous Conduction Mode and Eco-mode Boundary
- 8.2.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.3 Inverting Power
- 8.4 Split Rail Power Supply
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Layout is a critical portion of good power supply design. There are several signal paths that conduct fast changing currents or voltages that can interact with stray inductance or parasitic capacitance to generate noise or degrade performance.
- To reduce parasitic effects, the VIN terminal should be bypassed to ground with a low ESR ceramic bypass capacitor with X5R or X7R dielectric.
- Care should be taken to minimize the loop area formed by the bypass capacitor connections, the VIN terminal, and the anode of the catch diode.
- The GND terminal should be tied directly to the power pad under the IC and the PowerPAD™.
- The PowerPAD™ should be connected to internal PCB ground planes using multiple vias directly under the IC.
- The SW terminal should be routed to the cathode of the catch diode and to the output inductor.
- Since the SW connection is the switching node, the catch diode and output inductor should be located close to the SW terminals, and the area of the PCB conductor minimized to prevent excessive capacitive coupling.
- For operation at full rated load, the top side ground area must provide adequate heat dissipating area.
- The RT/CLK terminal is sensitive to noise so the RT resistor should be located as close as possible to the IC and routed with minimal lengths of trace.
- The additional external components can be placed approximately as shown.
- It may be possible to obtain acceptable performance with alternate PCB layouts, however this layout has been shown to produce good results and is meant as a guideline.
10.2 Layout Examples
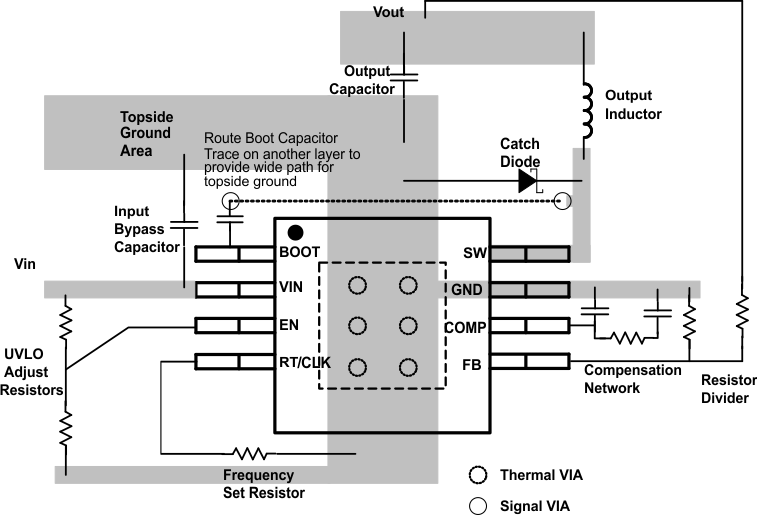 Figure 58. PCB Layout Example
Figure 58. PCB Layout Example
10.2.1 Estimated Circuit Area
Boxing in the components in the design of Figure 33 the estimated printed circuit board area is 1.025 in2 (661 mm2). This area does not include test points or connectors.