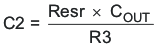ZHCSLU7A September 2020 – August 2021 TPS54618C-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation and Output Current
- 7.3.3 Bootstrap Voltage (Boot) and Low Dropout Operation
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.8 Soft-Start Pin
- 7.3.9 Sequencing
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.12 Frequency Shift
- 7.3.13 Reverse Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.14 Synchronize Using the RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.15 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.16 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.17 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Step One: Select the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Step Two: Select the Output Inductor
- 8.2.2.3 Step Three: Choose the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Step Four: Select the Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Step Five: Choose the Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Step Six: Select the Bootstrap Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Step Eight: Select Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors
- 8.2.2.8 Step Nine: Select Loop Compensation Components
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.2 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
The TPS54618C-Q1 uses a transconductance amplifier for the error amplifier and readily supports two of the commonly used frequency compensation circuits. The compensation circuits are shown in Figure 7-14. The Type-2 circuits are most likely implemented in high-bandwidth power supply designs using low-ESR output capacitors. In Type 2A, one additional high-frequency pole is added to attenuate high-frequency noise.
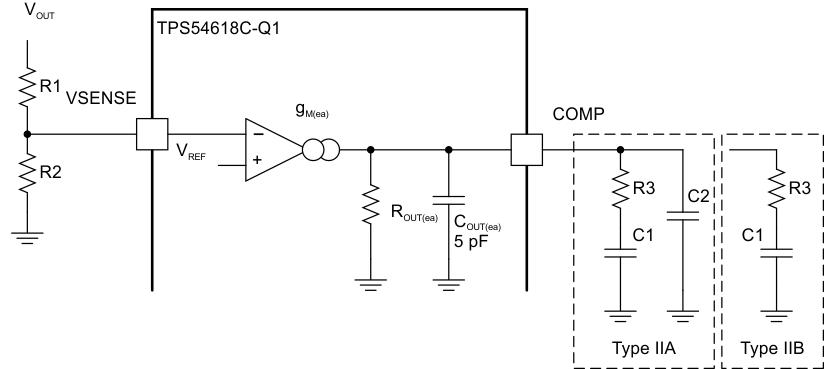 Figure 7-14 Types of Frequency Compensation
Figure 7-14 Types of Frequency CompensationThe design guidelines for TPS54618C-Q1 loop compensation are as follows:
- The modulator pole, fpmod, and the esr zero, fz1,
must be calculated using Equation 15 and Equation 16. Derating the output capacitor (COUT) can be needed if the output
voltage is a high percentage of the capacitor rating. Use the capacitor
manufacturer information to derate the capacitor value. Use Equation 17 and Equation 18 to estimate a starting point for the crossover frequency, fc. Equation 17 is the geometric mean of the modulator pole and the esr zero and Equation 18 is the mean of modulator pole and the switching frequency. Use the lower
value of Equation 17 or Equation 18 as the maximum crossover frequency. Equation 15.
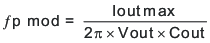 Equation 16.
Equation 16.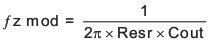 Equation 17.
Equation 17. Equation 18.
Equation 18.
- R3 can be determined by Equation 19:
Equation 19.
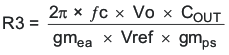
where
- the gmea amplifier gain (245 μA/V)
- gmps is the power stage gain (25 A/V)
- Place a compensation zero at the dominant pole:
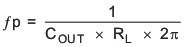
C1 can be determined by Equation 20:Equation 20.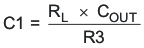
- C2 is optional. It can be used to cancel the zero from the ESR of COUT.
Equation 21.