ZHCSOA1A July 2021 – July 2021 TPS548B27
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Internal VCC LDO and Using External Bias on VCC Pin
- 7.3.2 Enable
- 7.3.3 Output Voltage Setting
- 7.3.4 Internal Fixed Soft Start and External Adjustable Soft Start
- 7.3.5 External REFIN For Output Voltage Tracking
- 7.3.6 Frequency and Operation Mode Selection
- 7.3.7 D-CAP3 Control
- 7.3.8 Low-Side FET Zero-Crossing
- 7.3.9 Current Sense and Positive Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.10 Low-Side FET Negative Current Limit
- 7.3.11 Power Good
- 7.3.12 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.13 Out-Of-Bounds (OOB) Operation
- 7.3.14 Output Voltage Discharge
- 7.3.15 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Output Voltage Setting Point
- 8.2.2.2 Choose the Switching Frequency and the Operation Mode
- 8.2.2.3 Choose the Inductor
- 8.2.2.4 Set the Current Limit (TRIP)
- 8.2.2.5 Choose the Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Choose the Input Capacitors (CIN)
- 8.2.2.7 Soft-Start Capacitor (SS/REFIN Pin)
- 8.2.2.8 EN Pin Resistor Divider
- 8.2.2.9 VCC Bypass Capacitor
- 8.2.2.10 BOOT Capacitor
- 8.2.2.11 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10布局
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.9 Current Sense and Positive Overcurrent Protection
For a buck converter, during the on time of the high-side FET, the switch current increases at a linear rate determined by input voltage, output voltage, the on time, and the output inductor value. During the on time of the low-side FET, this current decreases linearly. The average value of the switch current equals to the load current.
The output overcurrent limit (OCL) in the TPS548B27 device is implemented using a cycle-by-cycle valley current detect control circuit. The inductor current is monitored during the on time of the low-side FET by measuring the low-side FET drain-to-source current. If the measured drain-to-source current of the low-side FET is above the current limit threshold, the low-side FET stays ON until the current level becomes lower than the current limit threshold. This type of behavior reduces the average output current sourced by the device. During an overcurrent condition, the current to the load exceeds the current to the output capacitors. Thus, the output voltage tends to decrease. Eventually, when the output voltage falls below the undervoltage-protection threshold (80%), the UVP comparator detects it and shuts down the device after a wait time of 68 µs. The device then enters a hiccup sleep period for approximately 14 ms. After this waiting period, the device attempts to start up again. Figure 7-4 shows the cycle-by-cycle valley current limit behavior as well as the wait time before the device shuts down.
If an OCL condition happens during start-up, the device still has cycle-by-cycle current limit based on low-side valley current. After soft start is finished, the UV event which is caused by the OC event, shuts down the device and enters Hiccup mode with a wait time of 68 µs.
The resistor, RTRIP, connected from the TRIP pin to AGND sets current limit threshold. A ±1% tolerance resistor is highly recommended because a worse tolerance resistor provides less accurate OCL threshold. Equation 4 calculates the RTRIP for a given overcurrent limit threshold on the device. To simplify the calculation, use a constant, KOCL, to replace the value of 12 × 104. Equation 4 calculates the overcurrent limit threshold for a given RTRIP value. The tolerance of KOCL is listed in Section 6.5 to help the user analyze the tolerance of the overcurrent limit threshold.
To protect the device from unexpected connection on the TRIP pin, an internal fixed OCL clamp is implemented. This internal OCL clamp limits the maximum valley current on LS FET when TRIP pin has too small resistance to AGND, or is accidentally shorted to ground.
where
- IOCLIM is overcurrent limit threshold for load current in A
- RTRIP is TRIP resistor value in Ω
- KOCL is a constant for the calculation
- VIN is input voltage value in V
- VO is output voltage value in V
- L is output inductor value in µH
- fSW is switching frequency in MHz
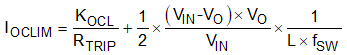
- IOCLIM is overcurrent limit threshold for load current in A
- RTRIP is TRIP resistor value in Ω
- KOCL is a constant for the calculation
- VIN is input voltage value in V
- VO is output voltage value in V
- L is output inductor value in µH
- fSW is switching frequency in MHz
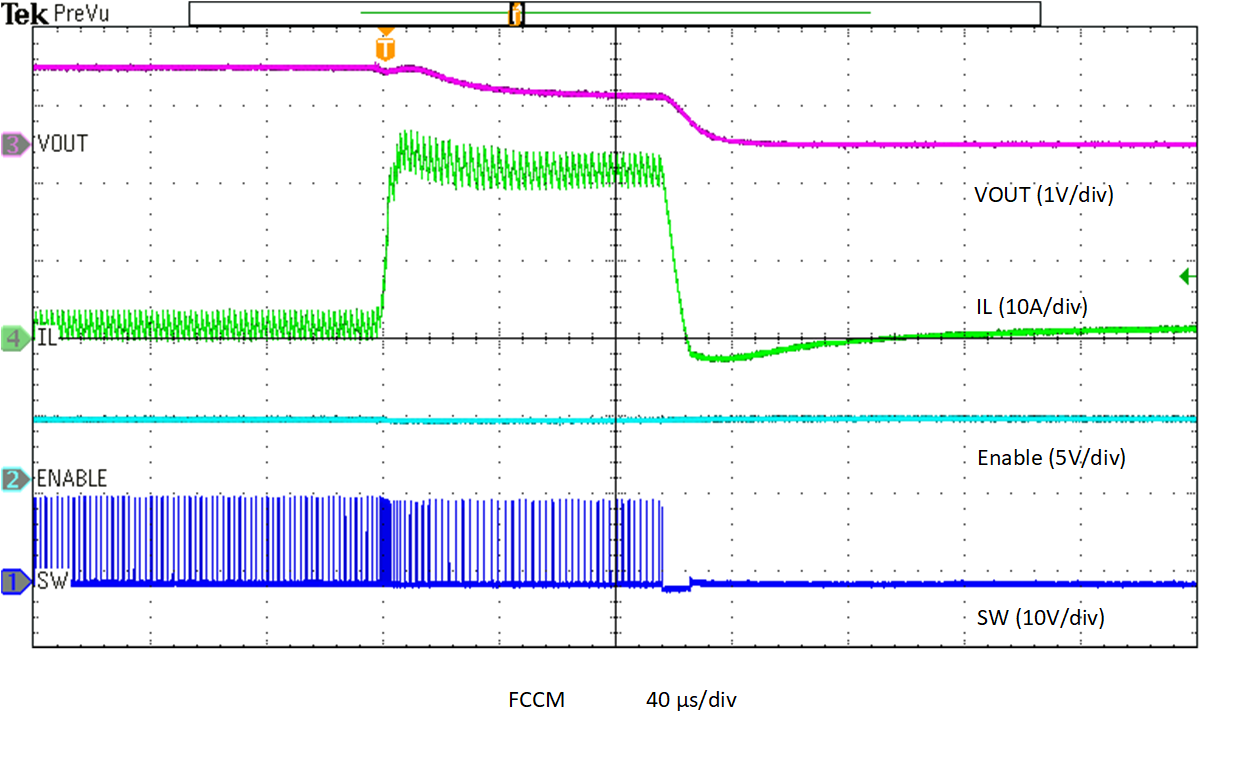 Figure 7-4 Overcurrent Protection
Figure 7-4 Overcurrent Protection