ZHCSFI8C June 2016 – June 2021 TPS62135
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
- 9.4.2 Power Save Mode Operation (PWM/PFM)
- 9.4.3 100% Duty-Cycle Operation
- 9.4.4 HICCUP Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (TPS62135 only)
- 9.4.5 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (TPS621351 only)
- 9.4.6 Soft-Start / Tracking (SS/TR)
- 9.4.7 Output Discharge Function (TPS62135 only)
- 9.4.8 Starting into a Pre-Biased Load (TPS621351 only)
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.1.5 Tracking Function
If a tracking function is desired, the SS/TR pin can be used for this purpose by connecting it to an external tracking voltage. The output voltage tracks that voltage with the typical gain and offset as specified in the electrical characteristics.
When the SS/TR pin voltage is above 0.7 V, the internal voltage is clamped and the device goes to normal regulation. This works for rising and falling tracking voltages with the same behavior, as long as the input voltage is inside the recommended operating conditions. For decreasing SS/TR pin voltage in PFM mode, the device does not sink current from the output. The resulting decrease of the output voltage may therefore be slower than the SS/TR pin voltage if the load is light. When driving the SS/TR pin with an external voltage, do not exceed the voltage rating of the SS/TR pin which is VIN + 0.3 V. The SS/TR pin is internally connected with a resistor to GND when EN = 0.
If the input voltage drops below undervoltage lockout, the output voltage will go to zero, independent of the tracking voltage. Figure 10-1 shows how to connect devices to get ratiometric and simultaneous sequencing by using the tracking function. See also Section 10.3.3 in the systems examples. SS/TR is internally clamped to approximately 3 V.
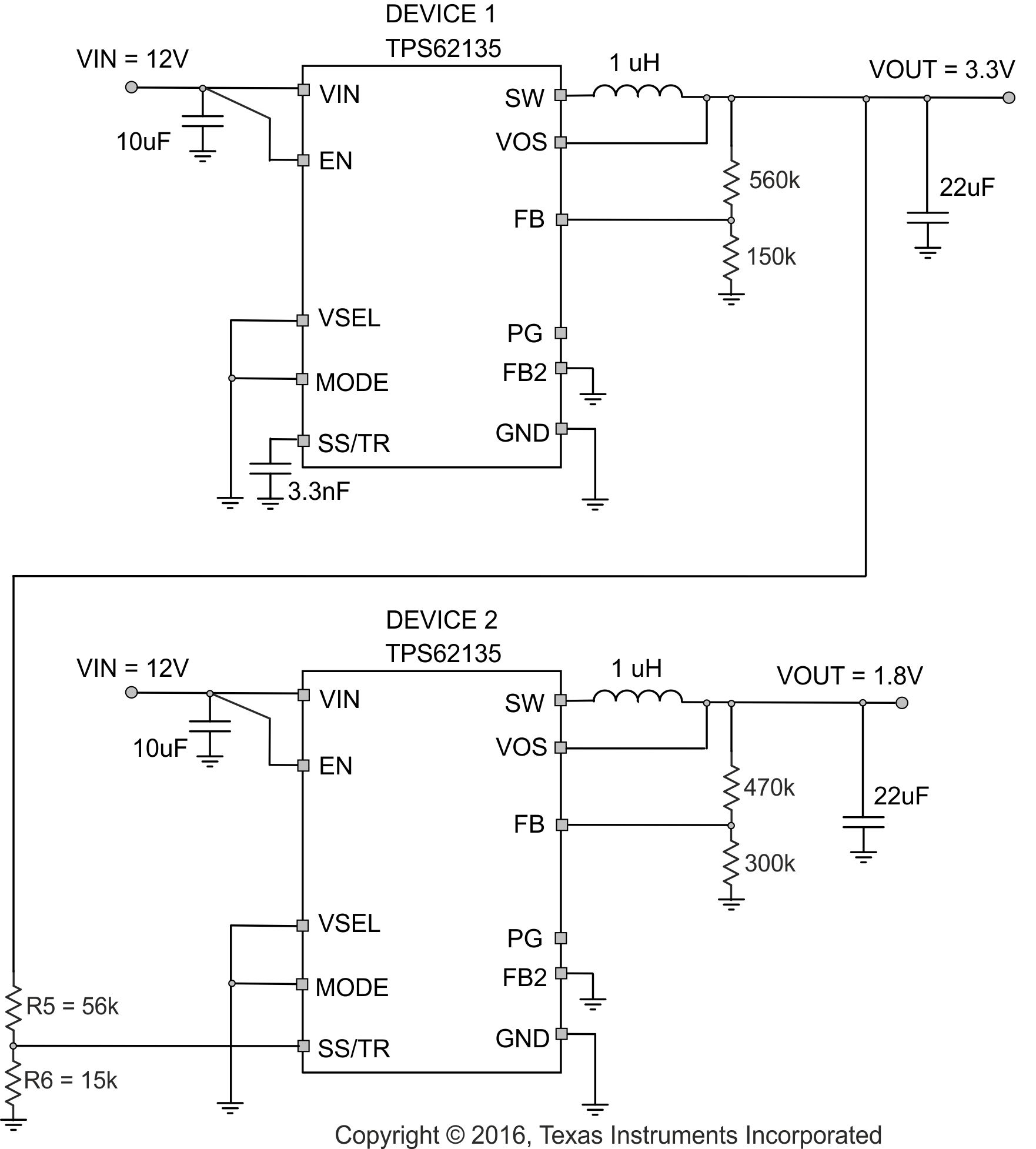 Figure 10-1 Schematic for Ratiometric and Simultaneous Startup
Figure 10-1 Schematic for Ratiometric and Simultaneous StartupThe resistive divider of R5 and R6 can be used to change the ramp rate of VOUT2 to be faster, slower or the same as VOUT1.
A sequential startup is achieved by connecting the PG pin of VOUT of DEVICE 1 to the EN pin of DEVICE2. PG requires a pull-up resistor. Ratiometric start up sequence happens if both supplies are sharing the same Soft-Start capacitor. Equation 12 gives the Soft-Start time, though the SS/TR current has to be doubled. Details about these and other tracking and sequencing circuits are found in SLVA470.
Note: If the voltage at the FB pin is below its typical value of 0.7 V, the output voltage accuracy may have a wider tolerance than specified. The current of 2.5 µA out of the SS/TR pin also has an influence on the tracking function, especially for high resistive external voltage dividers on the SS/TR pin.