-
具有 DCS-Control™ 的 TPS6217x 3V 至 17V 0.5A 降压转换器
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Voltage Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 System Examples
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
- 重要声明
具有 DCS-Control™ 的 TPS6217x 3V 至 17V 0.5A 降压转换器
1 特性
- DCS-Control™拓扑技术
- 输入电压范围为 3V 至 17V
- 输出电流高达 500mA
- 可调输出电压范围为 0.9V 至 6V
- 固定输出电压版本
- 无缝省电模式转换
- 静态电流典型值为 17µA
- 电源正常输出
- 100% 占空比模式
- 短路保护
- 过热保护
- 与 TPS62160 和 TPS62125 引脚兼容
- 采用 2mm x 2mm、8 引脚晶圆级小外形无引线 (WSON) 封装
- 结合使用 TPS62170 和 WEBENCH® 电源设计器创建定制设计方案
2 应用
- 标准 12V 导轨式电源
- 单一或者多个锂离子电池供电的负载点 (POL) 电源
- 低压降稳压器 (LDO) 替代米6体育平台手机版_好二三四
- 嵌入式系统
- 数码相机、数码摄像机
- 移动电脑、平板电脑、调制解调器
3 说明
TPS6217x 器件系列是易于使用的同步降压 DC-DC 转换器,针对 高功率密度的应用 进行了优化。该系列器件的开关频率典型值高达 2.25MHz,允许使用小型电感器,通过利用 DCS-Control™ 拓扑技术提供快速瞬态响应并实现高输出电压精度。
该系列器件具有 3V 至 17V 宽运行输入电压范围,非常适用于由锂离子或其他电池以及 12V 中间电源轨供电的系统。其输出电压为 0.9V 至 6V,支持高达 0.5A 的持续输出电流(使用 100% 占空比模式)。
此外,还可以通过配置使能引脚和开漏电源正常状态引脚实现电源排序。
在节能模式下,器件可根据输入电压 (VIN) 生成约 17μA 的静态电流。负载较小时可自动且无缝进入节能模式,同时该模式可保持整个负载范围内的高效率。该器件在关断模式下处于关断状态,期间的流耗低于 2μA。
此器件提供了可调节输出电压和固定输出电压版本,采用 2mm x 2mm 8 引脚 WSON 封装 (DSG)。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS6217x | WSON (8) | 2.00mm x 2.00mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购米6体育平台手机版_好二三四附录。
典型应用电路原理图
效率与输出电流间的关系
4 修订历史记录
Changes from D Revision (October 2014) to E Revision
- Added WEBENCH® 设计器链接Go
- Added "SW (AC), less than 10ns" specification to Absolute Maximum Ratings table Go
- Changed TJ MAX spec from "125" to "150" Go
- Changed Electrical Characteristics Conditions from "free-air temperature range" to "junction temperature range" Go
- Added IQ and ISD specifications Go
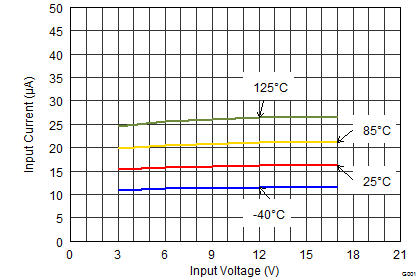
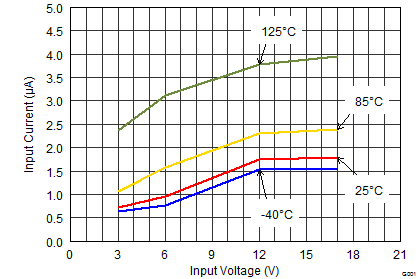
- Added 125°C plot line in Figure 1 and Figure 4 Typical Characteristics graphic entities. Go
- Added Power Good Pin Logic Table Go
Changes from C Revision (August 2013) to D Revision
- Added 引脚配置和功能部分,ESD 额定值表,特性 说明 部分、器件功能模式、应用和实施 部分、电源相关建议 部分、布局 部分、器件和文档支持 部分以及机械、封装和可订购信息 部分Go
Changes from B Revision (August 2013) to C Revision
- Changed 50mV/μs to 50mV/s in Enable and Shutdown (EN) section Go
Changes from A Revision (April 2012) to B Revision
Changes from * Revision (November 2011) to A Revision
5 Device Voltage Options
| OUTPUT VOLTAGE(1) | PART NUMBER | PACKAGE |
|---|---|---|
| adjustable | TPS62170 | WSON (8) |
| 1.8 V | TPS62171 | |
| 3.3 V | TPS62172 | |
| 5.0 V | TPS62173 |
6 Pin Configuration and Functions

Pin Functions
| PIN(1) | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | ||
| PGND | 1 | — | Power ground |
| VIN | 2 | IN | Supply voltage |
| EN | 3 | IN | Enable input (High = enabled, Low = disabled) |
| AGND | 4 | — | Analog ground |
| FB | 5 | IN | Voltage feedback of adjustable version. Connect resistive voltage divider to this pin. It is recommended to connect FB to AGND on fixed output voltage versions for improved thermal performance. |
| VOS | 6 | IN | Output voltage sense pin and connection for the control loop circuitry. |
| SW | 7 | OUT | Switch node, which is connected to the internal MOSFET switches. Connect inductor between SW and output capacitor. |
| PG | 8 | OUT | Output power good (High = VOUT ready, Low = VOUT below nominal regulation); open drain (requires pull-up resistor; goes high impedance, when device is switched off) |
| Exposed Thermal Pad | — | Must be connected to AGND. Must be soldered to achieve appropriate power dissipation and mechanical reliability. | |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin voltage range(2) | VIN | –0.3 | 20 | V |
| EN, SW (DC) | –0.3 | VIN+ 0.3 | V | |
| SW (AC), less than 10ns(3) | –2 | 24.5 | ||
| FB, PG, VOS | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| Power good sink current | PG | 10 | mA | |
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 150 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage, VIN | 3 | 17 | V | |
| Output Voltage, VOUT | 0.9 | 6 | V | |
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 125 | °C |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS6217x | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSG (WSON) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 61.8 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 61.3 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 15.5 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.4 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 15.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 8.6 | °C/W |
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Over junction temperature range (TJ = –40°C to +125°C), typical values at VIN = 12 V and TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY | |||||||
| VIN | Input voltage range(1) | 3 | 17 | V | |||
| IQ | Operating quiescent current | EN = High, IOUT = 0 mA, device not switching | 17 | 30 | µA | ||
| TJ = -40°C to +85°C | 17 | 25 | |||||
| ISD | Shutdown current(2) | EN = Low | 1.5 | 25 | µA | ||
| TJ = -40°C to +85°C | 1.5 | 4 | |||||
| VUVLO | Undervoltage lockout threshold | Falling input voltage | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.82 | V | |
| Hysteresis | 180 | mV | |||||
| TSD | Thermal shutdown temperature | rising temperature | 160 | °C | |||
| Thermal shutdown hysteresis | falling temperature | 20 | |||||
| CONTROL (EN, PG) | |||||||
| VEN_H | High level input threshold voltage (EN) | 0.9 | 0.6 | V | |||
| VEN_L | Low level input threshold voltage (EN) | 0.56 | 0.3 | V | |||
| ILKG_EN | Input leakage current (EN) | EN = VIN or GND | 0.01 | 1 | µA | ||
| VTH_PG | Power good threshold voltage | Rising (%VOUT) | 92% | 95% | 98% | ||
| Falling (%VOUT) | 87% | 90% | 93% | ||||
| VOL_PG | Power good output low voltage | IPG = –2 mA | 0.07 | 0.3 | V | ||
| ILKG_PG | Input leakage current (PG) | VPG = 1.8 V | 1 | 400 | nA | ||
| POWER SWITCH | |||||||
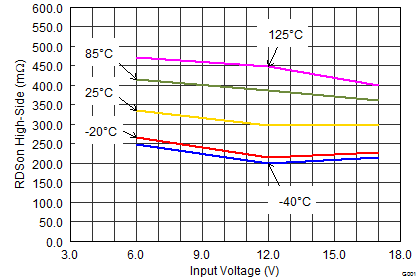
| RDS(ON) | High-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN ≥ 6 V | 300 | 600 | mΩ | ||
| VIN= 3 V | 430 | ||||||
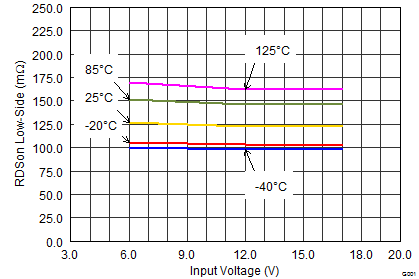
| Low-side MOSFET ON-resistance | VIN≥ 6 V | 120 | 200 | mΩ | |||
| VIN = 3 V | 165 | ||||||
| ILIMF | High-side MOSFET forward current limit(3) | VIN = 12 V, TJ= 25°C | 0.85 | 1.05 | 1.35 | A | |
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| VREF | Internal reference voltage(4) | 0.8 | V | ||||
| ILKG_FB | Pin leakage current (FB) | TPS62170, VFB= 1.2 V | 5 | 400 | nA | ||
| VOUT | Output voltage range (TPS62170) | VIN ≥ VOUT | 0.9 | 6.0 | V | ||
| Initial output voltage accuracy(5) | PWM mode operation, VIN ≥ VOUT + 1 V | –3% | 3% | ||||
| Power save mode operation, COUT= 22 µF | -3.5% | 4% | |||||
| DC output voltage load regulation | VIN = 12 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, PWM mode operation | 0.05 | %/A | ||||
| DC output voltage line regulation | 3 V ≤ VIN ≤ 17 V, VOUT = 3.3 V, IOUT = 0.5 A, PWM mode operation | 0.02 | %/V | ||||
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The TPS6217x synchronous step-down DC-DC converters are based on DCS-Control™ (Direct Control with Seamless transition into power save mode), an advanced regulation topology, that combines the advantages of hysteretic, voltage mode and current mode control including an AC loop directly associated to the output voltage. This control loop takes information about output voltage changes and feeds it directly to a fast comparator stage. It sets the switching frequency, which is constant for steady state operating conditions, and provides immediate response to dynamic load changes. To get accurate DC load regulation, a voltage feedback loop is used. The internally compensated regulation network achieves fast and stable operation with small external components and low ESR capacitors.
The DCS-Control™ topology supports pulse width modulation (PWM) mode for medium and heavy load conditions and a power save mode at light loads. During PWM mode, it operates at its nominal switching frequency in continuous conduction mode. This frequency is typically about 2.25 MHz with a controlled frequency variation depending on the input voltage. If the load current decreases, the converter enters power save mode to sustain high efficiency down to very light loads. In power save mode, the switching frequency decreases linearly with the load current. Since DCS-Control™ supports both operation modes within one single building block, the transition from PWM to power save mode is seamless without effects on the output voltage.
Fixed output voltage versions provide smallest solution size and lowest current consumption, requiring only 3 external components. An internal current limit supports nominal output currents of up to 500 mA.
The TPS6217x family offers both excellent DC voltage and superior load transient regulation, combined with very low output voltage ripple, minimizing interference with RF circuits.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
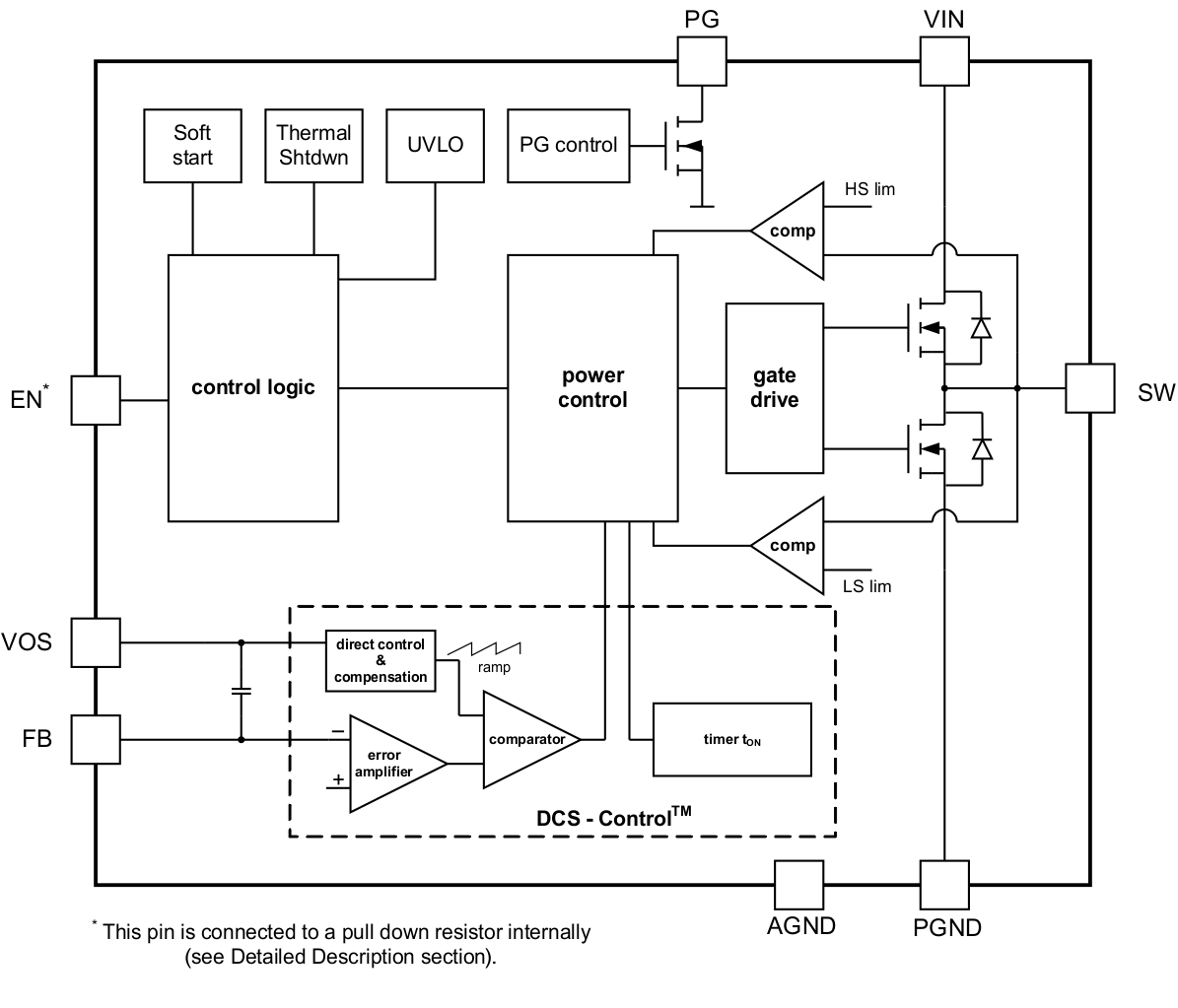 Figure 5. TPS62170 (Adjustable Output Voltage)
Figure 5. TPS62170 (Adjustable Output Voltage)
 Figure 6. TPS62171/TPS62172/TPS62173 (Fixed Output Voltage)
Figure 6. TPS62171/TPS62172/TPS62173 (Fixed Output Voltage)
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Enable and Shutdown (EN)
When enable (EN) is set high, the device starts operation.
Shutdown is forced if EN is pulled low with a shutdown current of typically 1.5 µA. During shutdown, the internal power MOSFETs as well as the entire control circuitry are turned off. The internal resistive divider pulls down the output voltage smoothly. If the EN pin is low, an internal pull-down resistor of about 400 kΩ is connected and keeps it low, to avoid bouncing.
Connecting the EN pin to an appropriate output signal of another power rail provides sequencing of multiple power rails.
8.3.2 Current Limit and Short Circuit Protection
The TPS6217x devices are protected against heavy load and short circuit events. At heavy loads, the current limit determines the maximum output current. If the current limit is reached, the high-side FET is turned off. Avoiding shoot-through current, the low-side FET is switched on to allow the inductor current to decrease. The high-side FET turns on again, only if the current in the low-side FET decreases below the low-side current limit threshold of typically 0.7A.
The output current of the device is limited by the current limit (see Electrical Characteristics). Due to internal propagation delay, the actual current can exceed the static current limit during that time. The dynamic current limit is calculated as follows:
space
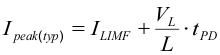
where
- ILIMF is the static current limit, specified in Electrical Characteristics
- L is the inductor value
- VL is the voltage across the inductor
- tPD is the internal propagation delay
space
The dynamic high-side switch peak current is calculated as follows:
space
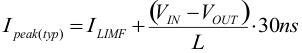
space
Take care with the current limit, if the input voltage is high and very small inductances are used.
8.3.3 Power Good (PG)
The TPS6217x has a built in power good (PG) function to indicate whether the output voltage has reached its appropriate level or not. The PG signal can be used for startup sequencing of multiple rails. The PG pin is an open-drain output that requires a pull-up resistor (to any voltage below 7 V). It can sink 2 mA of current and maintain its specified logic low level. It is high impedance when the device is turned off due to EN, UVLO or thermal shutdown. If not used, the PG pin should be connected to GND but may be left floating.
space
Table 1. Power Good Pin Logic Table
space
8.3.4 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
If the input voltage drops, the under voltage lockout prevents misoperation of the device by switching off both the power FETs. The under voltage lockout threshold is set typically to 2.7 V. The device is fully operational for voltages above the UVLO threshold and turns off if the input voltage trips the threshold. The converter starts operation again once the input voltage exceeds the threshold by a hysteresis of typically 180 mV.
8.3.5 Thermal Shutdown
The junction temperature (Tj) of the device is monitored by an internal temperature sensor. If Tj exceeds 160°C (typical), the device goes into thermal shut down. Both the high-side and low-side power FETs are turned off and PG goes high impedance. When Tj decreases below the hysteresis amount, the converter resumes normal operation, beginning with soft start. To avoid unstable conditions, a hysteresis of typically 20°C is implemented on the thermal shut down temperature.
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Soft Start
The internal soft start circuitry controls the output voltage slope during startup. This avoids excessive inrush current and ensures a controlled output voltage rise time. It also prevents unwanted voltage drops from high-impedance power sources or batteries. When EN is set to start device operation, the device starts switching after a delay of about 50 µs and VOUT rises with a slope of about 25 mV/µs. See Figure 30 and Figure 31 for typical startup operation.
The TPS6217x can start into a pre-biased output. During monotonic pre-biased startup, the low-side MOSFET is not allowed to turn on until the device's internal ramp sets an output voltage above the pre-bias voltage.
8.4.2 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
The TPS6217x operates with pulse width modulation in continuous conduction mode (CCM) with a nominal switching frequency of about 2.25 MHz. The frequency variation in PWM is controlled and depends on VIN, VOUT and the inductance. The device operates in PWM mode as long the output current is higher than half the inductor's ripple current. To maintain high efficiency at light loads, the device enters power save mode at the boundary to discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). This happens if the output current becomes smaller than half the inductor's ripple current.
8.4.3 Power Save Mode Operation
The TPS6217x's built in power save mode is entered seamlessly, if the load current decreases. This secures a high efficiency in light load operation. The device remains in power save mode as long as the inductor current is discontinuous.
In power save mode the switching frequency decreases linearly with the load current maintaining high efficiency. The transition into and out of power save mode happens within the entire regulation scheme and is seamless in both directions.
TPS6217x includes a fixed on-time circuitry. This on-time, in steady-state operation, is estimated as:
space
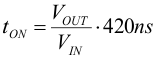
space
For very small output voltages, the on-time increases beyond the result of Equation 3, to stay above an absolute minimum on-time, tON(min), which is around 80 ns, to limit switching losses. The peak inductor current in PSM is approximated by:
space
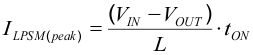
space
When VIN decreases to typically 15% above VOUT, the TPS6217x does not enter power save mode, regardless of the load current. The device maintains output regulation in PWM mode.
8.4.4 100% Duty-Cycle Operation
The duty cycle of the buck converter is given by D = VOUT/VIN and increases as the input voltage comes close to the output voltage. In this case, the device starts 100% duty cycle operation turning on the high-side switch 100% of the time. The high-side switch stays turned on as long as the output voltage is below the internal setpoint. This allows the conversion of small input to output voltage differences, such as for the longest operation time of battery-powered applications. In 100% duty cycle mode, the low-side FET is switched off.
The minimum input voltage to maintain output voltage regulation, depending on the load current and the output voltage level, is calculated as:
space
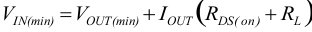
where
- IOUT is the output current
- RDS(on) is the RDS(on) of the high-side FET
- RL is the DC resistance of the inductor used
9 Application and Implementation
NOTE
Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validate and test their design implementation to confirm system functionality.
9.1 Application Information
The TPS6217x device family are easy to use synchronous step-down DC-DC converters optimized for applications with high power density. A high switching frequency of typically 2.25 MHz allows the use of small inductors and provides fast transient response as well as high output voltage accuracy by utilization of the DCS-Control™ topology. With its wide operating input voltage range of 3 V to 17 V, the devices are ideally suited for systems powered from either a Li-Ion or other battery as well as from 12-V intermediate power rails. It supports up to 0.5-A continuous output current at output voltages between 0.9 V and 6 V (with 100% duty cycle mode).
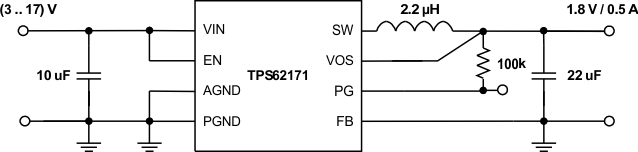
9.2 Typical Application
space
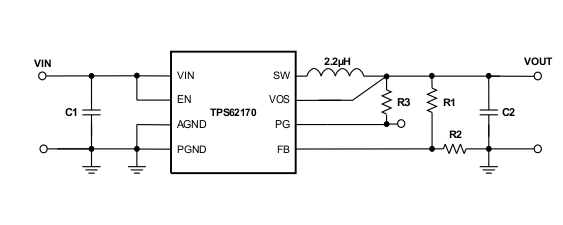 Figure 7. TPS62170 Adjustable Power Supply
Figure 7. TPS62170 Adjustable Power Supply
space
9.2.1 Design Requirements
The design guideline provides a component selection to operate the device within the Recommended Operating Conditions.
9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
9.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
Click here to create a custom design using the TPS62170 device with the WEBENCH® Power Designer.
- Start by entering your VIN, VOUT, and IOUT requirements.
- Optimize your design for key parameters like efficiency, footprint and cost using the optimizer dial and compare this design with other possible solutions from Texas Instruments.
- The WEBENCH Power Designer provides you with a customized schematic along with a list of materials with real time pricing and component availability.
- In most cases, you will also be able to:
- Run electrical simulations to see important waveforms and circuit performance
- Run thermal simulations to understand the thermal performance of your board
- Export your customized schematic and layout into popular CAD formats
- Print PDF reports for the design, and share your design with colleagues
- Get more information about WEBENCH tools at www.ti.com/WEBENCH.
9.2.2.2 Programming the Output Voltage
While the output voltage of the TPS62170 is adjustable, the TPS62171/TPS62172/TPS62173 are programmed to fixed output voltages. For fixed output versions, the FB pin is pulled down internally and may be left floating. it is recommended to connect it to AGND to improve thermal resistance. The adjustable version can be programmed for output voltages from 0.9 V to 6 V by using a resistive divider from VOUT to AGND. The voltage at the FB pin is regulated to 800 mV. The value of the output voltage is set by the selection of the resistive divider from Equation 6. It is recommended to choose resistor values which allow a current of at least 2 uA, meaning the value of R2 should not exceed 400 kΩ. Lower resistor values are recommended for highest accuracy and most robust design. For applications requiring lowest current consumption, the use of fixed output voltage versions is recommended.
spacing
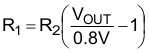
spacing
In case the FB pin gets opened, the device clamps the output voltage at the VOS pin to about 7.4 V.
9.2.2.3 External Component Selection
The external components have to fulfill the needs of the application, but also the stability criteria of the devices control loop. The TPS6217x is optimized to work within a range of external components. The LC output filter's inductance and capacitance have to be considered together, creating a double pole, responsible for the corner frequency of the converter (see Output Filter and Loop Stability). Table 2 can be used to simplify the output filter component selection. Checked cells represent combinations that are proven for stability by simulation and lab test. Further combinations should be checked for each individual application.
space
Table 2. Recommended LC Output Filter Combinations(1)
| 4.7µF | 10µF | 22µF | 47µF | 100µF | 200µF | 400µF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1µH | |||||||
| 2.2µH | √ | √(2) | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 3.3µH | √ | √ | √ | √ | |||
| 4.7µH |
space
More detailed information on further LC combinations can be found in SLVA463.
9.2.2.3.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor selection is affected by several effects like inductor ripple current, output ripple voltage, PWM-to-PSM transition point and efficiency. In addition, the inductor selected has to be rated for appropriate saturation current and DC resistance (DCR). Equation 7 and Equation 8 calculate the maximum inductor current under static load conditions.
spacing
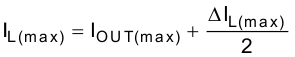
spacing
spacing

where
- IL(max) is the maximum inductor current
- ΔIL is the peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- L(min) is the minimum effective inductor value
- fSW is the actual PWM switching frequency
spacing
Calculating the maximum inductor current using the actual operating conditions gives the minimum saturation current of the inductor needed. A margin of about 20% is recommended to add. A larger inductor value is also useful to get lower ripple current, but increases the transient response time and size as well. Table 3 lists inductors that are recommended for use with the TPS6217x.
Table 3. List of Inductors
| Type | Inductance [µH] | Current [A](1) | Dimensions [L x B x H] mm | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLF3012ST-2R2M1R4 | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.9 A | 3.0 x 2.8 x 1.2 | TDK |
| VLF302512MT-2R2M | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.9 A | 3.0 x 2.5 x 1.2 | TDK |
| VLS252012-2R2 | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.3 A | 2.5 x 2.0 x 1.2 | TDK |
| XFL3012-222MEC | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.9 A | 3.0 x 3.0 x 1.2 | Coilcraft |
| XFL3012-332MEC | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 1.6 A | 3.0 x 3.0 x 1.2 | Coilcraft |
| XPL2010-222MLC | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.3 A | 1.9 x 2.0 x 1.0 | Coilcraft |
| XPL2010-332MLC | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 1.1 A | 1.9 x 2.0 x 1.0 | Coilcraft |
| LPS3015-332ML | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 1.4 A | 3.0 x 3.0 x 1.4 | Coilcraft |
| PFL2512-222ME | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.0 A | 2.8 x 2.3 x 1.2 | Coilcraft |
| PFL2512-333ME | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 0.78 A | 2.8 x 2.3 x 1.2 | Coilcraft |
| 744028003 | 3.3 µH, ±30% | 1.0 A | 2.8 x 2.8 x 1.1 | Wuerth |
| PSI25201B-2R2MS | 2.2 uH, ±20% | 1.3 A | 2.0 x 2.5 x 1.2 | Cyntec |
| NR3015T-2R2M | 2.2 uH, ±20% | 1.5 A | 3.0 x 3.0 x 1.5 | Taiyo Yuden |
| BRC2012T2R2MD | 2.2 µH, ±20% | 1.0 A | 2.0 x 1.25 x 1.4 | Taiyo Yuden |
| BRC2012T3R3MD | 3.3 µH, ±20% | 0.87 A | 2.0 x 1.25 x 1.4 | Taiyo Yuden |
TPS6217x can operate with an inductor as low as 2.2 µH. However, for applications running with low input voltages, 3.3 µH is recommended, to allow the full output current. The inductor value also determines the load current at which power save mode is entered:
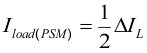
Using Equation 8, this current level is adjusted by changing the inductor value.
9.2.2.4 Capacitor Selection
9.2.2.4.1 Output Capacitor
The recommended value for the output capacitor is 22 µF. The architecture of the TPS6217x allows the use of tiny ceramic output capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR). These capacitors provide low output voltage ripple and are recommended. To keep its low resistance up to high frequencies and to get narrow capacitance variation with temperature, it is recommended to use an X7R or X5R dielectric. Using a higher value can have some advantages like smaller voltage ripple and a tighter DC output accuracy in power save mode (see SLVA463).
Note: In power save mode, the output voltage ripple depends on the output capacitance, its ESR and the peak inductor current. Using ceramic capacitors provides small ESR and low ripple.
9.2.2.4.2 Input Capacitor
For most applications, 10 µF is sufficient and is recommended, though a larger value reduces input current ripple further. The input capacitor buffers the input voltage for transient events and also decouples the converter from the supply. A low ESR multilayer ceramic capacitor is recommended for best filtering and should be placed between VIN and PGND as close as possible to those pins.
spacing
NOTE
DC bias effect: High capacitance ceramic capacitors have a DC bias effect, which has a strong influence on the final effective capacitance. Therefore the right capacitor value has to be chosen carefully. Package size and voltage rating in combination with dielectric material are responsible for differences between the rated capacitor value and the effective capacitance.
spacing
9.2.2.5 Output Filter and Loop Stability
The devices of the TPS6217x family are internally compensated to be stable with L-C filter combinations corresponding to a corner frequency calculated with Equation 10:
space
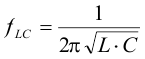
space
Proven nominal values for inductance and ceramic capacitance are given in Table 2 and are recommended for use. Different values may work, but care has to be taken on the loop stability which is affected. More information including a detailed L-C stability matrix is found in SLVA463.
The TPS6217x devices, both fixed and adjustable versions, include an internal 25 pF feed forward capacitor, connected between the VOS and FB pins. This capacitor impacts the frequency behavior and sets a pole and zero in the control loop with the resistors of the feedback divider, per Equation 11 and Equation 12:
space
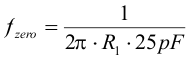
space
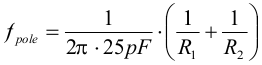
space
Though the TPS6217x devices are stable without the pole and zero being in a particular location, adjusting their location to the specific needs of the application can provide better performance in power save mode and/or improved transient response. An external feed-forward capacitor can also be added. A more detailed discussion on the optimization for stability vs. transient response can be found in SLVA289 and SLVA466.
If using ceramic capacitors, the DC bias effect has to be considered. The DC bias effect results in a drop in effective capacitance as the voltage across the capacitor increases (see NOTE in Capacitor selection section).
9.2.2.6 TPS6216x Components List
Table 4 shows the list of components for the Application Curves.
Table 4. List of Components
9.2.3 Application Curves
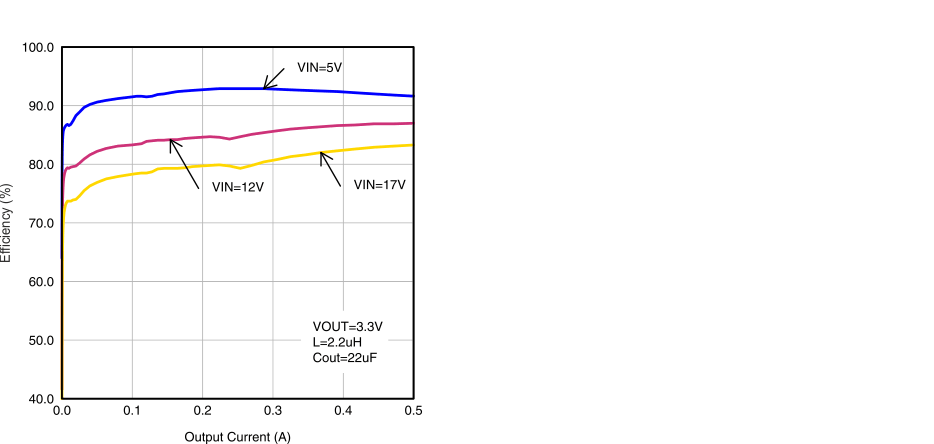
VIN = 12V, VOUT = 3.3V, TA=25°C, (unless otherwise noted)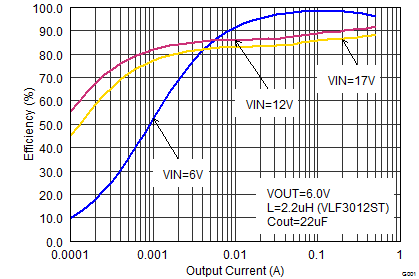 Figure 8. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 6 V
Figure 8. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 6 V
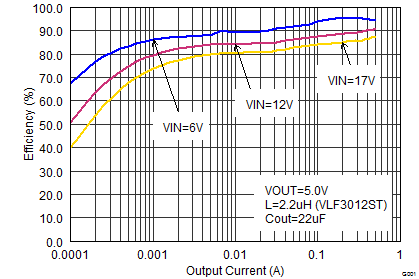 Figure 10. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 10. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 5 V
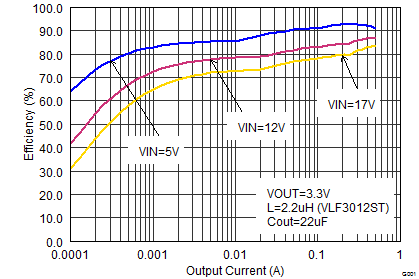 Figure 12. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 12. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 3.3 V
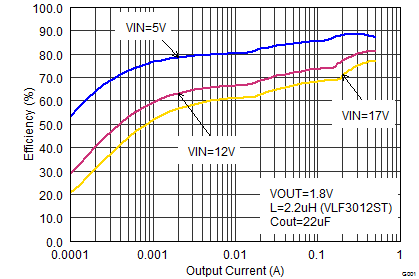 Figure 14. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 1.8 V
Figure 14. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 1.8 V
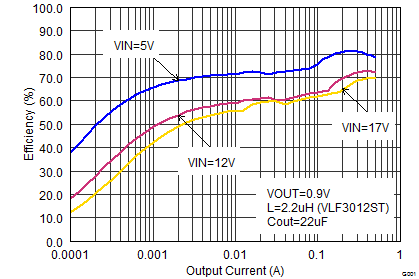 Figure 16. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 0.9 V
Figure 16. Efficiency vs Output Current, VOUT = 0.9 V
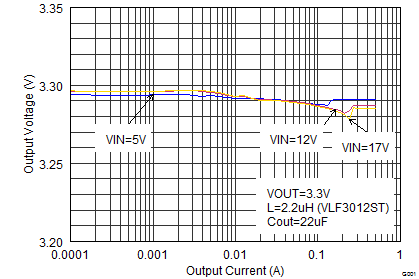 Figure 18. Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)
Figure 18. Output Voltage Accuracy (Load Regulation)
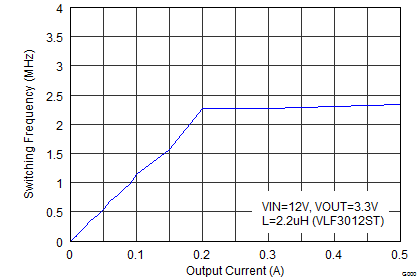 Figure 20. Switching Frequency vs Output Current
Figure 20. Switching Frequency vs Output Current
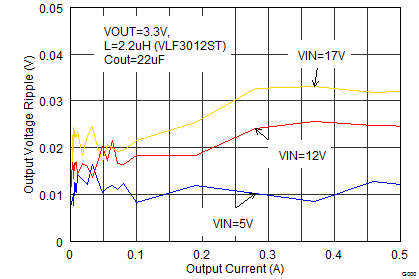 Figure 22. Output Voltage Ripple
Figure 22. Output Voltage Ripple
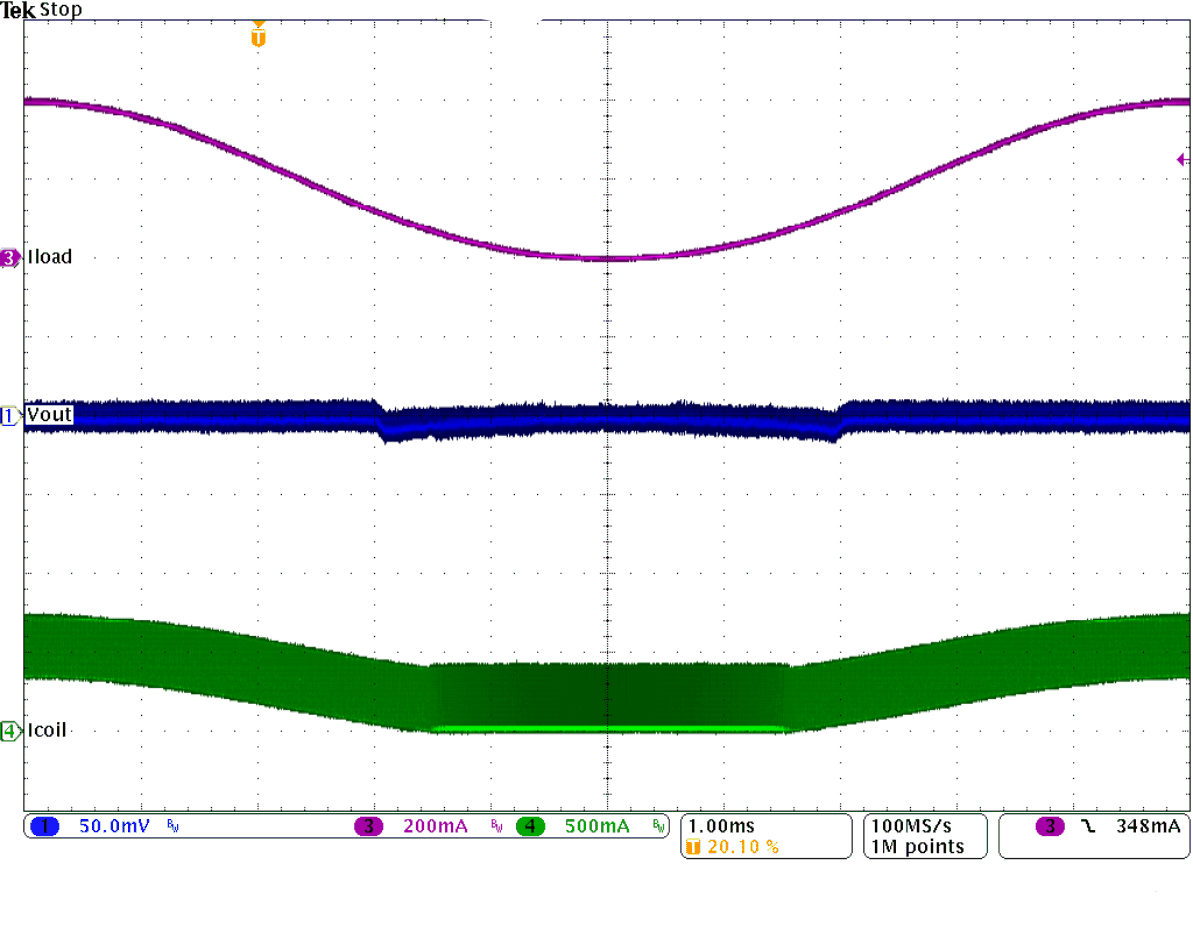 Figure 24. PWM to PSM Mode Transition
Figure 24. PWM to PSM Mode Transition
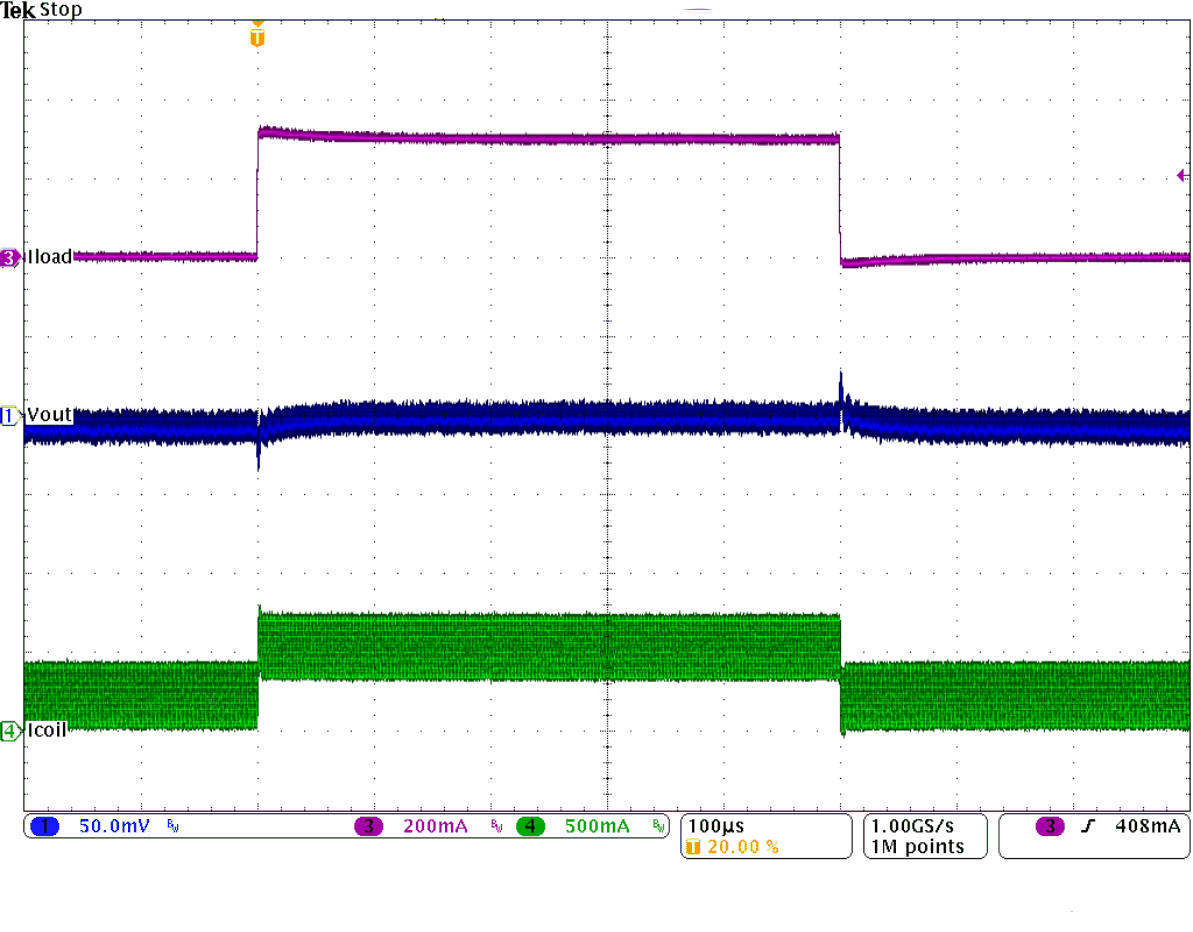 Figure 26. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode
Figure 26. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode (200 mA to 500 mA)
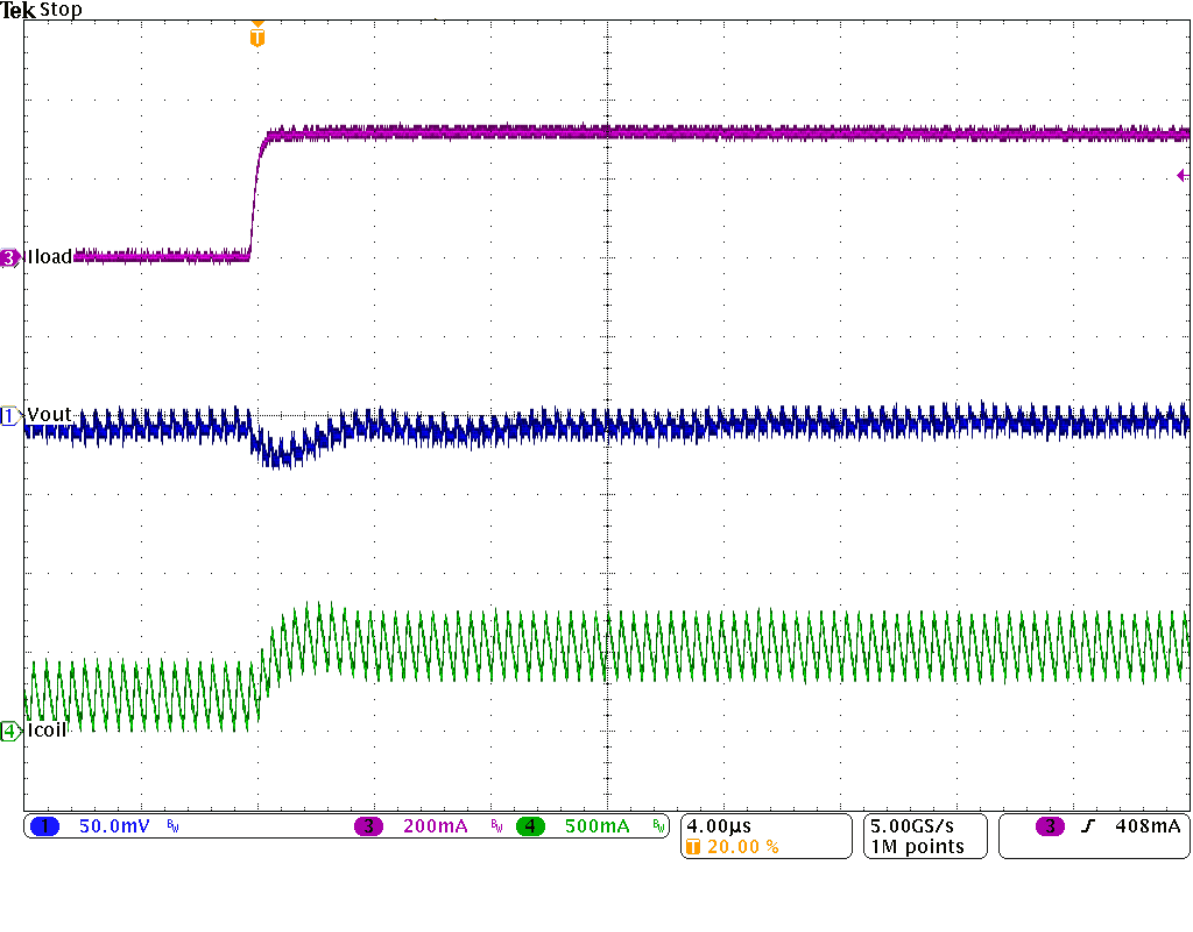 Figure 28. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode
Figure 28. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode (200 mA to 500 mA), Rising Edge
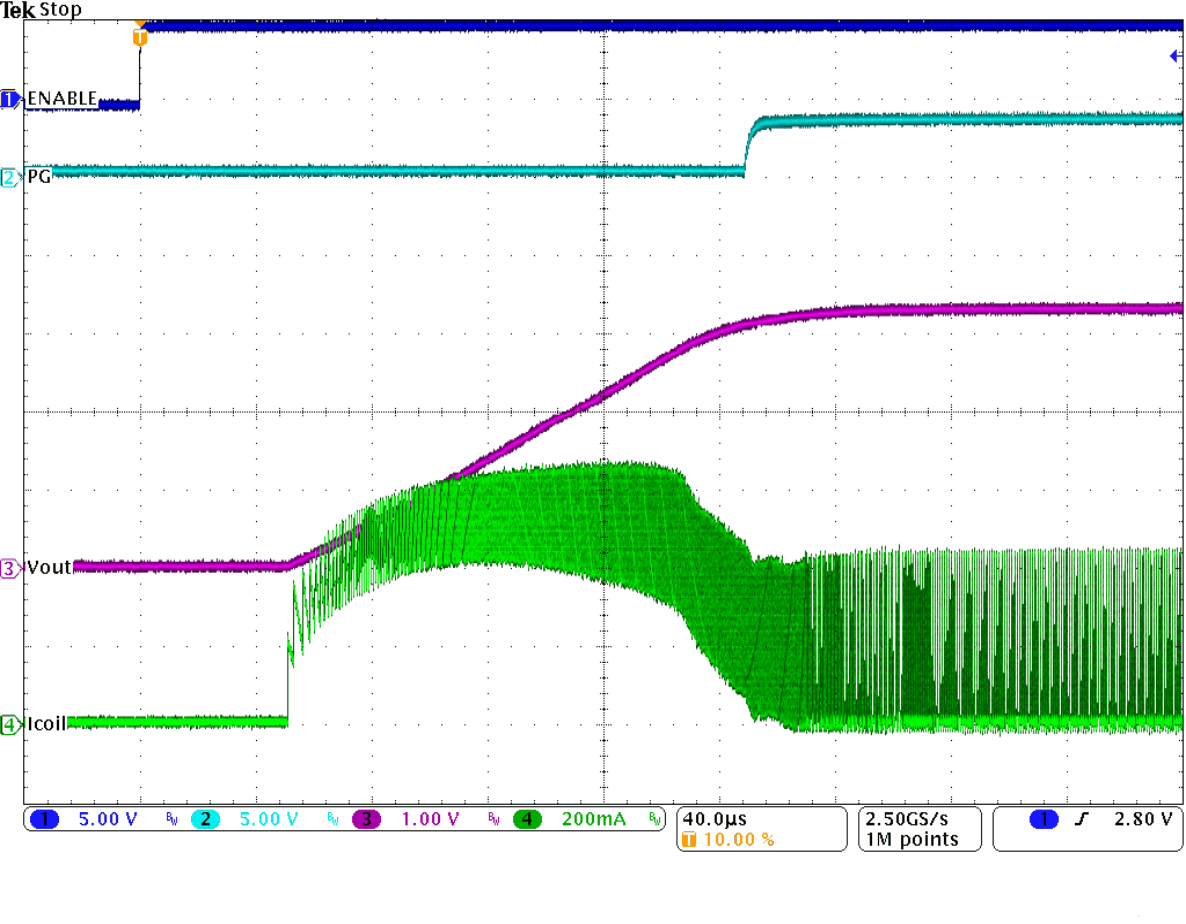 Figure 30. Startup with IOUT = 500 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 30. Startup with IOUT = 500 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
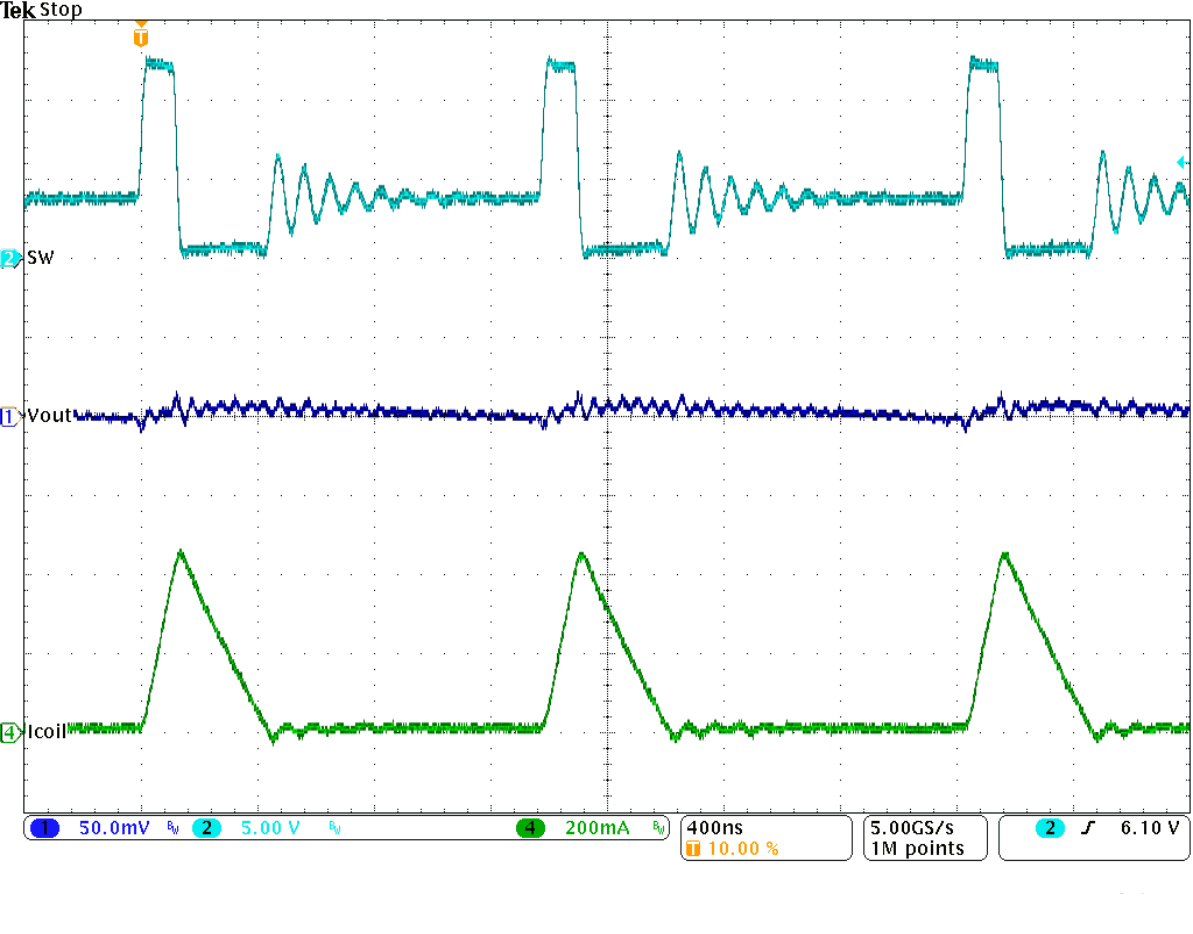 Figure 32. Typical Operation in Power Save Mode
Figure 32. Typical Operation in Power Save Mode (IOUT = 66 mA)
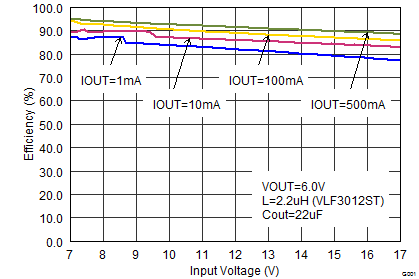 Figure 9. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 6 V
Figure 9. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 6 V
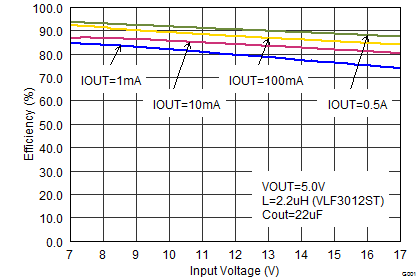 Figure 11. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
Figure 11. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 5 V
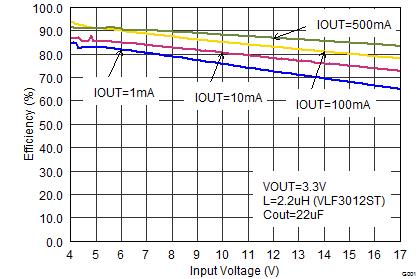 Figure 13. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 13. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 3.3 V
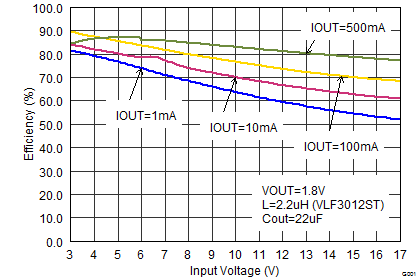 Figure 15. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 1.8 V
Figure 15. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 1.8 V
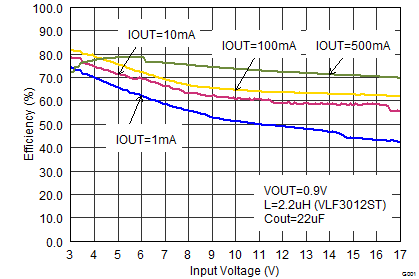 Figure 17. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 0.9 V
Figure 17. Efficiency vs Input Voltage, VOUT = 0.9 V
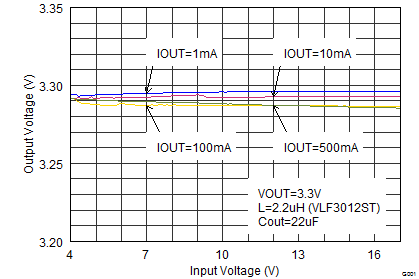 Figure 19. Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)
Figure 19. Output Voltage Accuracy (Line Regulation)
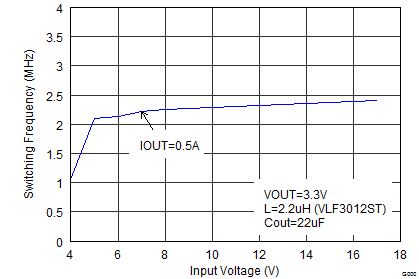 Figure 21. Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
Figure 21. Switching Frequency vs Input Voltage
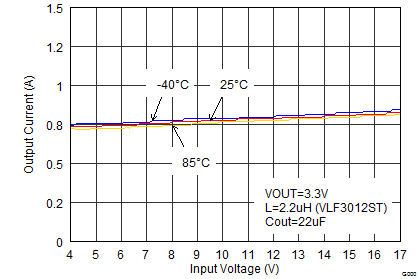 Figure 23. Maximum Output Current
Figure 23. Maximum Output Current
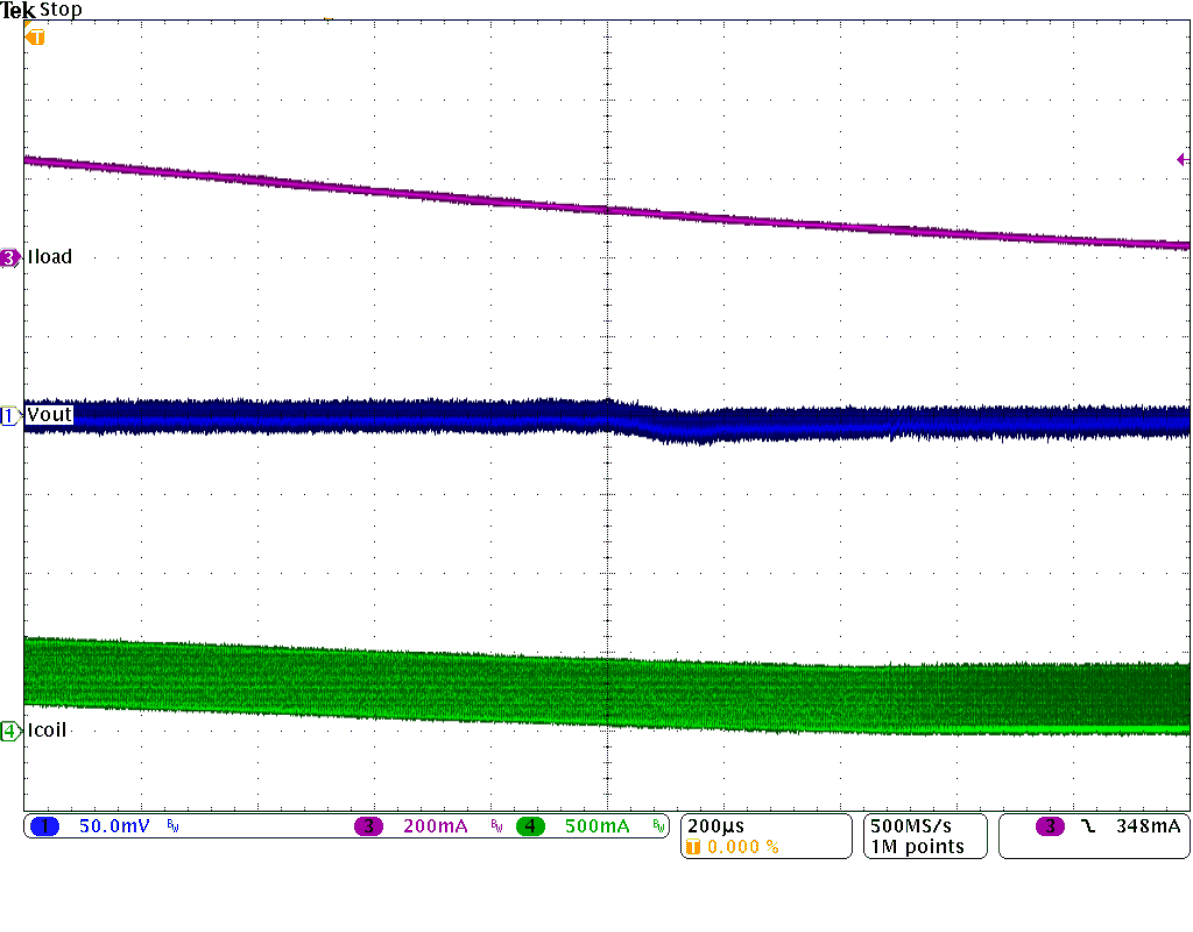 Figure 25. PSM to PWM Mode Transition
Figure 25. PSM to PWM Mode Transition
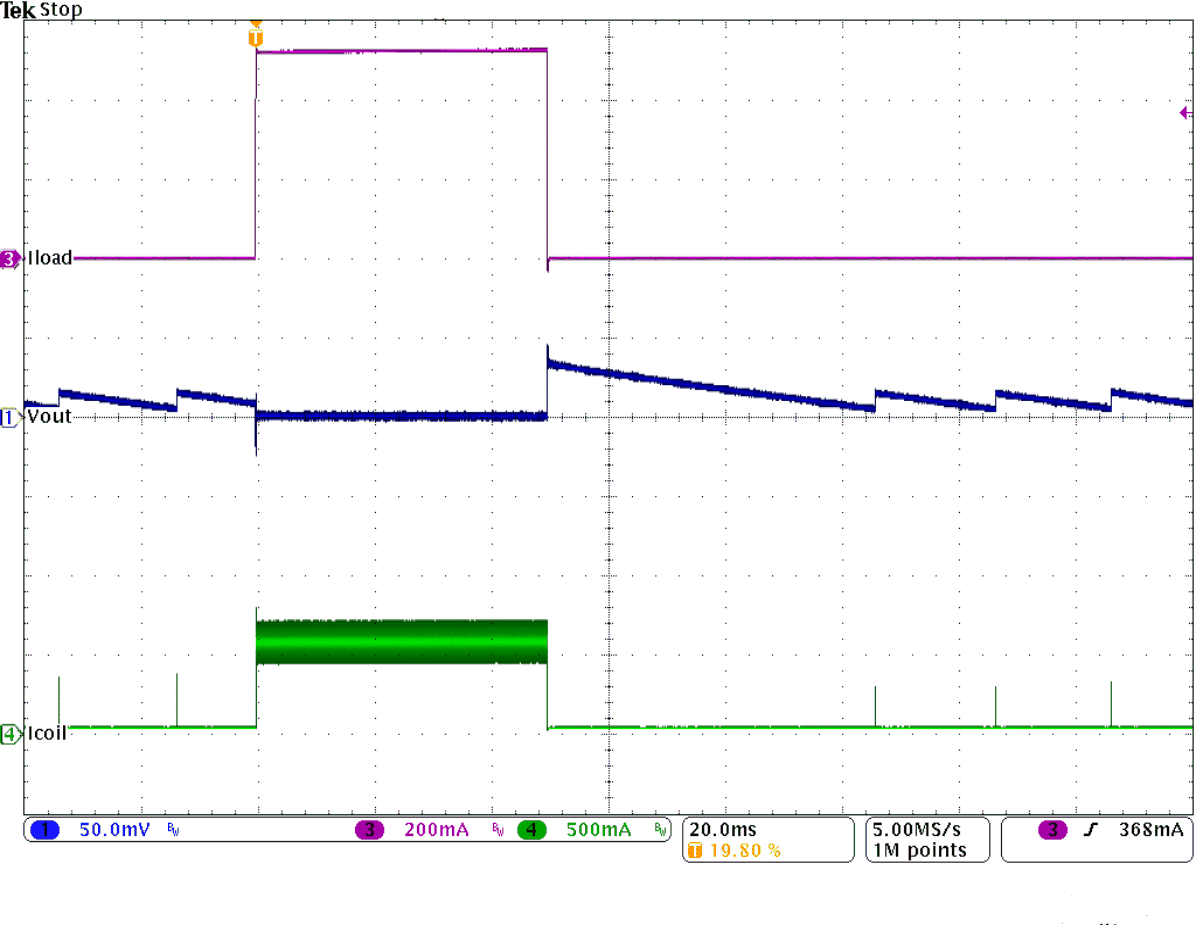 Figure 27. Load Transient Response from
Figure 27. Load Transient Response from Power Save Mode (100 mA to 500 mA)
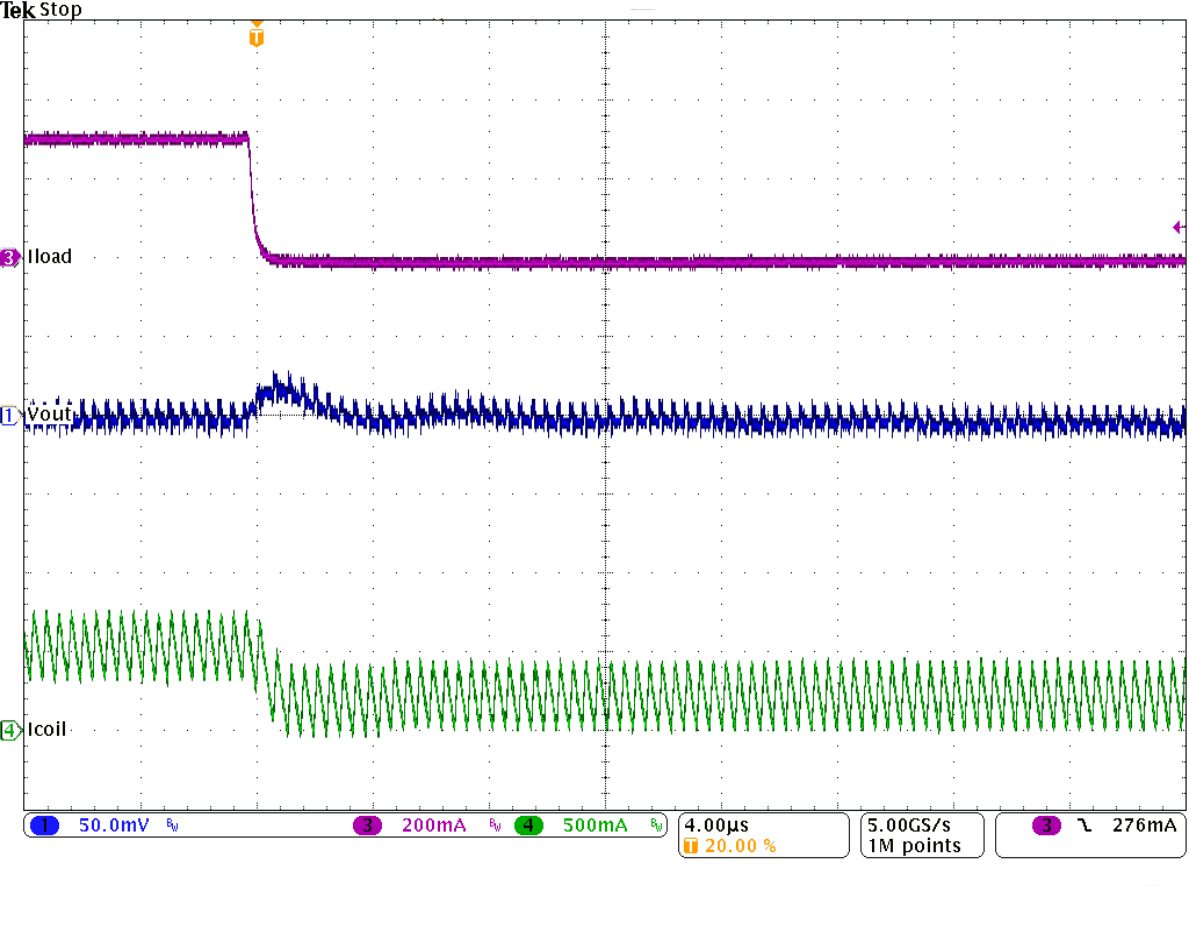 Figure 29. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode
Figure 29. Load Transient Response in PWM Mode (200 mA to 500 mA), Falling Edge
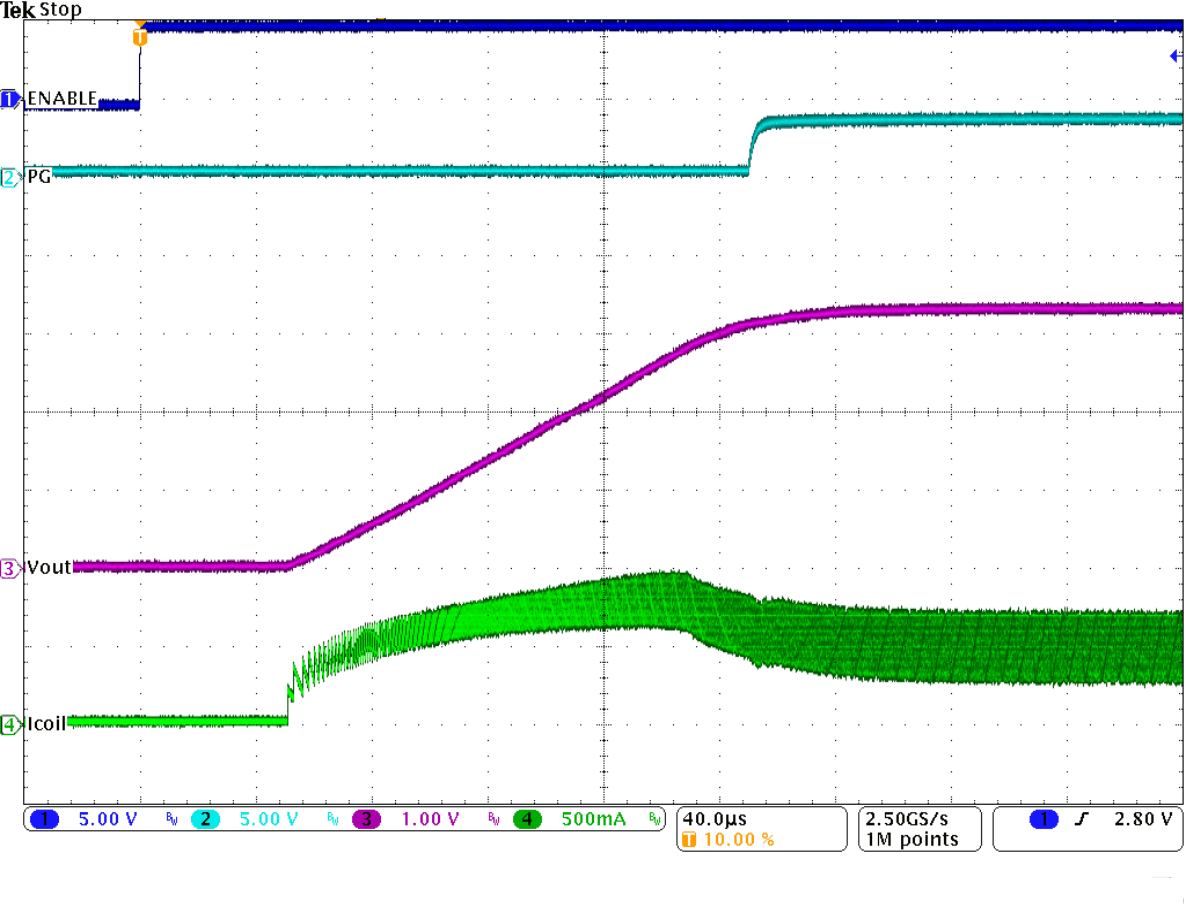 Figure 31. Startup with IOUT = 500 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
Figure 31. Startup with IOUT = 500 mA, VOUT = 3.3 V
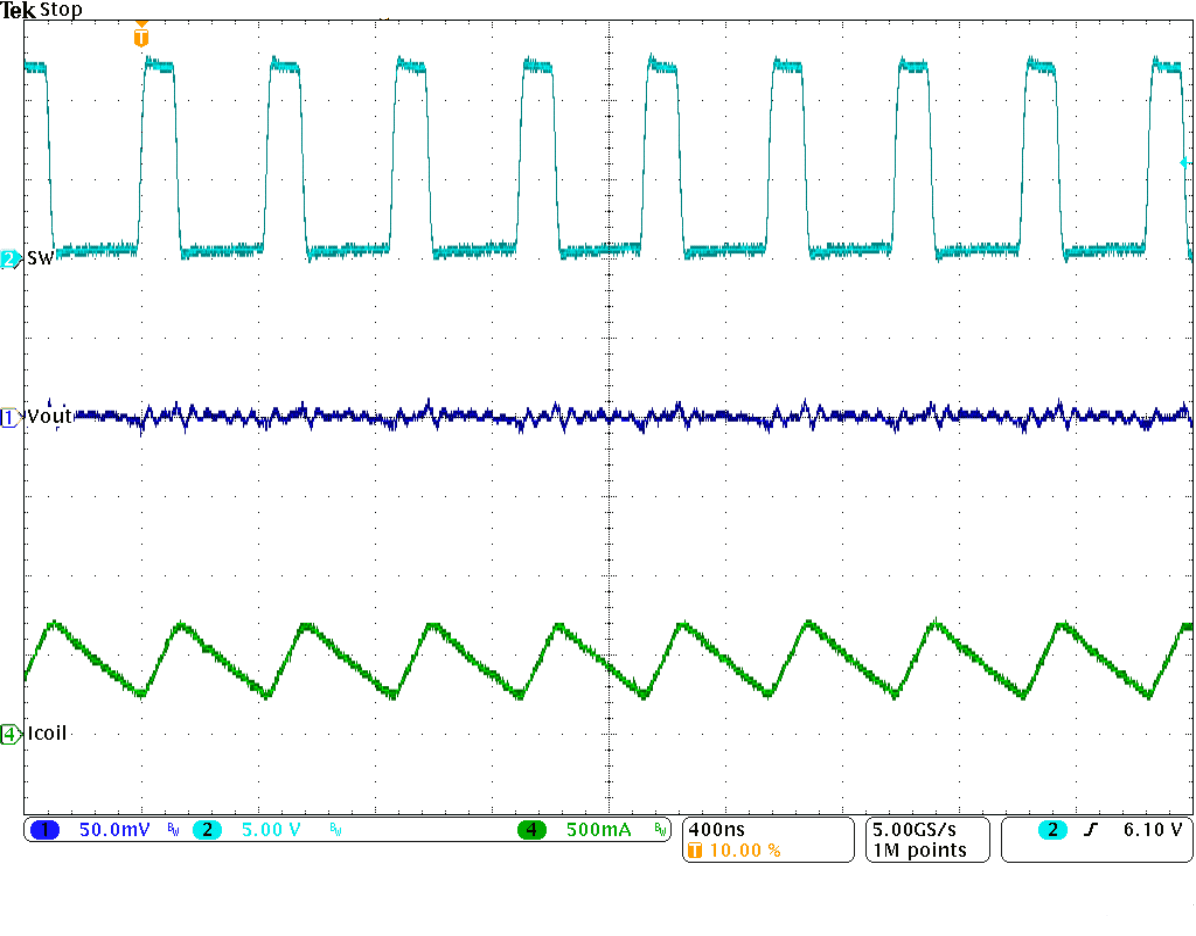 Figure 33. Typical Operation in PWM mode (IOUT = 500 mA)
Figure 33. Typical Operation in PWM mode (IOUT = 500 mA)
9.3 System Examples
Figure 34 through Figure 40 show various TPS6217x devices and input voltages that provide a 0.5-A power supply with output voltage options.
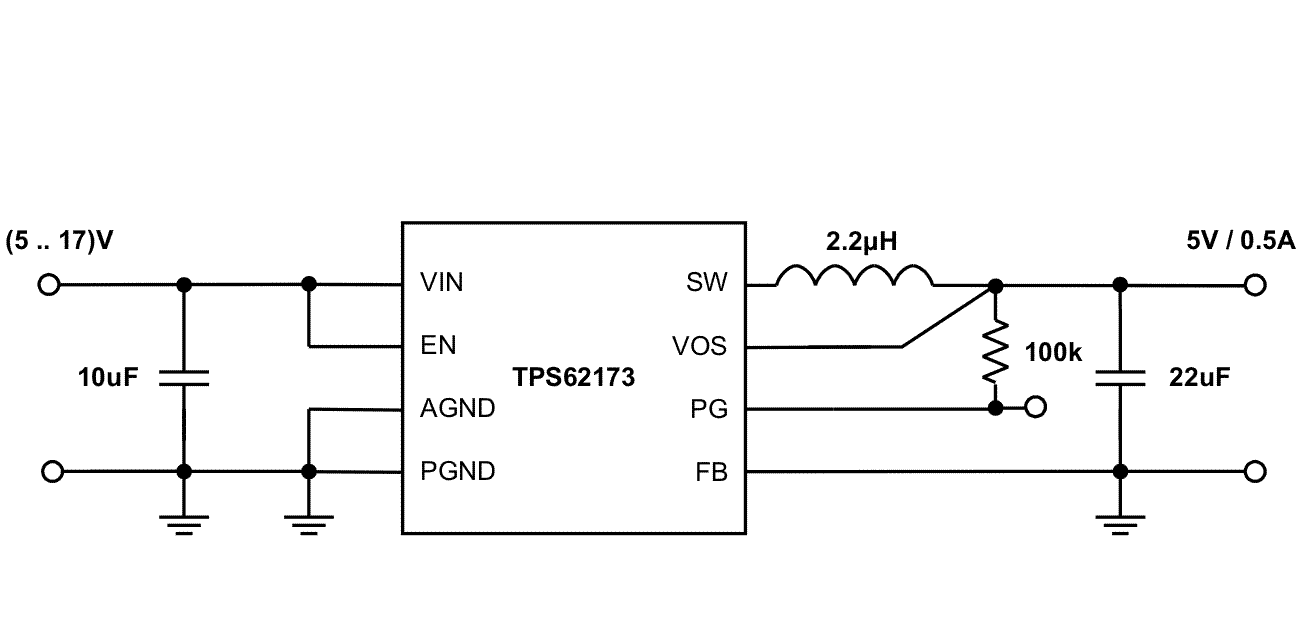 Figure 34. 5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 34. 5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
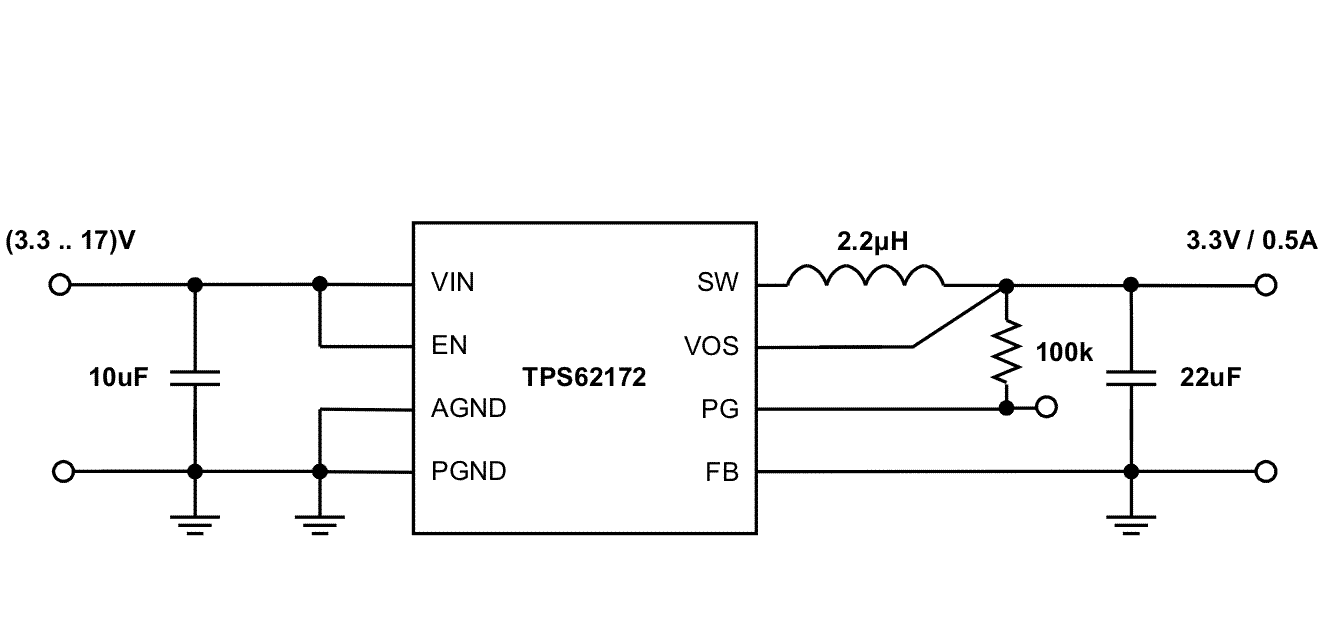 Figure 35. 3.3-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 35. 3.3-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
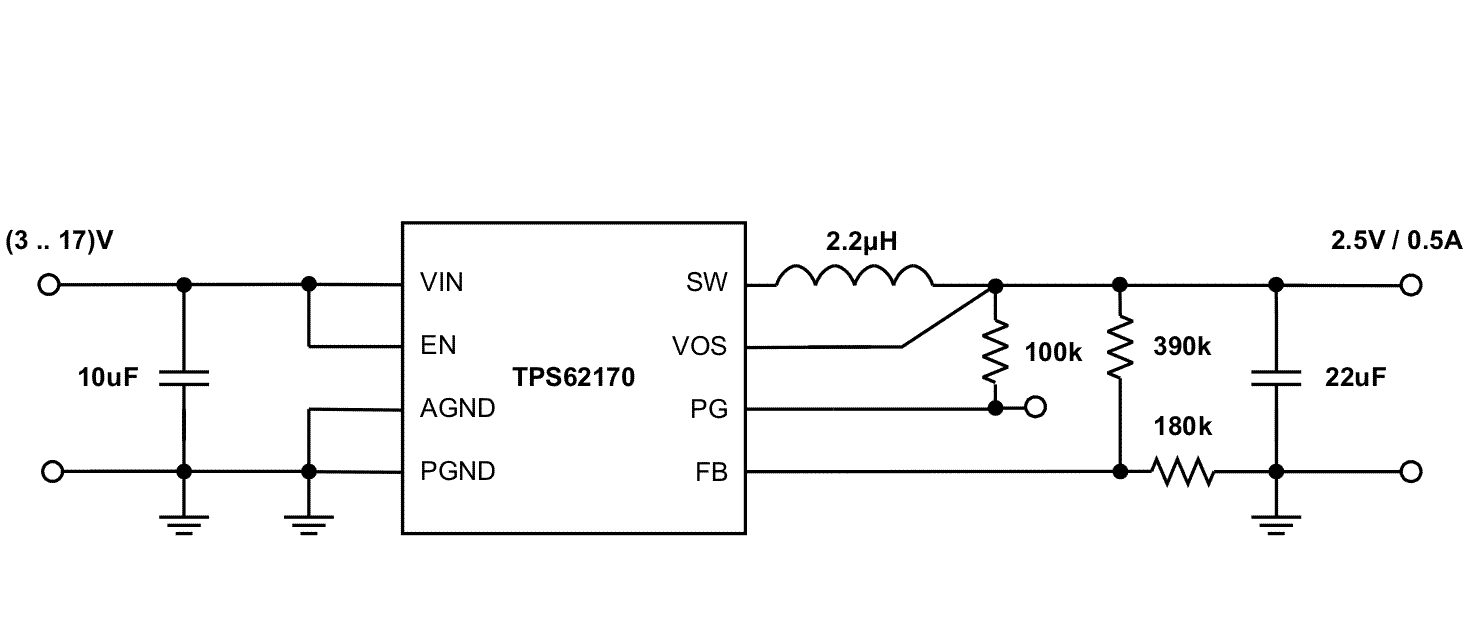 Figure 36. 2.5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 36. 2.5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
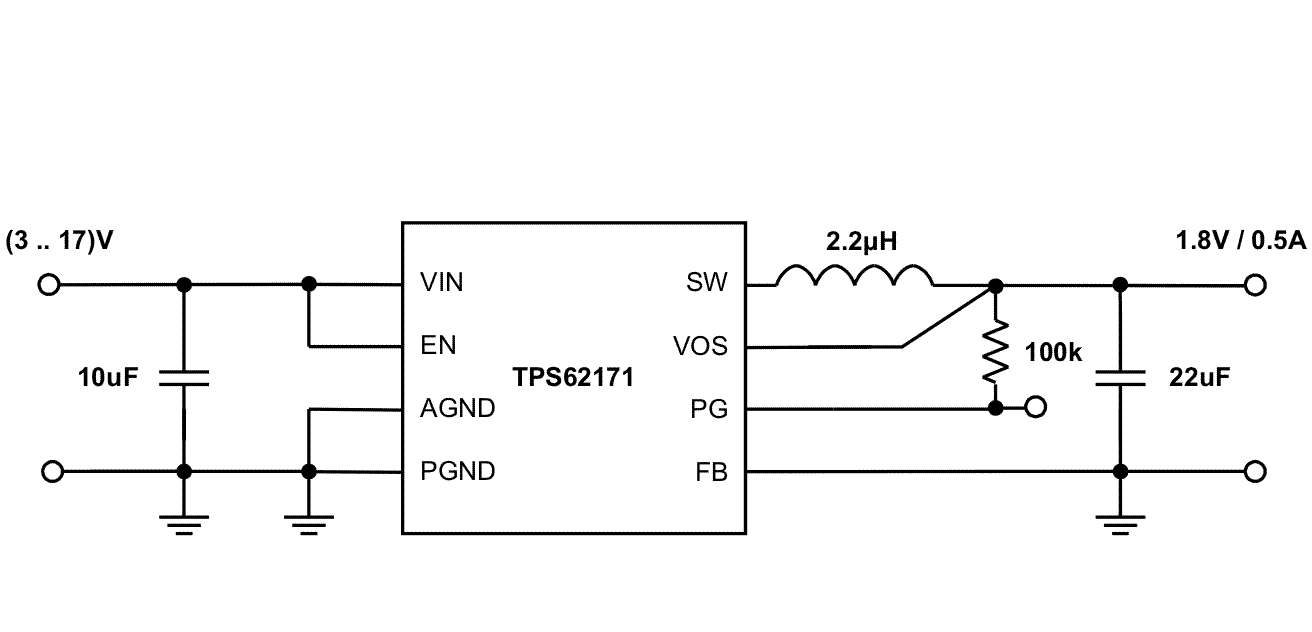 Figure 37. 1.8-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 37. 1.8-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
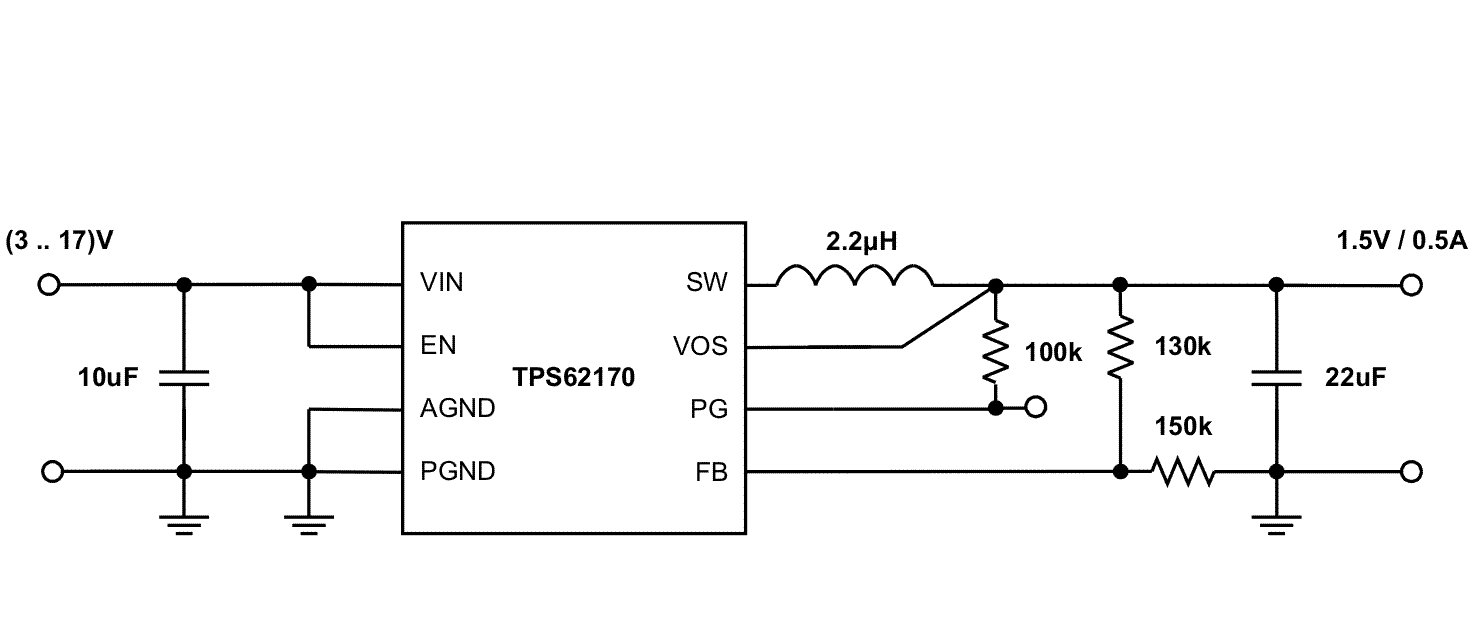 Figure 38. 1.5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 38. 1.5-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
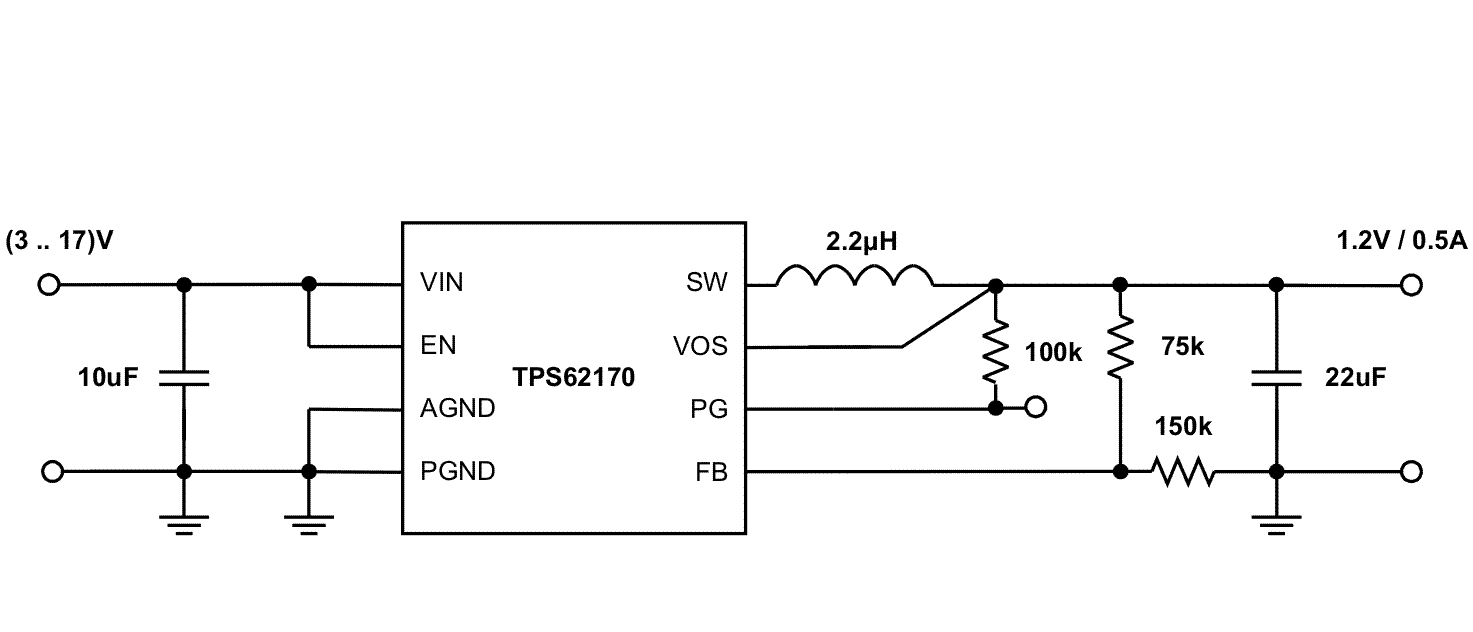 Figure 39. 1.2-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 39. 1.2-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
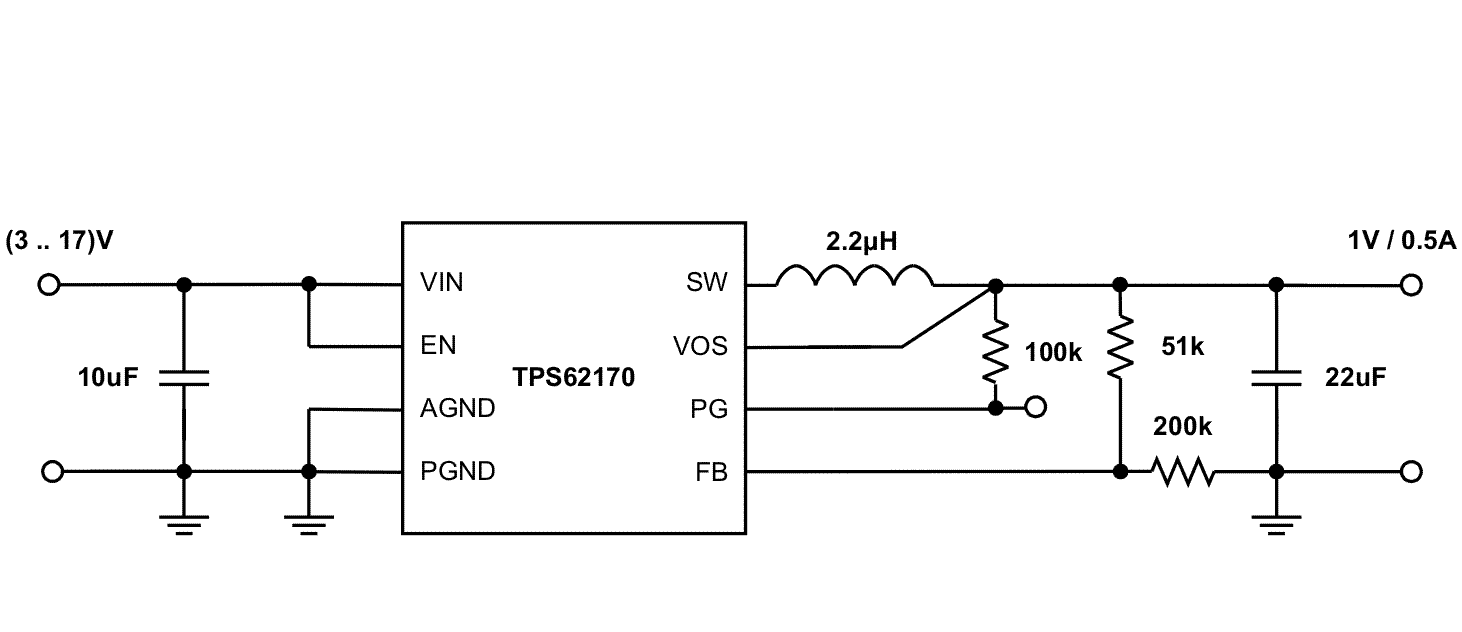 Figure 40. 1-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
Figure 40. 1-V and 0.5-A Power Supply
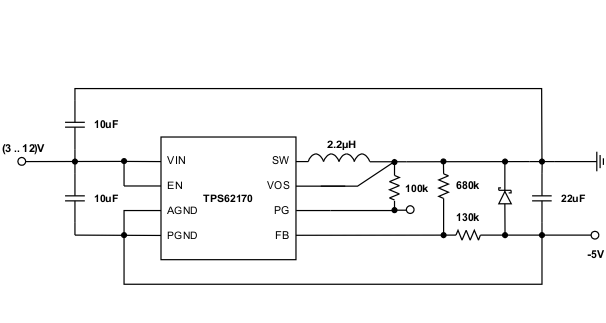
9.3.1 Inverting Power Supply
The TPS6217x can be used as inverting power supply by rearranging external circuitry as shown in Figure 41. As the former GND node now represents a voltage level below system ground, the voltage difference between VIN and VOUT has to be limited for operation to the maximum supply voltage of 17 V (see Equation 13).
space
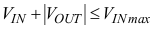
space
The transfer function of the inverting power supply configuration differs from the buck mode transfer function, incorporating a right half plane zero additionally. The loop stability has to be adapted and an output capacitance of at least 22 µF is recommended. A detailed design example is given in SLVA469.
10 Power Supply Recommendations
The TPS6217x device family has no special requirements for its input power supply. The input power supply's output current needs to be rated according to the supply voltage, output voltage and output current of the TPS6217x.