ZHCSHS4 March 2018 TPS62243-Q1 , TPS62244-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
9.2.2.1.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor value has a direct effect on the ripple current. The selected inductor must be rated for its DC resistance and saturation current (Table 3). The inductor ripple current (ΔIL) decreases with higher inductance and increases with higher VI or VO.
The inductor selection also has an impact on the output voltage ripple in the PFM mode. Higher inductor values lead to lower-output voltage ripple and higher PFM frequency, and lower inductor values lead to a higher-output voltage ripple with lower PFM frequency.
Equation 2 calculates the maximum inductor current in PWM mode under static load conditions. The saturation current of the inductor should be rated higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 3. This is the recommendation because during heavy-load transients the inductor current rises above the calculated value.
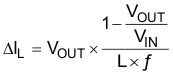
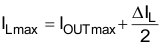
where
- ƒ = Switching frequency (2.25-MHz typical)
- L = Inductor value
- ΔIL = Peak-to-Peak inductor ripple current
- ILmax = Maximum inductor current
A more conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the maximum switch current limit ILIMF of the converter.
Accepting larger values of ripple current allows the use of low inductance values, but results in higher output voltage ripple, greater core losses, and lower output current capability.
The total losses of the coil strongly impact the efficiency of the DC-DC conversion and consist of both the losses in the DC resistance (R(DC)) and the following frequency-dependent components:
- The losses in the core material (magnetic hysteresis loss, especially at high switching frequencies)
- Additional losses in the conductor from the skin effect (current displacement at high frequencies)
- Magnetic field losses of the neighboring windings (proximity effect)
- Radiation losses
Table 3. List of Inductors
| INDUCTANCE (μH) | DIMENSIONS (mm) | PART NUMBER | MANUFACTURER(1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2.5 × 2 × 1 | MIPS2520D2R2 | FDK |
| 2 | 2.5 × 2 × 1.2 | MIPSA2520D2R2 | FDK |
| 2.2 | 2.5 × 2 × 1 | KSLI-252010AG2R2 | Hitachi Metals |
| 2.2 | 2.5 × 2 × 1.2 | LQM2HPN2R2MJ0L | Murata |
| 2.2 | 3 × 3 × 1.4 | LPS3015 | Coilcraft |