SLVSA67F February 2010 – April 2020 TPS62400-Q1 , TPS62402-Q1 , TPS62404-Q1 , TPS62405-Q1
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1
Output Voltage Setting
- 10.2.2.1.1 Converter 1 Adjustable Default Output-Voltage Setting: TPS62400-Q1
- 10.2.2.1.2 Converter 1 Fixed Default Output-Voltage Setting (TPS62402-Q1, TPS62404-Q1, and TPS62405-Q1)
- 10.2.2.1.3 Converter 2 Adjustable Default Output-Voltage Setting (TPS62400-Q1):
- 10.2.2.1.4 Converter 2 Fixed Default Output-Voltage Setting
- 10.2.2.2 Output Filter Design (Inductor and Output Capacitor)
- 10.2.2.1
Output Voltage Setting
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 System Examples
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.2.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
Select the inductor based on its ratings for dc resistance and saturation current. The dc resistance of the inductor directly influences the efficiency of the converter. Therefore, select an inductor with lowest dc resistance for highest efficiency.
Equation 6 calculates the maximum inductor current under static load conditions. The saturation-current rating of the inductor must be higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 7. TI makes this recommendation because during heavy load transients, the inductor current rises above the calculated value.
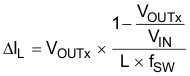
where
- ΔIL = peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- L = inductor value
- fSW = switching frequency (2.25 MHz typical)
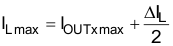
where
- ILmax = maximum inductor current and the highest inductor current occurs at maximum VIN
Open-core inductors have a soft saturation characteristic and they can usually handle higher inductor currents versus a comparable shielded inductor.
A more conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the maximum switch current of the corresponding converter. Take into consideration that the core material from inductor to inductor differs, and this difference has an impact on the efficiency.
See Table 7 and the typical application circuit examples for possible inductors.
Table 7. List of Inductors
| DIMENSIONS [mm] | INDUCTOR TYPE | SUPPLIER |
|---|---|---|
| 3.2 × 2.6 × 1 | MIPW3226 | FDK |
| 3 × 3 × 0.9 | LPS3010 | Coilcraft |
| 2.8 × 2.6 × 1 | VLF3010 | TDK |
| 2.8 x 2.6 × 1.4 | VLF3014 | TDK |
| 3 × 3 × 1.4 | LPS3015 | Coilcraft |
| 3.9 × 3.9 × 1.7 | LPS4018 | Coilcraft |