ZHCSNV8B December 2021 – August 2024 TPS63901
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3 Feature Description
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
The inductor selection is affected by several parameters such as inductor ripple current, output voltage ripple, transition point into power save mode, and efficiency. See Table 7-2 for typical inductors.
For high efficiencies, the inductor must have a low DC resistance to minimize conduction losses. Especially at high-switching frequencies, the core material has a high impact on efficiency. When using small chip inductors, the efficiency is reduced mainly due to higher inductor core losses, which needs to be considered when selecting the appropriate inductor. The inductor value determines the inductor ripple current. The larger the inductor value, the smaller the inductor ripple current and the lower the core and conduction losses of the converter. Conversely, larger inductor values cause a slower load transient response. To avoid saturation of the inductor, the peak current for the inductor in steady state operation is calculated using Equation 5. Only the equation that defines the switch current in boost mode is shown because this provides the highest value of current and represents the critical current value for selecting the right inductor.
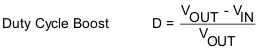
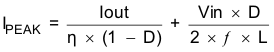
where
- D is duty cycle in boost mode.
- f is the converter switching frequency.
- L is the inductor value.
- η is the estimated converter efficiency (use the number from the efficiency curves or 0.9 as an assumption).
The calculation must be done for the minimum input voltage in boost mode.
Calculating the maximum inductor current using the actual operating conditions gives the minimum saturation current of the inductor needed. TI recommends choosing an inductor with a saturation current 20% higher than the value calculated using Equation 5. Possible inductors are listed in Table 7-2.
| Inductor Value [µH](1) | Saturation Current [A] | DCR [mΩ] | Part Number | Manufacturer | Size (L × W × H mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2 | 3.5 | 21 | XFL4020-222ME | Coilcraft | 4 × 4 × 2 |
| 2.2 | 1.7 | 72 | SRN3015TA-2R2M | Bourns | 3 × 3 × 1.5 |
| 2.2 | 3.3 | 82 | DFE252012F-2R2M | Murata | 2.5 × 2 × 1.2 |
| 2.2 | 2.4 | 116 | DFE201612E-2R2M | Murata | 2.0 × 1.6 × 1.2 |
| 2.2 | 2.0 | 190 | DFE201210U-2R2M | Murata | 2.0 × 1.2 × 1.0 |