ZHCSI59I July 2009 – May 2018 TPS65070 , TPS65072 , TPS65073 , TPS650731 , TPS650732
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Device Options
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.6 Electrical Characteristics - DCDC1 Converter
- 8.7 Electrical Characteristics - DCDC2 Converter
- 8.8 Electrical Characteristics - DCDC3 Converter
- 8.9 Electrical Characteristics - VLDO1 and VLDO2 Low Dropout Regulators
- 8.10 Electrical Characteristics - wLED Boost Converter
- 8.11 Electrical Characteristics - Reset, PB_IN, PB_OUT, PGood, Power_on, INT, EN_EXTLDO, EN_wLED
- 8.12 Electrical Characteristics - ADC Converter
- 8.13 Electrical Characteristics - Touch Screen Interface
- 8.14 Electrical Characteristics - Power Path
- 8.15 Electrical Characteristics - Battery Charger
- 8.16 Timing Requirements
- 8.17 Dissipation Ratings
- 8.18 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3
Feature Description
- 10.3.1 Battery Charger and Power Path
- 10.3.2 Power Down
- 10.3.3 Power-On Reset
- 10.3.4 Power-Path Management
- 10.3.5 Battery Charging
- 10.3.6 Battery Pack Temperature Monitoring
- 10.3.7 Battery Charger State Diagram
- 10.3.8 DC-DC Converters and LDOs
- 10.3.9 Power Save Mode
- 10.3.10 Short-Circuit Protection
- 10.3.11 Enable
- 10.3.12 Short-Circuit Protection
- 10.3.13 Thermal Shutdown
- 10.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6
Register Maps
- 10.6.1 PPATH1. Register Address: 01h
- 10.6.2 INT. Register Address: 02h
- 10.6.3 CHGCONFIG0. Register Address: 03h
- 10.6.4 CHGCONFIG1. Register Address: 04h
- 10.6.5 CHGCONFIG2. Register Address: 05h
- 10.6.6 CHGCONFIG3. Register Address: 06h
- 10.6.7 ADCONFIG. Register Address: 07h
- 10.6.8 TSCMODE. Register Address: 08h
- 10.6.9 ADRESULT_1. Register Address: 09h
- 10.6.10 ADRESULT_2. Register Address: 0Ah
- 10.6.11 PGOOD. Register Address: 0Bh
- 10.6.12 PGOODMASK. Register Address: 0Ch
- 10.6.13 CON_CTRL1. Register Address: 0Dh
- 10.6.14 CON_CTRL2. Register Address: 0Eh
- 10.6.15 CON_CTRL3. Register Address: 0Fh
- 10.6.16 DEFDCDC1. Register Address: 10h
- 10.6.17 DEFDCDC2_LOW. Register Address: 11h
- 10.6.18 DEFDCDC2_HIGH. Register Address: 12h
- 10.6.19 DEFDCDC3_LOW. Register Address: 13h
- 10.6.20 DEFDCDC3_HIGH. Register Address: 14h
- 10.6.21 DEFSLEW. Register Address: 15h
- 10.6.22 LDO_CTRL1. Register Address: 16h
- 10.6.23 DEFLDO2. Register Address: 17h
- 10.6.24 WLED_CTRL1. Register Address: 18h
- 10.6.25 WLED_CTRL2. Register Address: 19h
-
11Application and Implementation
- 11.1 Application Information
- 11.2
Typical Applications
- 11.2.1 General PMIC Application
- 11.2.2 Powering OMAP-L138
- 11.2.3 Powering Atlas IV
- 11.2.4 OMAP35xx (Supporting SYS-OFF Mode)
- 11.2.5 TPS650731 for OMAP35xx
- 11.2.6 Powering AM3505 Using TPS650732
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
10.3.13.4 Touch Screen Interface (only for TPS65070, TPS65073, TPS650731, TPS650732)
The touch screen itself consists of two parallel plates, called the X and Y plates, separated by short distance; contact is initiated by using a stylus or your finger. This action creates a series of resistances noted by RX1, RX2, RY1, RY2 , and Rcontact, shown in Figure 36. The points shown in the diagram as TSX1, TSX2, TSY1 and TSY2 are connected to the TPS6507x touch screen interface. The resistances RX1 and RX2 scale linearly with the x-position of the point of contact, where the RY1 and RY2 resistances scale with the y-position. The Rcontact resistance decreases as the pressure applied at the point of contact increases and increases as the pressure decreases. Using these relationships, the touch screen interface can make measurements of either position or pressure.
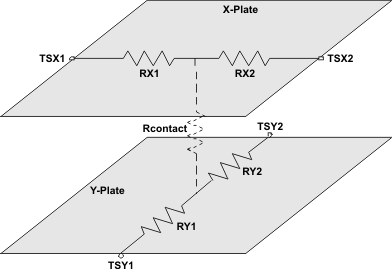 Figure 35. Touch Screen
Figure 35. Touch Screen The touch screen interface consists of a digital state machine, a voltage reference, and an analog switch matrix which is connected to the four wire resistive touch screen inputs (TSX1, TSX2, TSY1, TSY2) and an internal 10-Bit ADC. The state machine controls the sequencing of the switch matrix to cycle through the three types of measurement modes (position, pressure, plate resistance) and the low power standby mode. The separate internal voltage reference (TSREF) is disabled in standby and off modes. The voltage is generated by an internal LDO. Its voltage is bypassed by a capacitor connected to pin INT_LDO. The state of the touch screen is controlled by the TSC_M[2,0] Bits of the TSCMODE register (08h) as shown in Table 3. The touch screen controller uses transfer gates to the internal ADC on input channels AD_IN14 and AD_IN15.
Table 3. TSC Modes
| CONTROL MULTIPLEXER | CONNECTIONS | MODE | MEASUREMENT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSC_M2 | TSC_M1 | TSC_M0 | TSX1 | TSX2 | TSY1 | TSY2 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | TSREF
PMOS |
GND
NMOS |
ADC_IN3
TGATE |
ADC_IN4
TGATE |
X-Position | Voltage TSY1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | ADC_IN1
TGATE |
ADC_IN2
TGATE |
TSREF
PMOS |
GND
NMOS |
Y-Position | Voltage TSX1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | TSREF | TSREF | GND
NMOS |
GND
NMOS |
Pressure | Current TSX1 and TSX2 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | TSREF
PMOS |
GND
NMOS |
HiZ | HiZ | Plate X
Reading on ADC_IN14 |
Current TSX1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | HiZ | HiZ | TSREF
PMOS |
GND
NMOS |
Plate Y
Reading on ADC_IN14 |
Current TSY1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | TSREF
TGATE |
TSREF
TGATE |
GND
NMOS |
GND
NMOS |
TSC standby | Voltage TSX1 and TSX2 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | A/D
TGATE |
A/D
TGATE |
A/D
TGATE |
A/D
TGATE |
A/D | ADC used as stand alone
ADC using its analog inputs |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | OPEN | OPEN | OPEN | OPEN | Disabled (no interrupt) | None |
If the Touch screen multiplexer is set to disabled mode [111], touch to the screen will not be detected. Standby mode is entered by setting TSC_M[2:0] to 101. When there is a touch, the controller will detect a change in voltage at the TSX1 point and after a 8ms deglitch the INT pin will be asserted if the interrupt is unmasked in register INT. Once the host detects the interrupt signal, will enable the ADC converter and set the TSC_M<2:0> through the I2C bus to select any of five measurements (position, pressure, plate) as shown in Table 4.