ZHCSKK3B December 2019 – February 2022 TPS6594-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 General Purpose Low Drop-Out Regulators (LDO1, LDO2, LDO3)
- 7.6 Low Noise Low Drop-Out Regulator (LDO4)
- 7.7 Internal Low Drop-Out Regulators (LDOVRTC, LDOVINT)
- 7.8 BUCK1, BUCK2, BUCK3, BUCK4 and BUCK5 Regulators
- 7.9 Reference Generator (BandGap)
- 7.10 Monitoring Functions
- 7.11 Clocks, Oscillators, and PLL
- 7.12 Thermal Monitoring and Shutdown
- 7.13 System Control Thresholds
- 7.14 Current Consumption
- 7.15 Backup Battery Charger
- 7.16 Digital Input Signal Parameters
- 7.17 Digital Output Signal Parameters
- 7.18 I/O Pullup and Pulldown Resistance
- 7.19 I2C Interface
- 7.20 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.21 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 System Supply Voltage Monitor and Over-Voltage Protection
- 8.3.2
Power Resources (Bucks and LDOs)
- 8.3.2.1
Buck Regulators
- 8.3.2.1.1 BUCK Regulator Overview
- 8.3.2.1.2 Multi-Phase Operation and Phase-Adding or Shedding
- 8.3.2.1.3 Transition Between PWM and PFM Modes
- 8.3.2.1.4 Multi-Phase BUCK Regulator Configurations
- 8.3.2.1.5 Spread-Spectrum Mode
- 8.3.2.1.6 Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS) and Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) Support
- 8.3.2.1.7 BUCK Output Voltage Setting
- 8.3.2.1.8 BUCK Regulator Current Limit
- 8.3.2.1.9 SW_Bx Short-to-Ground Detection
- 8.3.2.1.10 Sync Clock Functionality
- 48
- 8.3.2.2 Low Dropout Regulators (LDOs)
- 8.3.2.1
Buck Regulators
- 8.3.3 Residual Voltage Checking
- 8.3.4 Output Voltage Monitor and PGOOD Generation
- 8.3.5 Thermal Monitoring
- 8.3.6 Backup Supply Power-Path
- 8.3.7 General-Purpose I/Os (GPIO Pins)
- 8.3.8 nINT, EN_DRV, and nRSTOUT Pins
- 8.3.9 Interrupts
- 8.3.10 RTC
- 8.3.11
Watchdog (WDOG)
- 8.3.11.1 Watchdog Fail Counter and Status
- 8.3.11.2 Watchdog Start-Up and Configuration
- 8.3.11.3 MCU to Watchdog Synchronization
- 8.3.11.4 Watchdog Disable Function
- 8.3.11.5 Watchdog Sequence
- 8.3.11.6 Watchdog Trigger Mode
- 8.3.11.7 WatchDog Flow Chart and Timing Diagrams in Trigger Mode
- 79
- 8.3.11.8 Watchdog Question-Answer Mode
- 8.3.12 Error Signal Monitor (ESM)
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1
Device State Machine
- 8.4.1.1 Fixed Device Power FSM
- 8.4.1.2
Pre-Configurable Mission States
- 8.4.1.2.1
PFSM Commands
- 8.4.1.2.1.1 REG_WRITE_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.2 REG_WRITE_MASK_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.3 REG_WRITE_MASK_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.4 REG_WRITE_BIT_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.5 REG_WRITE_WIN_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.6 REG_WRITE_VOUT_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.7 REG_WRITE_VCTRL_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.8 REG_WRITE_MASK_SREG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.9 SREG_READ_REG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.10 SREG_WRITE_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.11 WAIT Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.12 DELAY_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.13 DELAY_SREG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.14 TRIG_SET Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.15 TRIG_MASK Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.16 END Command
- 8.4.1.2.2 Configuration Memory Organization and Sequence Execution
- 8.4.1.2.3 Mission State Configuration
- 8.4.1.2.4 Pre-Configured Hardware Transitions
- 8.4.1.2.1
PFSM Commands
- 8.4.1.3 Error Handling Operations
- 8.4.1.4 Device Start-up Timing
- 8.4.1.5 Power Sequences
- 8.4.1.6 First Supply Detection
- 8.4.1.7 Register Power Domains and Reset Levels
- 8.4.2 Multi-PMIC Synchronization
- 8.4.1
Device State Machine
- 8.5 Control Interfaces
- 8.6 Configurable Registers
- 8.7 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
Figure 6-1 shows the 56-pin RWE plastic quad-flatpack no-lead (VQFNP) pin assignments and thermal pad.
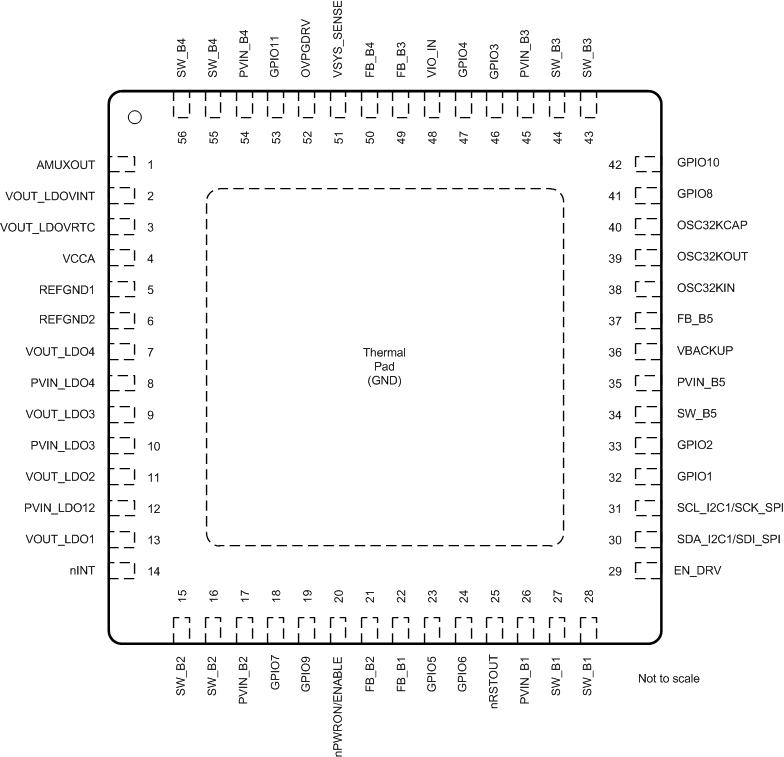 Figure 6-1 56-Pin RWE (VQFNP) Package, 0.5-mm Pitch, With Thermal Pad (Top
View)
Figure 6-1 56-Pin RWE (VQFNP) Package, 0.5-mm Pitch, With Thermal Pad (Top
View)Table 6-1 Pin Attributes
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | CONNECTION IF NOT USED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| STEP-DOWN CONVERTERS (BUCKs) | ||||
| FB_B1 | 22 | I | Output voltage-sense (feedback) input for BUCK1 or differential voltage-sense (feedback) positive input for BUCK12/123/1234 in multi-phase configuration. | Ground |
| FB_B2 | 21 | I | Output voltage-sense (feedback) input for BUCK2 or differential voltage-sense (feedback) negative input for BUCK12/123/1234 in multi-phase configuration. | Ground |
| FB_B3 | 49 | I | Output voltage-sense (feedback) input for BUCK3 or differential voltage-sense (feedback) positive input for BUCK34 in dual-phase configuration. | Ground |
| FB_B4 | 50 | I | Output voltage-sense (feedback) input for BUCK4 or differential voltage-sense (feedback) negative input for BUCK34 in dual-phase configuration. | Ground |
| FB_B5 | 37 | I | Output voltage-sense (feedback) input for BUCK5 | Ground |
| PVIN_B1 | 26 | I | Power input for BUCK1 | VCCA |
| PVIN_B2 | 17 | I | Power input for BUCK2 | VCCA |
| PVIN_B3 | 45 | I | Power input for BUCK3 | VCCA |
| PVIN_B4 | 54 | I | Power input for BUCK4 | VCCA |
| PVIN_B5 | 35 | I | Power input for BUCK5 | VCCA |
| SW_B1 | 27 | O | Switch node of BUCK1 | Floating |
| SW_B1 | 28 | O | Switch node of BUCK1 | Floating |
| SW_B2 | 15 | O | Switch node of BUCK2 | Floating |
| SW_B2 | 16 | O | Switch node of BUCK2 | Floating |
| SW_B3 | 43 | O | Switch node of BUCK3 | Floating |
| SW_B3 | 44 | O | Switch node of BUCK3 | Floating |
| SW_B4 | 55 | O | Switch node of BUCK4 | Floating |
| SW_B4 | 56 | O | Switch node of BUCK4 | Floating |
| SW_B5 | 34 | O | Switch node of BUCK5 | Floating |
| LOW-DROPOUT REGULATORS | ||||
| PVIN_LDO3 | 10 | I | Power input voltage for LDO3 regulator | VCCA |
| PVIN_LDO4 | 8 | I | Power input voltage for LDO4 regulator | VCCA |
| PVIN_LDO12 | 12 | I | Power input voltage for LDO1 and LDO2 regulator | VCCA |
| VOUT_LDO1 | 13 | O | LDO1 output voltage | Floating |
| VOUT_LDO2 | 11 | O | LDO2 output voltage | Floating |
| VOUT_LDO3 | 9 | O | LDO3 output voltage | Floating |
| VOUT_LDO4 | 7 | O | LDO4 output voltage | Floating |
| LOW-DROPOUT REGULATORS (INTERNAL) | ||||
| VOUT_LDOVINT | 2 | O | LDOVINT output for connecting to the filtering capacitor. Not for external loading. | — |
| VOUT_LDOVRTC | 3 | O | LDOVRTC output for connecting to the filtering capacitor. Not for external loading. | — |
| CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR | ||||
| OSC32KCAP | 40 | O | Filtering capacitor for the 32 KHz crystal Oscillator, connected to VRTC through an internal 100 Ω resistor. | Floating |
| OSC32KIN | 38 | I | 32-KHz crystal oscillator input | Ground |
| OSC32KOUT | 39 | O | 32-KHz crystal oscillator output | Floating |
| SYSTEM CONTROL | ||||
| AMUXOUT | 1 | O | Buffered bandgap output | Floating |
| EN_DRV | 29 | O | Enable Drive output pin to indicate the device entering safe state (set low when ENABLE_DRV bit is '0'). | Floating |
| GPIO1 | 32 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I | Alternative function: SCL_I2C2, which is the Q&A WatchDog I2C serial clock (external pull-up). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: CS_SPI, which is the SPI chip enable signal. | Ground | ||
| O | Alternative function: nRSTOUT_SoC, which is the SoC reset or power on output (Active Low). | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO2 | 33 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I/O | Alternative function: SDA_I2C2, which is the Q&A WatchDog I2C serial bidirectional data (external pull-up). | Ground | ||
| O | Alternative function: SDO_SPI, which is the SPI output data signal. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: TRIG_WDOG, which is the watchdog trigger input signal for Watchdog Trigger mode. | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO3 | 46 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I | Alternative function: nERR_SoC, which is the system error count down input signal from the SoC (Active Low). | Floating | ||
| O | Alternative function: CLK32KOUT, which is the output of the 32 KHz crystal oscillator clock. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: LP_WKUP1 or LP_WKUP2, which are capable of processing a wake-up request for the device to go to higher power states while the device is in LP STANDBY state. They can also be used as regular WKUP1 or WKUP2 pins while the device is in mission states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO4 | 47 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| O | Alternative function: CLK32KOUT, which is the output of the 32 KHz crystal oscillator clock. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: LP_WKUP1 or LP_WKUP2, which are capable of processing a wake-up request for the device to go to higher power states while the device is in LP STANDBY state. They can also be used as regular WKUP1 or WKUP2 pins while the device is in mission states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO5 | 23 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I/O | Alternative function: SCLK_SPMI, which is the Multi-PMIC SPMI serial interface clock signal. It is an output pin for the SPMI controller device, and an input pin for the SPMI peripheral device. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO6 | 24 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I/O | Alternative function: SDATA_SPMI, which is the Multi-PMIC SPMI serial interface bidirectional data signal. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO7 | 18 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I | Alternative function: nERR_MCU, which is the system error count down input signal from the MCU (Active Low). | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO8 | 41 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| O | Alternative function: SYNCCLKOUT, which is a clock output synchronized to the switching clock signals for the bucks in the device. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: DISABLE_WDOG, which is the input to disable the watchdog monitoring function. | Floating | ||
| O | Alternative function: CLK32KOUT, which is the output of the 32 KHz crystal oscillator clock. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO9 | 19 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| O | Alternative function: PGOOD, which is the indication signal for valid regulator output voltages and currents | Floating | ||
| O | Alternative function: SYNCCLKOUT, which is the internal fallback switching clock for BUCK. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: DISABLE_WDOG, which is the input to disable the watchdog monitoring function. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO10 | 42 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I | Alternative function: SYNCCLKIN, which is the external switching clock input for BUCK. | Floating | ||
| O | Alternative function: SYNCCLKOUT, which is the internal fallback switching clock for BUCK. | Floating | ||
| O | Alternative function: CLK32KOUT, which is the output of the 32 KHz crystal oscillator clock. | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| GPIO11 | 53 | I/O | Primary function: General-purpose input(1) and output. When configured as an output pin, it can be included as part of the power sequencer output signal to enable an external regulator. |
Input: Ground Output: Floating |
| I | Alternative function: TRIG_WDOG, which is the watchdog trigger input signal for Watchdog Trigger mode. | Ground | ||
| O | Alternative function: nRSTOUT_SoC, which is the SoC reset or power on output (Active Low). | Floating | ||
| I | Alternative function: nSLEEP1 or nSLEEP2, which are the sleep request signals for the device to go to lower power states (Active Low). | Ground | ||
| I | Alternative function: WKUP1 or WKUP2, which are the wake-up request signals for the device to go to higher power states. | Ground | ||
| nINT | 14 | O | Maskable interrupt output request to the host processor (Active Low) | Floating |
| nPWRON/ENABLE | 20 | I | NPWRON_SEL = '0': ENABLE- Level sensitive input pin to power up the device, with configurable polarity | Floating |
| I | NPWRON_SEL = '1': nPWRON - Active low edge sensitive button press pin to power up the device | Ground | ||
| OVPGDRV | 52 | O | Gate drive output for input over voltage protection FET | Floating |
| nRSTOUT | 25 | O | MCU reset or power on reset output (Active Low) | Floating |
| SCL_I2C1/SCK_SPI | 31 | I | If SPI is the default interface: SCL_I2C1 - I2C serial clock (external pullup) | Ground |
| I | If I2C is the default interface: CLK_SPI - SPI clock signal | Ground | ||
| SDA_I2C1/SDI_SPI | 30 | I/O | If SPI is the default interface: SDA_I2C1 - I2C serial bidirectional data (external pullup) | Ground |
| I | If I2C is the default interface: SDI_SPI - SPI input data signal | Ground | ||
| POWER SUPPLIES AND REFERENCE GROUNDS | ||||
| PGND/ThermalPad | — | — | Power Ground, which is also the thermal pad of the package. Connect to PCB ground planes with multiple vias. | — |
| REFGND1 | 5 | — | System reference ground | — |
| REFGND2 | 6 | — | System reference ground | — |
| VBACKUP | 36 | I | Backup power source input pin | Ground |
| VCCA | 4 | I | Analog input voltage for the internal LDOs and other internal blocks | — |
| VIO_IN | 48 | I | Digital supply input for GPIOs and I/O supply voltage | — |
| VSYS_SENSE | 51 | I | Analog input sense pin | Ground |
(1) Default option before NVM settings are loaded into the
device.