ZHCSKK3B December 2019 – February 2022 TPS6594-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 General Purpose Low Drop-Out Regulators (LDO1, LDO2, LDO3)
- 7.6 Low Noise Low Drop-Out Regulator (LDO4)
- 7.7 Internal Low Drop-Out Regulators (LDOVRTC, LDOVINT)
- 7.8 BUCK1, BUCK2, BUCK3, BUCK4 and BUCK5 Regulators
- 7.9 Reference Generator (BandGap)
- 7.10 Monitoring Functions
- 7.11 Clocks, Oscillators, and PLL
- 7.12 Thermal Monitoring and Shutdown
- 7.13 System Control Thresholds
- 7.14 Current Consumption
- 7.15 Backup Battery Charger
- 7.16 Digital Input Signal Parameters
- 7.17 Digital Output Signal Parameters
- 7.18 I/O Pullup and Pulldown Resistance
- 7.19 I2C Interface
- 7.20 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 7.21 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 System Supply Voltage Monitor and Over-Voltage Protection
- 8.3.2
Power Resources (Bucks and LDOs)
- 8.3.2.1
Buck Regulators
- 8.3.2.1.1 BUCK Regulator Overview
- 8.3.2.1.2 Multi-Phase Operation and Phase-Adding or Shedding
- 8.3.2.1.3 Transition Between PWM and PFM Modes
- 8.3.2.1.4 Multi-Phase BUCK Regulator Configurations
- 8.3.2.1.5 Spread-Spectrum Mode
- 8.3.2.1.6 Adaptive Voltage Scaling (AVS) and Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) Support
- 8.3.2.1.7 BUCK Output Voltage Setting
- 8.3.2.1.8 BUCK Regulator Current Limit
- 8.3.2.1.9 SW_Bx Short-to-Ground Detection
- 8.3.2.1.10 Sync Clock Functionality
- 48
- 8.3.2.2 Low Dropout Regulators (LDOs)
- 8.3.2.1
Buck Regulators
- 8.3.3 Residual Voltage Checking
- 8.3.4 Output Voltage Monitor and PGOOD Generation
- 8.3.5 Thermal Monitoring
- 8.3.6 Backup Supply Power-Path
- 8.3.7 General-Purpose I/Os (GPIO Pins)
- 8.3.8 nINT, EN_DRV, and nRSTOUT Pins
- 8.3.9 Interrupts
- 8.3.10 RTC
- 8.3.11
Watchdog (WDOG)
- 8.3.11.1 Watchdog Fail Counter and Status
- 8.3.11.2 Watchdog Start-Up and Configuration
- 8.3.11.3 MCU to Watchdog Synchronization
- 8.3.11.4 Watchdog Disable Function
- 8.3.11.5 Watchdog Sequence
- 8.3.11.6 Watchdog Trigger Mode
- 8.3.11.7 WatchDog Flow Chart and Timing Diagrams in Trigger Mode
- 79
- 8.3.11.8 Watchdog Question-Answer Mode
- 8.3.12 Error Signal Monitor (ESM)
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1
Device State Machine
- 8.4.1.1 Fixed Device Power FSM
- 8.4.1.2
Pre-Configurable Mission States
- 8.4.1.2.1
PFSM Commands
- 8.4.1.2.1.1 REG_WRITE_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.2 REG_WRITE_MASK_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.3 REG_WRITE_MASK_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.4 REG_WRITE_BIT_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.5 REG_WRITE_WIN_PAGE0_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.6 REG_WRITE_VOUT_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.7 REG_WRITE_VCTRL_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.8 REG_WRITE_MASK_SREG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.9 SREG_READ_REG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.10 SREG_WRITE_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.11 WAIT Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.12 DELAY_IMM Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.13 DELAY_SREG Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.14 TRIG_SET Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.15 TRIG_MASK Command
- 8.4.1.2.1.16 END Command
- 8.4.1.2.2 Configuration Memory Organization and Sequence Execution
- 8.4.1.2.3 Mission State Configuration
- 8.4.1.2.4 Pre-Configured Hardware Transitions
- 8.4.1.2.1
PFSM Commands
- 8.4.1.3 Error Handling Operations
- 8.4.1.4 Device Start-up Timing
- 8.4.1.5 Power Sequences
- 8.4.1.6 First Supply Detection
- 8.4.1.7 Register Power Domains and Reset Levels
- 8.4.2 Multi-PMIC Synchronization
- 8.4.1
Device State Machine
- 8.5 Control Interfaces
- 8.6 Configurable Registers
- 8.7 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.1 System Supply Voltage Monitor and Over-Voltage Protection
The TPS6594-Q1 device includes an over-voltage protection mechanism through a 12-V compliant input monitor at the VSYS_SENSE pin. When an over-voltage is detected at the VSYS_SENSE pin, OVPGDRV pin is pulled low to disable the external high voltage load switch, which connects the VSYS supply to the VCCA pin. After the over-voltage condition is cleared, the voltage at the OVPGDRV pin recovers after the voltage at the VSYS_SENSE pin stays below VVSYS_RC_TH for at least VSYS_RC_TH.
The voltage at the OVPDRV has following relation with the voltage at the VSYS-SENSE pin:
- For VSYS_SENSE < 2.7V: OVPGDRV = 0V
- For 2.7V ≤ VSYS_SENSE ≤ 4.5V: OVPGDRV ≈ 0.9 * 3 * VSYS_SENSE
- For 4.5V < VSYS_SENSE ≤ 6V: OVPGDRV = 12V (in case of a fault in the regulation loop of the internal charge pump, OVPGDRV is limited to 12.5V)
- For VSYS_SENSE > 6V: OVPGDRV = 0V
TI recommends connecting a 10-V zener diode to ground at the VSYS_SENSE pin and one or more series resistors between the VSYS_SENSE pin and the pre-regulator output to limit the current surge and protect the VSYS_SENSE pin from an over-voltage condition due to possible short at the pre-regulator output. The voltage slew rate at the VSYS_SENSE pin must be limited to ≤ VVSYS_SR to prevent possible damage to the device.
After the TPS6594-Q1 device has detected a VCCA over voltage condition, the VCCA domain is unpowered and does not signal the over voltage condition to the VSYS over-voltage protection module. Therefore, a dead-lock mechanism is implemented in the VSYS domain by setting a latch to keep the external high voltage load switch (between VSYS and VCCA) open once the TPS6594-Q1 device has detected a VCCA over voltage condition.
The TPS6594-Q1 first checks for possible fail-short condition of the external FET at initial power up. The diagnostic mechanism pulls the OVPDGRV pin low when VCCA reaches VOVP_FET_Short_TH, and waits until the voltage on the VCCA pin decreases by VOVP_FET_Short_Hyst before it pulls the OVPGDRV pin high again. This mechanism effectively disconnects the VCCA pin from VSYS in case of a FET fail-short condition; with the addition of the diagnostic comparator, however, it also causes a non-monotonic power up behavior with an RC delay at the VCCA pin. The RC-delay is associated with the input capacitance at the VCCA pin and the internal pull-down resistor value RVCCA_OVP_PD.
The comparator module in TPS6594-Q1, which monitors the voltage on the VCCA pins, controls the power state machine of the device. VCCA voltage detection outputs determine the power states of the device as follows:
-
VCCA_UVLO
The TPS6594-Q1
returns to the BACKUP state. LDOVRTC is
powered by the output of the Backup Supply Management (BSM) module
during the BACKUP state. The device returns to the NO SUPPLY
state and is completely shut down when the input supply of the LDOVRTC
falls below the operating range. The
device cannot return to the BACKUP state from the NO SUPPLY
state.
-
VCCA_UV
The TPS6594-Q1 transitions from the NO SUPPLY
state to the INIT state when the voltage on the VCCA pin rises above
VCCA_UV during initial power-up.
-
VCCA_OVP
If the voltage on VCCA pin rises above the VCCA_OVP threshold while TPS6594-Q1 is in operation , despite the OVPGDRV
mechanism, then the device clears the ENABLE_DRV bit and
starts the immediate shutdown sequence.
A separate voltage comparator monitors whether or not the VCCA voltage is within the expected PGOOD range when VCCA is expected to be 5-V or 3.3-V. This voltage comparator checks at device power-up whether the voltage on the VCCA supply pin is above the VCCA_UV threshold. Refer to Section 8.3.4 for additional detail on the operation of the PGOOD monitor function.
LDOVINT, which is the internal supply to the digital core of the device, may attempt to restart the device when the input voltage at VCCA pin falls or stays between VCCA_UVLO and VCCA_UV voltage levels; the voltage at the VCCA pin, however, must be above the VCCA_UV voltage level for the device to power up properly.
Figure 8-1 shows a block diagram of the system input monitoring and over-voltage protection mechanism, and the generation of the VCCA_UVLO and VCCA_OVP power state control signals.
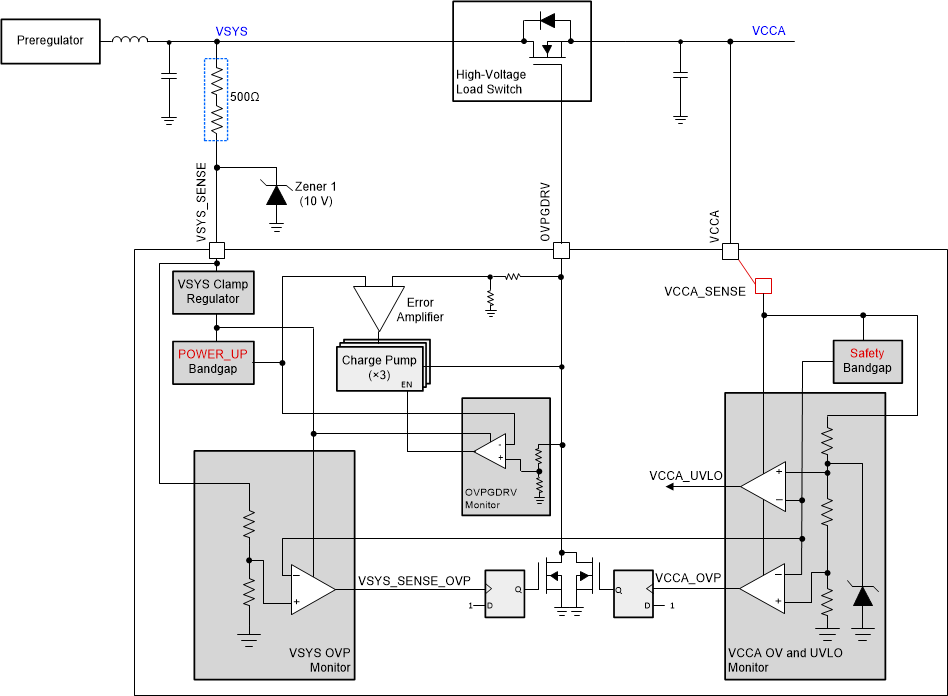 Figure 8-1 VSYS
Monitor and OVPGDRV Output Generation
Figure 8-1 VSYS
Monitor and OVPGDRV Output Generation