ZHCSIY2B July 2018 – August 2021 TPS65988
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Supply Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.6 Power Consumption Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.8 Cable Detection Characteristics
- 6.9 USB-PD Baseband Signal Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.10 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.11 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.12 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.13 I/O Characteristics
- 6.14 PWM Driver Characteristics
- 6.15 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.16 SPI Controller Timing Requirements
- 6.17 HPD Timing Requirements
- 6.18 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Port Power Switches
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Dead Battery Operation
- 8.3.6 Battery Charger Detection and Advertisement
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 DisplayPort HPD
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 PWM Driver
- 8.3.11 Digital Core
- 8.3.12 I2C Interfaces
- 8.3.13 SPI Controller Interface
- 8.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.15 Oscillators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Type-C VBUS Design Considerations
- 9.2.2 Dual Port Thunderbolt Notebook with AR Supporting USB PD Charging
- 9.2.3 Dual Port USB & Displayport Notebook Supporting PD Charging
- 9.2.4 USB Type-C & PD Monitor/Dock
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
-
11Layout
- 11.1 Layout Guidelines
- 11.2 Layout Example
- 11.3 Stack-Up and Design Rules
- 11.4 Main Component Placement
- 11.5 1.4 Super Speed Type-C Connectors
- 11.6 Capacitor Placement
- 11.7 CC1/2 Capacitors & ADCIN1/2 Resistors
- 11.8 CC & SBU Protection Placement
- 11.9 CC Routing
- 11.10 DRAIN1 and DRAIN2 Pad Pours
- 11.11 USB2 Routing for ESD Protection and BC1.2
- 11.12 VBUS Routing
- 11.13 Completed Layout
- 11.14 Power Dissipation
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.3 Dual Port USB & Displayport Notebook Supporting PD Charging
Certain SoCs can support USB and DisplayPort and the muxing required for Type-C. The systems that use this architecture may need a re-driver to ensure signal signal integrity to from the SoC to the Type-C connectors. Generally the SoC is controlled through I2C and must be connected to the I2C1 Master on the TPS65988. A re-driver can be controlled through GPIO or I2C. The Embedded controller is connected to the I2C2 Slave on the TPS65988. Figure 9-9 shows the SoC controlled though I2C and the Re-Driver controlled through GPIO. Figure 9-10 shows the SoC & Re-Driver controlled though I2C. The TPS65988’s two internal power paths provide VBUS which is taken from the System 5 V for Port and will control the external sink path to charge the system through USB PD. The System 5 V will also power PP_CABLE1/2 on the TPS65988 to supply VCONN to Type-C e-marked cables and Type-C accessories. An embedded controller EC is used to communicate to the TPS65988 for additional control and to relay information back to the operating system. An embedded controller can control additional features such as entering and exiting sleep modes, changing source and sink capabilities depending on the state of the battery, UCSI support, control alternate modes, etc. Refer to the Host Interface and Firmware users guide for additional information.
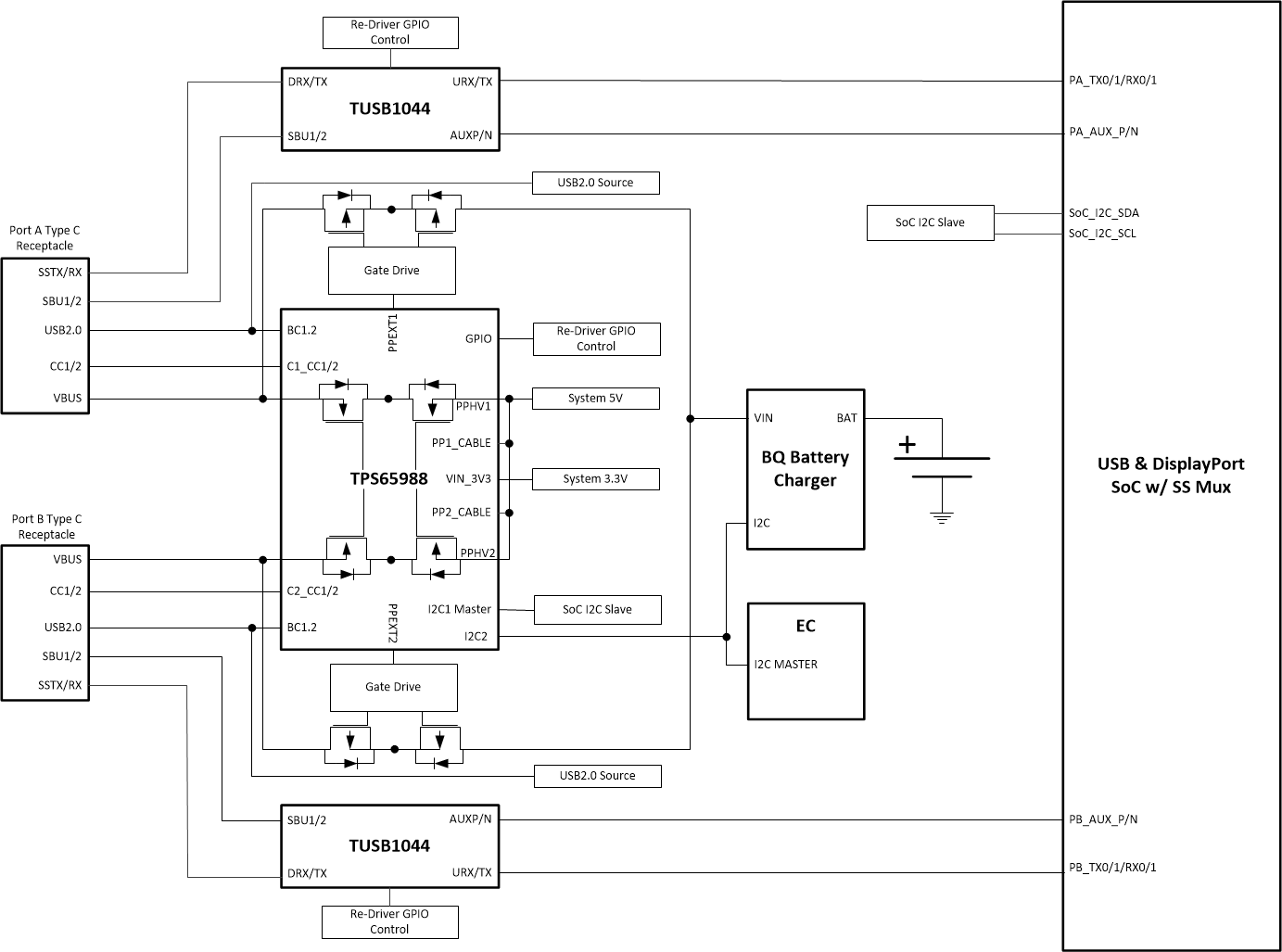 Figure 9-9 TPS65988 and SoC I2C with Re-Driver
GPIO
Figure 9-9 TPS65988 and SoC I2C with Re-Driver
GPIO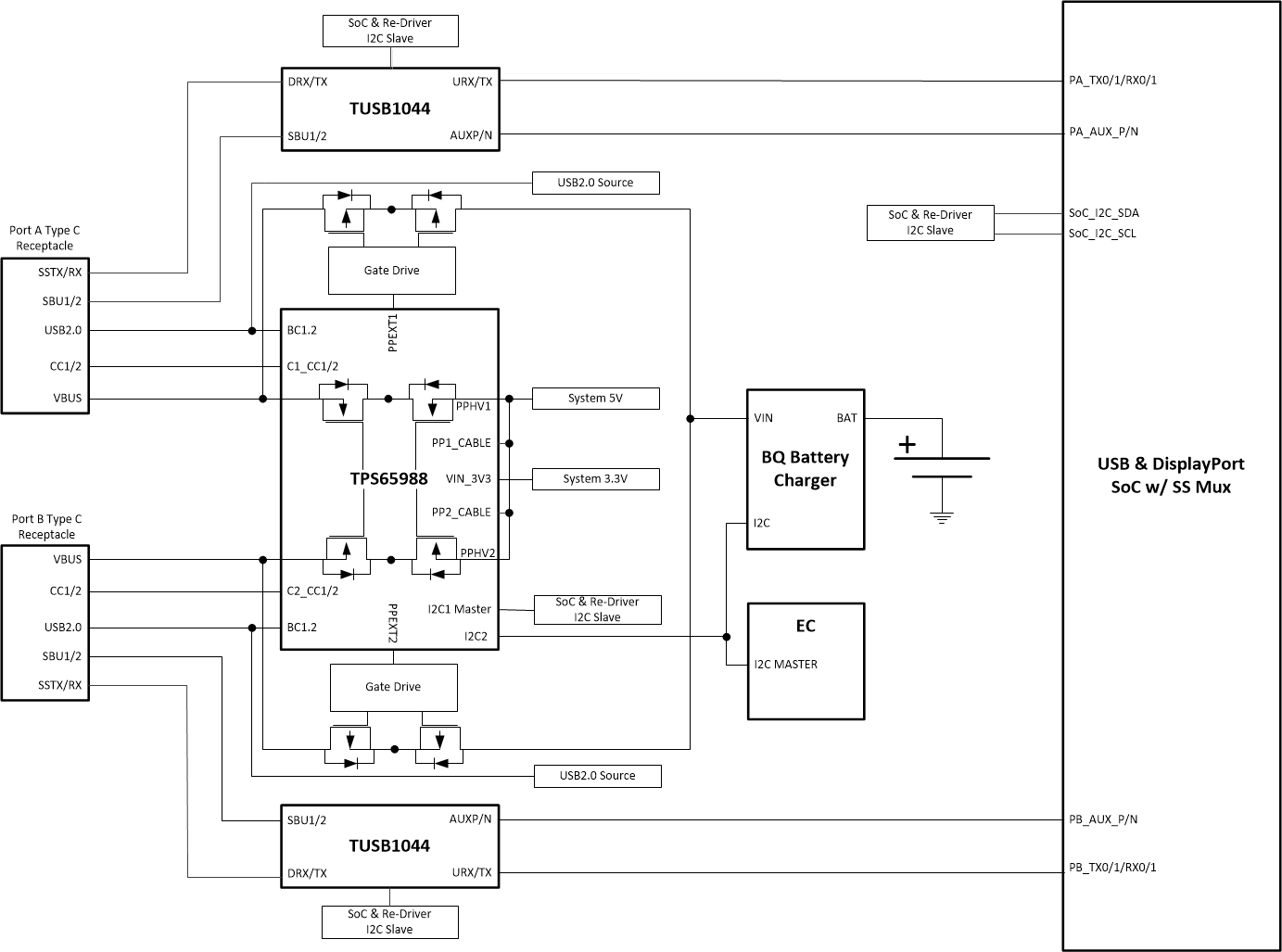 Figure 9-10 TPS65988 and SoC & Redriver I2C
Figure 9-10 TPS65988 and SoC & Redriver I2C