ZHCSIY2B July 2018 – August 2021 TPS65988
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Power Supply Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.6 Power Consumption Characteristics
- 6.7 Power Switch Characteristics
- 6.8 Cable Detection Characteristics
- 6.9 USB-PD Baseband Signal Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.10 BC1.2 Characteristics
- 6.11 Thermal Shutdown Characteristics
- 6.12 Oscillator Characteristics
- 6.13 I/O Characteristics
- 6.14 PWM Driver Characteristics
- 6.15 I2C Requirements and Characteristics
- 6.16 SPI Controller Timing Requirements
- 6.17 HPD Timing Requirements
- 6.18 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 USB-PD Physical Layer
- 8.3.2 Power Management
- 8.3.3 Port Power Switches
- 8.3.4 Cable Plug and Orientation Detection
- 8.3.5 Dead Battery Operation
- 8.3.6 Battery Charger Detection and Advertisement
- 8.3.7 ADC
- 8.3.8 DisplayPort HPD
- 8.3.9 Digital Interfaces
- 8.3.10 PWM Driver
- 8.3.11 Digital Core
- 8.3.12 I2C Interfaces
- 8.3.13 SPI Controller Interface
- 8.3.14 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.15 Oscillators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1 Type-C VBUS Design Considerations
- 9.2.2 Dual Port Thunderbolt Notebook with AR Supporting USB PD Charging
- 9.2.3 Dual Port USB & Displayport Notebook Supporting PD Charging
- 9.2.4 USB Type-C & PD Monitor/Dock
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
-
11Layout
- 11.1 Layout Guidelines
- 11.2 Layout Example
- 11.3 Stack-Up and Design Rules
- 11.4 Main Component Placement
- 11.5 1.4 Super Speed Type-C Connectors
- 11.6 Capacitor Placement
- 11.7 CC1/2 Capacitors & ADCIN1/2 Resistors
- 11.8 CC & SBU Protection Placement
- 11.9 CC Routing
- 11.10 DRAIN1 and DRAIN2 Pad Pours
- 11.11 USB2 Routing for ESD Protection and BC1.2
- 11.12 VBUS Routing
- 11.13 Completed Layout
- 11.14 Power Dissipation
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.1.4 USB-PD BMC Transmitter
The TPS65988 transmits and receives USB-PD data over one of the Cx_CCn pins for a given CC pin pair (one pair per USB Type-C port). The Cx_CCn pins are also used to determine the cable orientation (see the Section 8.3.4 section) and maintain cable/device attach detection. Thus, a DC bias exists on the Cx_CCn pins. The transmitter driver overdrives the Cx_CCn DC bias while transmitting, but returns to a Hi-Z state allowing the DC voltage to return to the Cx_CCn pin when not transmitting. Figure 8-5 shows the USB-PD BMC TX and RX driver block diagram.
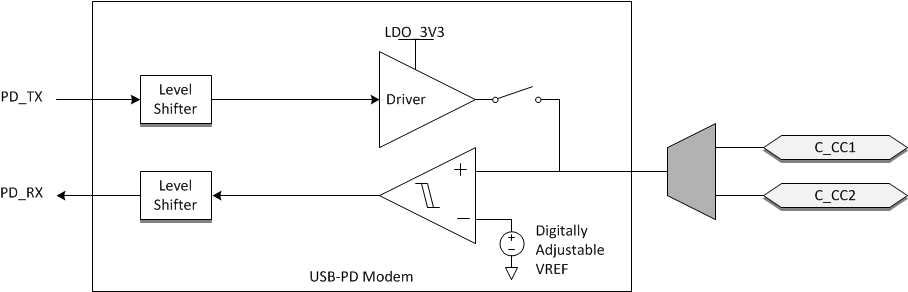 Figure 8-5 USB-PD BMC TX/Rx Block Diagram
Figure 8-5 USB-PD BMC TX/Rx Block DiagramFigure 8-6 shows the transmission of the BMC data on top of the DC bias. Note, The DC bias can be anywhere between the minimum threshold for detecting a UFP attach (VD_CCH_USB) and the maximum threshold for detecting a UFP attach to a DFP (VD_CCH_3P0). This means that the DC bias can be below VOH of the transmitter driver or above VOH.
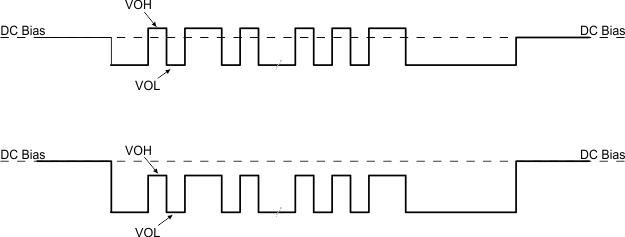 Figure 8-6 TX Driver Transmission with DC Bias
Figure 8-6 TX Driver Transmission with DC BiasThe transmitter drives a digital signal onto the Cx_CCn lines. The signal peak, VTXP, is set to meet the TX masks defined in the USB-PD Specifications.
When driving the line, the transmitter driver has an output impedance of ZDRIVER. ZDRIVER is determined by the driver resistance and the shunt capacitance of the source and is frequency dependent. ZDRIVER impacts the noise ingression in the cable.
Figure 8-7 shows the simplified circuit determining ZDRIVER. It is specified such that noise at the receiver is bounded.
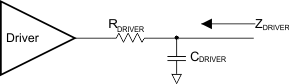 Figure 8-7 ZDRIVER Circuit
Figure 8-7 ZDRIVER Circuit