ZHCSC15C December 2013 – June 2018 TPS709-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DBV|5
- DRV|6
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DRV|6
订购信息
10.1.2 Power Dissipation
The ability to remove heat from the die is different for each package type, presenting different considerations in the printed circuit board (PCB) layout. The PCB area around the device that is free of other components moves the heat from the device to the ambient air. Performance data for JEDEC low- and high-K boards are given in the Thermal Information. Using heavier copper increases the effectiveness in removing heat from the device. The addition of plated through-holes to heat-dissipating layers also improves the heatsink effectiveness.
Power dissipation depends on input voltage and load conditions. Power dissipation (PD) can be approximated by the product of the output current times the voltage drop across the output pass element (VIN to VOUT), as shown in Equation 1.
Figure 45 shows the maximum ambient temperature versus the power dissipation of the TPS709-Q1. This figure assumes the device is soldered on a JEDEC standard, high-K layout with no airflow over the board. Actual board thermal impedances vary widely. If the application requires high power dissipation, having a thorough understanding of the board temperature and thermal impedances is helpful to ensure the TPS709-Q1 does not operate above a junction temperature of 125°C.
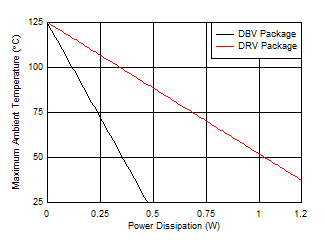 Figure 45. Maximum Ambient Temperature vs Device Power Dissipation
Figure 45. Maximum Ambient Temperature vs Device Power Dissipation Estimating the junction temperature can be done by using the thermal metrics ΨJT and ΨJB, shown in the Thermal Information. These metrics are a more accurate representation of the heat transfer characteristics of the die and the package than RθJA. The junction temperature can be estimated with Equation 2.
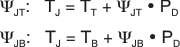
where
- PD is the power dissipation shown by Equation 1,
- TT is the temperature at the center-top of the IC package,
- TB is the PCB temperature measured 1 mm away from the IC package on the PCB surface.
NOTE
Both TT and TB can be measured on actual application boards using a thermo‐gun (an infrared thermometer).
For more information about measuring TT and TB, see the application note Using New Thermal Metrics (SBVA025), available for download at www.ti.com.