ZHCSUK3O December 2005 – October 2024 TPS74201
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.1.5 Programmable Soft-Start
The TPS742 devices feature a programmable, monotonic, voltage-controlled soft start that is set with an external capacitor (CSS). This feature is important for many applications, because power-up initialization problems are eliminated when powering FPGAs, DSPs, or other processors. The controlled voltage ramp of the output also reduces peak inrush current during start-up, minimizing start-up transients to the input power bus.
To achieve a linear and monotonic soft-start, the TPS742 error amplifier tracks the voltage ramp of the external soft-start capacitor until the voltage exceeds the internal reference. The soft-start ramp time depends on the soft-start charging current (ISS), soft-start capacitance (CSS), and the internal reference voltage (VREF), and can be calculated using Equation 2:
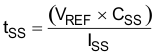
If large output capacitors are used, the device current limit (ICL) and the output capacitor can set the start-up time. In this case, the start-up time is given by Equation 3:
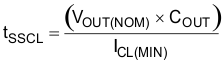
VOUT(NOM) is the nominal set output voltage as set by the user, COUT is the output capacitance, and ICL(MIN) is the minimum current limit for the device. In applications where monotonic start-up is required, the soft-start time given by Equation 2 must be set to be greater than Equation 3.
The maximum recommended soft-start capacitor is 0.015 μF. Larger soft-start capacitors can be used and do not damage the device; however, the soft-start capacitor discharge circuit is not always able to fully discharge the soft-start capacitor when enabled. Soft-start capacitors larger than 0.015 μF can be a problem in applications where the user must rapidly pulse the enable pin and still requires the device to soft-start from ground. CSS must be low-leakage; X7R, X5R, or C0G dielectric materials are preferred. See Table 7-1 for suggested soft-start capacitor values.
(See Equation 4)
| CSS | SOFT-START TIME |
|---|---|
| Open | 0.1 ms |
| 470 pF | 0.5 ms |
| 1000 pF | 1 ms |
| 4700 pF | 5 ms |
| 0.01 μF | 10 ms |
| 0.015 μF | 16 ms |
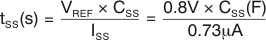
where
- tSS(s) = soft-start time in seconds