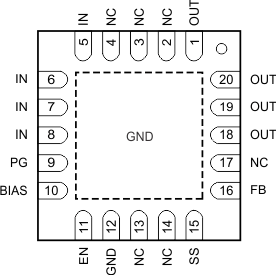
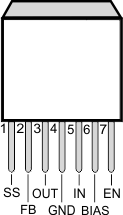
| BIAS |
6 |
10 |
I |
Bias input voltage for error amplifier, reference, and internal control circuits.
A 1-µF or larger bias capacitor is recommended for optimal performance.
If IN is connected to BIAS, use a 4.7 µF or larger capacitor. |
| EN |
7 |
11 |
I |
Enable pin. Driving this pin high enables the regulator. Driving this pin low puts the regulator into shutdown mode. This pin must not be left floating. |
| FB |
2 |
16 |
I |
This pin is the feedback connection to the center tap of an external resistor divider network that sets the output voltage. This pin must not be left floating. |
| GND |
4 |
12 |
— |
Ground |
| IN |
5 |
5–8 |
I |
Unregulated input to the device.
An input capacitor of 1 µF or greater is recommended for optimal performance. |
| NC |
N/A |
2–4, 13, 14, 17 |
— |
No connection. This pin can be left floating or connected to GND to allow better thermal contact to the top-side plane. |
| OUT |
3 |
1, 18–20 |
O |
Regulated output voltage. No capacitor is required on this pin for stability, but is recommended for optimal performance. |
| PAD/TAB |
— |
— |
— |
Must be soldered to the ground plane for increased thermal performance.
Internally connected to ground. |
| PG |
N/A |
9 |
O |
Power-good (PG) is an open-drain, active-high output that indicates the status of VOUT. When VOUT exceeds the PG trip threshold, the PG pin goes into a high-impedance state. When VOUT is below this threshold, the pin is driven to a low-impedance state. Connect a pullup resistor from 10 kΩ to 1 MΩ from this pin to a supply up to 5.5 V. The supply can be higher than the input voltage.
Alternatively, the PG pin can be left floating if output monitoring is not necessary. |
| SS |
1 |
15 |
— |
Soft-start pin. A capacitor connected on this pin to ground sets the start-up time.
If this pin is left floating, the regulator output soft-start ramp time is typically 100 µs. |