ZHCSN52D April 2010 – December 2023 TPS74701-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.2.2.3 Sequencing Requirements
VIN, VBIAS, and VEN can be sequenced in any order without causing damage to the device. However, for the soft-start function to work as intended, certain sequencing rules must be applied. Connecting EN to IN is acceptable for most applications, as long as VIN is greater than 1.1 V and the ramp rate of VIN and VBIAS is faster than the set soft-start ramp rate. If the ramp rate of the input sources is slower than the set soft-start time, the output tracks the slower supply minus the dropout voltage until reaching the set output voltage. If EN is connected to BIAS, the device soft-starts as programmed, provided that VIN is present before VBIAS. If VBIAS and VEN are present before VIN is applied and the set soft-start time has expired, then VOUT tracks VIN. If the soft-start time has not expired, the output tracks VIN until VOUT reaches the value set by the charging soft-start capacitor. Figure 7-2 shows the use of an RC delay circuit to hold off VEN until VBIAS has ramped. This technique can also be used to drive EN from VIN. An external control signal can also be used to enable the device after VIN and VBIAS are present.
When VBIAS and VEN are present and VIN is not supplied, this device outputs approximately 50 μA of current from OUT. Although this condition does not cause any damage to the device, the output current can charge up the OUT node if total resistance between OUT and GND (including external feedback resistors) is greater than 10 kΩ.
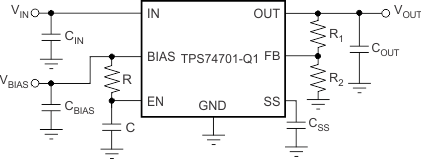 Figure 7-2 Soft-Start Delay Using an RC Circuit to Enable the Device
Figure 7-2 Soft-Start Delay Using an RC Circuit to Enable the Device