ZHCSHE9J June 2010 – January 2018 TPS7A80
PRODUCTION DATA.
7.3.3 Start-Up
Through a lower resistance, the band-gap reference can quickly charge the noise reduction capacitor (CNR). The TPS7A80 have a quick-start circuit to quickly charge CNR, if present; see the Functional Block Diagram. At start-up, this quick-start switch is closed, with only 33 kΩ of resistance between the band-gap reference and the NR pin. The quick-start switch opens approximately 2ms after any device enabling event, and the resistance between the band-gap reference and the NR pin becomes higher in value (approximately 250 kΩ) to form a very good low-pass (RC) filter. This low-pass filter achieves very good noise reduction for the reference voltage.
Inrush current can be a problem in many applications. The 33-kΩ resistance during the start-up period is intentionally put there to slow down the reference voltage ramp up, thus reducing the inrush current. For example, the capacitance of connecting the recommended CNR value of 0.01 μF along with the 33-kΩ resistance causes approximately 1-ms RC delay. Start-up time with the other CNR values can be calculated as Equation 1:
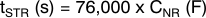
Equation 1 is valid up to tSTR = 2 ms or CNR = 26 nF, whichever is smaller.
Although the noise reduction effect is nearly saturated at 0.01 μF, connecting a CNR value greater than 0.01 μF can help reduce noise slightly more; however, start-up time will be extremely long because the quick-start switch opens after approximately 2 ms. That is, if CNR is not fully charged during this 2 ms period, CNR finishes charging through a higher resistance of 250 kΩ, and takes much longer to fully charge.
A low leakage CNR should be used; most ceramic capacitors are suitable.