ZHCSEI2B January 2016 – June 2021 TPS7A84
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configurations and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1
Application Information
- 8.1.1 Recommended Capacitor Types
- 8.1.2 Input and Output Capacitor Requirements (CIN and COUT)
- 8.1.3 Noise-Reduction and Soft-Start Capacitor (CNR/SS)
- 8.1.4 Feed-Forward Capacitor (CFF)
- 8.1.5 Soft-Start and In-Rush Current
- 8.1.6 Optimizing Noise and PSRR
- 8.1.7 Charge Pump Noise
- 8.1.8 ANY-OUT Programmable Output Voltage
- 8.1.9 ANY-OUT Operation
- 8.1.10 Increasing ANY-OUT Resolution for LILO Conditions
- 8.1.11 Current Sharing
- 8.1.12 Adjustable Operation
- 8.1.13 Sequencing Requirements
- 8.1.14 Power-Good Operation
- 8.1.15 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Operation
- 8.1.16 Dropout Voltage (VDO)
- 8.1.17 Behavior when Transitioning from Dropout into Regulation
- 8.1.18 Load Transient Response
- 8.1.19 Negatively-Biased Output
- 8.1.20 Reverse Current Protection
- 8.1.21 Power Dissipation (PD)
- 8.1.22 Estimating Junction Temperature
- 8.1.23 Recommended Area for Continuous Operation (RACO)
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.1
Application Information
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1.20 Reverse Current Protection
As with most LDOs, this device can be damaged by excessive reverse current.
Conditions where excessive reverse current can occur are outlined in this section, all of which can exceed the absolute maximum rating of VOUT > VIN + 0.3 V:
- If the device has a large COUT, then the input supply collapses quickly and the load current becomes very small
- The output is biased when the input supply is not established
- The output is biased above the input supply
If an excessive reverse current flow is expected in the application, then external protection must be used to protect the device. Figure 8-12 shows one approach of protecting the device.
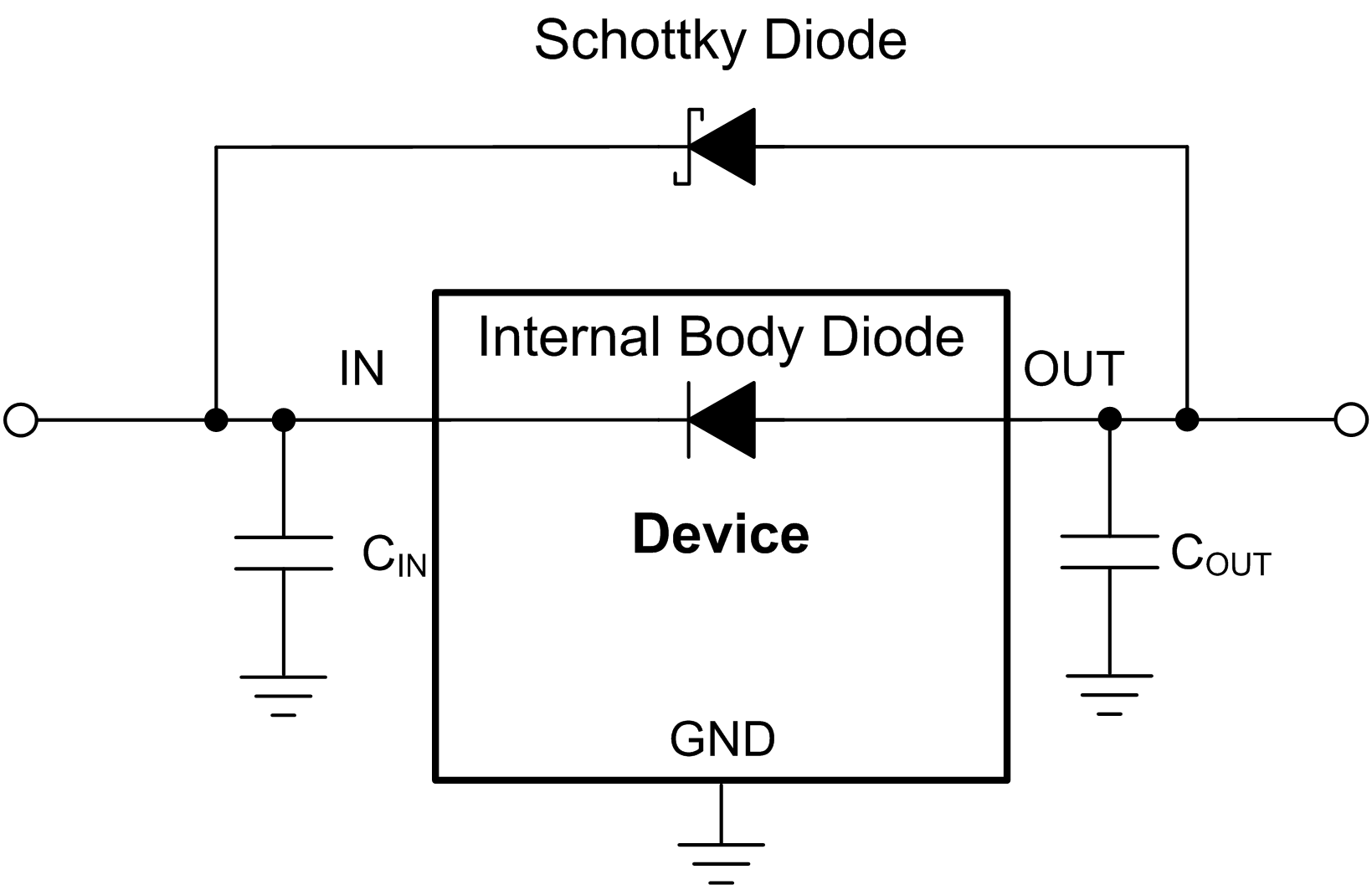 Figure 8-12 Example Circuit for Reverse Current Protection Using a Schottky Diode
Figure 8-12 Example Circuit for Reverse Current Protection Using a Schottky Diode