ZHCSL07C September 2019 – August 2021 TPS8802
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 System Power-up
- 8.3.2 LDO Regulators
- 8.3.3 Photo Chamber AFE
- 8.3.4 LED Driver
- 8.3.5 Carbon Monoxide Sensor AFE
- 8.3.6 Boost Converter
- 8.3.7 Interconnect Driver
- 8.3.8 Piezoelectric Horn Driver
- 8.3.9 Battery Test
- 8.3.10 AMUX
- 8.3.11 Analog Bias Block and 8 MHz Oscillator
- 8.3.12 Interrupt Signal Alerts
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 REVID Register (Offset = 0h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.2 STATUS1 Register (Offset = 1h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.3 STATUS2 Register (Offset = 2h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.4 MASK Register (Offset = 3h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.5 CONFIG1 Register (Offset = 4h) [reset = 20h]
- 8.6.6 CONFIG2 Register (Offset = 5h) [reset = 2h]
- 8.6.7 ENABLE1 Register (Offset = 6h) [reset = 10h]
- 8.6.8 ENABLE2 Register (Offset = 7h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.9 CONTROL Register (Offset = 8h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.10 SLPTMR1 Register (Offset = 9h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.11 SLPTMR2 Register (Offset = Ah) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.12 GPIO_AMUX Register (Offset = Bh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.13 CO_BATTEST Register (Offset = Ch) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.14 CO Register (Offset = Dh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.15 VBOOST Register (Offset = Eh) [reset = F2h]
- 8.6.16 LEDLDO Register (Offset = Fh) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.17 PH_CTRL Register (Offset = 10h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.18 LED_DAC_A Register (Offset = 11h) [reset = 0h]
- 8.6.19 LED_DAC_B Register (Offset = 12h) [reset = 0h]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3.6.1 Boost Hysteretic Control
The hysteretic control guarantees stability across input and output voltages and has a fast transient response. When the VBST voltage is below its target (as programmed in the VBOOST register), a charging cycle initiates by enabling the VLX switch until the current through the inductor exceeds the programmable inductor peak current setting. After the peak current is reached, the VLX switch is disabled and the inductor charges the VBST output capacitor. The charging cycle completes when the inductor current reaches zero, and a new cycle initiates when VBST drops again. Because of the hysteretic control scheme, the average output voltage varies depending on the input voltage, inductor peak current, inductance, output capacitor, output voltage, and output load.
When the VBST voltage is above the boost regulation voltage, the boost does not switch. In a battery backup system, the battery draws no power if the DC supply is providing a VBST voltage above the boost regulation voltage. The boost starts switching if the DC supply drops, drawing power from the battery to regulate VBST. A timer, BST_nACT, monitors the time that the boost is not switching to notify the MCU if the boost is inactive. This timer is programmable from 100 µs to 100 ms. This timer can be used to determine if the battery voltage is higher than the regulation voltage or if an DC supply is connected.
The default inductor peak current is 500 mA. This sets the boost converter to provide maximum output current. After the TPS8802 is powered, the peak current can be adjusted using the I2C interface to change the boost switching frequency or to limit the battery current. The switching frequency is inversely proportional to the square of the current limit. For example, changing the current limit from 500 mA to 50 mA causes the frequency to increase by a factor of 100. The peak current determines how much current the boost converter can output. Equation 1 calculates the maximum boost output current.
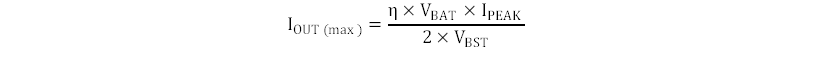
Typical boost efficiency is shown in Figure 9-5. If the boost output current draw exceeds the maximum, the boost voltage drops until the converter can supply the output current draw.