ZHCSMJ4 March 2021 TPS92391
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Interface
- 7.3.2 Function Setting
- 7.3.3 Device Supply (VDD)
- 7.3.4 Enable (EN)
- 7.3.5 Charge Pump
- 7.3.6 Boost Controller
- 7.3.7 LED Current Sinks
- 7.3.8 Brightness Control
- 7.3.9
Protection and Fault Detections
- 7.3.9.1 Supply Faults
- 7.3.9.2
Boost Faults
- 7.3.9.2.1 Boost Overvoltage Faults (BSTOVPL, BSTOVPH)
- 7.3.9.2.2 Boost Overcurrent Faults (BSTOCP)
- 7.3.9.2.3 LEDSET Resistor Missing Faults (LEDSET)
- 7.3.9.2.4 MODE Resistor Missing Faults (MODESEL)
- 7.3.9.2.5 FSET Resistor Missing Faults (FSET)
- 7.3.9.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
- 7.3.9.2.7 Thermal Shutdown Faults (TSD)
- 7.3.9.3 LED Faults
- 7.3.9.4 Overview of the Fault and Protection Schemes
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.6 Output Diode
- 8.2.1.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Application With Basic/Minimal Operation
- 8.2.3
SEPIC Mode Application
- 8.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.2 Coupling Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.5 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.6 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.3.2.8 Output Diode
- 8.2.3.2.9 Switching Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.10 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.3.2.11 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.12 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
Figure 8-7 shows the critical part of circuitry: SEPIC components, the TPS92391 internal charge pump for gate-driver powering, and powering/grounding of TPS92391. Schematic example is shown below.
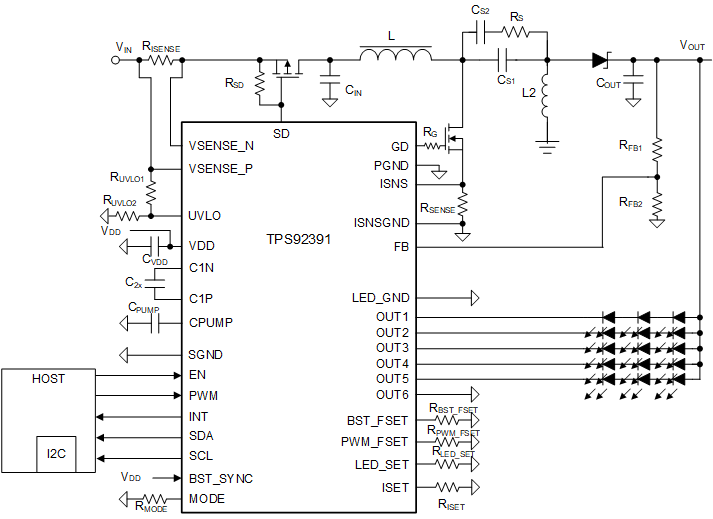 Figure 8-7 SEPIC Mode with
Three LEDs in Series
Figure 8-7 SEPIC Mode with
Three LEDs in SeriesTable 8-7 Recommended Components for SEPIC
Design Example
| REFERENCE DESIGNATOR | DESCRIPTION | NOTE |
|---|---|---|
| RISENSE | 20 mΩ, 1 W | Input current sensing resistor |
| RSD | 20 kΩ, 0.1 W | Power-line FET gate pullup resistor |
| RSENSE | 50 mΩ, 1 W | Boost current sensing resistor |
| RG | 15 Ω, 0.1 W | Gate resistor to control the rising/falling time of nMOSFET for EMC |
| RUVLO1 | 76.8 kΩ, 0.1 W | These UVLO resistor settings set the VIN_UVLO rising voltage at 3.75 V, VIN_UVLO falling voltage at 3.35 V |
| RUVLO2 | 20.5 kΩ, 0.1 W | |
| RFB2 | 60 kΩ, 0.1 W | Bottom feedback divider resistor |
| RFB1 | 330 kΩ, 0.1 W | Top feedback divider resistor |
| RBST_FSET | 124 kΩ, 0.1 W | Boost frequency set resistor (2200 kHz) |
| RISET | 38.7 kΩ, 0.1 W | Current set resistor (80 mA per channel) |
| RPWM_FSET | 4.75 kΩ, 0.1 W | Output PWM frequency set resistor (305-Hz PWM frequency) |
| RMODE | 3.92 kΩ, 0.1 W | Mode resistor (Phase-Shift PWM mode with 0x2B I2C address) |
| RLED_SET | 4.75 kΩ, 0.1 W | LED_SET resistor (5 channels configuration) |
| CPUMP | 10-µF, 10-V ceramic | Charge-pump output capacitor |
| C2X | 2.2-µF, 10-V ceramic | Flying capacitor |
| CVDD | 4.7-µF + 0.1-µF, 10-V ceramic | VDD bypass capacitor |
| CIN | 1 × 33-µF, 50-V electrolytic + 1 × 10-µF, 50-V ceramic | Boost input capacitor |
| COUT | 1 × 33-µF, 50-V electrolytic + 1 × 10-µF, 50-V ceramic | Boost output capacitor |
| CS1 | 10-µF, 50-V ceramic | SEPIC coupling capacitor |
| CS2 | 33-µF, 50-V electrolytic | SEPIC coupling capacitor |
| RS | 2 Ω, 0.125 W | SEPIC resistor |
| L1 | 4.7-µH saturation current 3 A | SEPIC inductor |
| L2 | 4.7-µH saturation current 3 A | SEPIC inductor |
| D1 | 50-V 10-A Schottky diode | SEPIC Schottky diode |
| Q1 | 60-V, 25-A nMOSFET | SEPIC nMOSFET |
| Q2 | 60-V, 30-A pMOSFET | Power-line FET |